
In the symphony of technology and nature, this collection of studies unfolds like a multidimensional canvas of agricultural revolution. From the three-dimensional reconstruction technology weaving holographic blueprints of crop growth in digital precision, to the gradual replacement of roaring diesel engines with the silent, zero-emission hum of electric tractors; from the genetic "whispers" in cornfields (the yield miracle of the L10×T2 hybrid) unlocking productivity barriers, to smallholder farmers in Afghanistan’s rugged terrain battling climate extremes with ancient wisdom; and along the Nile, rice growers navigating water scarcity and policy puzzles to decode the mathematical enigma of supply elasticity—these studies collectively sketch a global agricultural transformation spanning technology, ecology, and humanity. The highlights lie in how AI and sensors equip farming with "intelligent eyes," clean-energy machinery reshapes the rhythm of fields, genetic compatibility reveals golden rules of life’s propagation, and social-ecological perspectives translate the struggles of vulnerable regions into resilient strategies. Each paper is both a laboratory-crafted equation and a story rooted in soil, offering scholars a key: how to balance the race of innovation with nature’s limits, crafting a sustainable future for global food security.
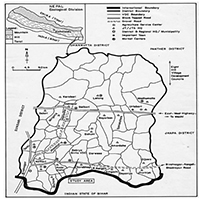
Recent studies have identified several challenges associated with rice production, which hinder the achievement of self-sufficiency in rice. As a crop that heavily relies on irrigation water, rice production has implications for the nation’s water security. Nevertheless, there is still hope for reducing the future food gap by implementing agricultural policies that encourage farmers to increase production. Therefore, it has become essential to understand the responsiveness of rice cultivation area supply to changes, as this is crucial for making decisions regarding agricultural policies related to production and farm prices during the period from 2010 to 2023. The aim is to estimate farmers’ responsiveness, and the time required to achieve this response, as well as the supply elasticity. To achieve the research objective, both descriptive and quantitative statistical analysis were used, applying the Stepwise method in its logarithmic form to estimate the Supply Response. The elasticity of supply response for the rice cultivation area was estimated to be approximately 1.86% in the short term and 2.09% in the long term. It was also found that the response time of the cultivated rice area supply in Egypt to changes is low, estimated at around 1.12. This may be due to the inability to expand the cultivated area of this crop in the following year, as rice cultivation requires large amounts of water, posing a challenge given the scarcity of water resources. Additionally, farmers aim to maximize profits from the crops they cultivate.
Climate change vulnerability and adaptation strategies for smallholder farmers in Afghanistan are critical issues that require urgent attention from national, regional, and global climate-savvy stakeholders. This study investigates the climate change perception and adaptation strategies of smallholder farmers in Nangarhar province, utilizing the social-ecological systems perspective. The study employs a qualitative research design, conducting 11 semi-structured interviews with smallholder farmers to explore their lived experience about climate change, adaptation challenges, and indigenous coping strategies. The study used thematic analysis to examine the collected data. The analysis revealed several key themes that emerged from the data, namely climate change perception, adaptation challenges, indigenous coping strategies, government support and intervention, crop-specific impact, economic impact and livelihood, information sources and communication channels, and concerns about floods. The study highlights the challenges faced by farmers, including difficulties in crop production, limited access to quality inputs, and the adverse effects of drought on agricultural productivity. The findings underscore the importance of developing effective adaptation strategies to mitigate the adverse effects of climate change on the agricultural sector and the livelihoods of smallholder farmers in Afghanistan. The study contributes to the understanding of the vulnerability of smallholder farmers to climate change and the importance of enhancing their adaptive capacity, with a specific focus on conflict-affected agrarian regions like Afghanistan.
Combining ability analysis serves as an invaluable tool for evaluating the compatibility of parental lines and testers, as well as for elucidating the intricate genetic mechanisms at play within their hybrid progeny. This study was designed to ascertain the combining ability of maize lines when paired with testers, specifically focusing on yield-related traits through the utilization of a line × tester mating design. A total of fifteen advanced lines were systematically crossbred with three distinct testers to produce forty-five hybrid test crosses. The performance of these progenies was rigorously assessed across three distinct locations, thereby enhancing the robustness of the findings. The field trials were conducted using an alpha lattice design. Variance analysis, combining ability effects, and genetic components were estimated following a line × tester analysis. Employing variance analysis, significant variations were discerned in both general and specific combining abilities, underscoring the contribution of both additive and non-additive gene actions to the expression of the targeted traits. Notably, the magnitudes variance component indicated the prevalence of additive gene effects across the traits studied. Amidst the comprehensive exploration of parental lines and testers, it was evident that lines L10 and Tester T2 exhibited notable compatibility as general combiners, particularly in the context of maize grain yield. Additionally, Line L12 demonstrated favorable characteristics related to earliness. The superior performance of certain hybrid combinations emerged as a noteworthy outcome of this investigation. Specifically, the hybrid cross L10 × T2 displayed remarkable performance in terms of grain yield, while L12 × T1 demonstrated strong potential for the trait days to anthesis. Furthermore, in terms of specific combining ability, the cross L13 × T1 demonstrated the most pronounced effect, particularly concerning grain yield. Following closely were the combinations L5 × T1 and L2 × T2, each exhibiting significant potential for enhancing maize productivity. To conclude, this study underscores the indispensable role of combining ability analysis in elucidating the interplay between parental lines and testers, thus unraveling the intricate genetic dynamics within their hybrid offspring. The insights gathered hold promise for advancing maize production by employing judicious selection strategies, with a specific focus on the highlighted hybrid combinations.
Electric tractors with its cutting-edge technological improvements represent a transformative shift in agricultural technology for achieving the broad objectives of sustainable and environment friendly farming practices. This review examines the current status, performance characteristics, and future perspectives of electric tractors, focusing on their potential to replace traditional diesel models. The analysis highlights the advantages of electric tractors, including lower operational costs, reduced maintenance, and zero emissions, which contribute to quieter and cleaner agricultural operations. This transformation is witnessing several challenges in terms of high initial costs, limited battery life and the need for extensive charging infrastructure. The performance of electric tractors, particularly in extreme climates, is also a significant concern, with battery efficiency and power output varying under different environmental conditions. Despite these challenges, advancements in battery technology and propulsion systems, along with supportive government policies, are paving the way for greater adoption of electric tractors. The review also discusses the variability in regional adoption rates, with Europe leading due to strong regulatory support, while other regions like North America and Asia-Pacific are witnessing sluggish growth. The integration of electric tractors into precision agriculture and smart farming systems presents exciting opportunities for the future, boosting both productivity and sustainability. The investment in innovations and infrastructure related to electric tractor and renewed supportive policies from the governmental sector can usher a revolution in agricultural production system with lower environmental impact.
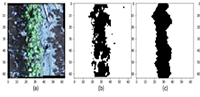
The timely acquisition of agricultural information is fundamental to smart agriculture, providing a basis for decision-making in agricultural production and ensuring protection against risks. With advancements in computer vision and machine learning, 3D reconstruction, the process of generating detailed digital models, has demonstrated substantial potential for mining and recording crucial information from objects, including geometry, structural attributes, visual appearance and other properties. This paper summarizes the applications of 3D reconstruction and measurement in the field of agricultural information acquisition based on prior research. It first reviews the 3D reconstruction and its related techniques and algorithms, then conducts a comprehensive analysis of the applications of 3D reconstruction and measurement in crop cultivation, animal husbandry, aquaculture and post-harvest products. It can be concluded that compared to traditional two-dimensional imagery, 3D reconstruction and measurement offer richer and more comprehensive information for agricultural practices, showing better performance in tasks such as organ segmentation, geometry measurement, health monitoring and simulation analysis. Future works can be launched from keeping up with the latest reconstruction technology, accelerating the 3D reconstruction, fusing multi-sensor data and combining 3D reconstruction with other information acquisition technologies.

Prof. Zhengjun Qiu
Zhejiang University, China

Cheng Sun
Academician of World Academy of Productivity Science; Executive Chairman, World Confederation of Productivity Science China Chapter, China
Indexing & Archiving
In the realm of modern agriculture, the integration of cutting-edge technologies is revolutionizing the way we approach sustainable farming practices. A recent study published in Advances in Modern Agriculture titled "Classification of cotton water stress using convolutional neural networks and UAV-based RGB imagery" has garnered significant attention for its innovative approach to precision irrigation management. Conducted by researchers from Institute of Data Science and the AgriLife Research and Extension Center of Texas A&M University (authors's information is below). This study introduces a novel method for classifying cotton water stress using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), offering a powerful solution for optimizing water use in agriculture.
Modern agricultural technology is evolving rapidly, with scientists collaborating with leading agricultural enterprises to develop intelligent management practices. These practices utilize advanced systems that provide tailored fertilization and treatment options for large-scale land management.
This journal values human initiative and intelligence, and the employment of AI technologies to write papers that replace the human mind is expressly prohibited. When there is a suspicious submission that uses AI tools to quickly piece together and generate research results, the editorial board of the journal will reject the article, and all journals under the publisher's umbrella will prohibit all authors from submitting their articles.
Readers and authors are asked to exercise caution and strictly adhere to the journal's policy regarding the usage of Artificial Intelligence Generated Content (AIGC) tools.
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.


 Open Access
Open Access

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
