
As a technology-intensive sector, modern agriculture is becoming more and more dependent on the ongoing development of new technological inputs, which serve as both its foundation and its engine. These new technologies include biotechnology, information technology, cultivation technology, water-saving irrigation technology, etc. The application of agricultural technologies has many advantages: firstly, it can increase the yield of agricultural products per unit; secondly, it can improve the quality of agricultural products; thirdly, it can reduce labor intensity; and fourthly, it can save energy and improve the ecological environment. Agriculture has developed quickly as a result of those new technology, which is quite advantageous to the general public and practitioners that are involved. This issue offers readers a discussion of the implications of numerous new technologies being applied to various connections in agriculture, along with interesting facts about these applications. Those findings suggest that appropriate use of modern technologies in agriculture could provide economic benefits without endangering the natural environment. More specifically, the use of irrigation technology, the promotion of crop growth, and the impact of technology on agriculture are the three key topics of this issue.
The growing demand for food in the country has required an increase in agricultural production levels and, with it, an increase in irrigation systems. Among the most widespread are central pivot irrigation systems, but their large number and variety make their optimal configuration difficult, generating overexploitation of natural resources such as water and threatening the sustainability of agriculture and the country. For this reason, the objective of this research was to implement software that would allow obtaining the appropriate configuration of this equipment using information on the type of crop, the agro-climatic conditions of the region, and the soil in order to obtain maximum utilization. As a result, an application capable of performing the calculations so that the value of water delivered by the system is closer to the estimated needs for a crop in each of its phases was achieved. To demonstrate this, an experimental study was carried out in field conditions in the agricultural enterprise La Cuba in Ciego de Avila; it showed that, with the use of the software, there was a saving of up to 94.5% of the water previously misused. In addition, the level of liquid provided allows the sowing to be in better conditions to reach its optimum yield. As an added value, the software has a minimalist and intuitive interface, which allows real-time visualization of field information.
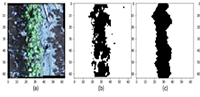
Objective: The study sought to investigate the distribution law of the diameter, velocity, and kinetic energy of water droplets in specially designed nozzles. Method: An indoor windless water droplet dispersion test on the PY15 rocker-arm sprinkler was performed using a video raindrop spectrometer at five working pressures: 100 kPa, 150 kPa, 200 kPa, 250 kPa, and 300 kPa. Result: The equal-flow nozzle has the following range: circle > rhombus > ellipse; the shape coefficient of the special-shaped nozzle decreases with increasing outlet diameter and increases with increasing aspect ratio; the diameter of the rhombus nozzle’s water droplet increases radially. Conclusion: Under the same working pressure, the diameter of the water droplet at the end decreases as the form coefficient increases. The wider the outlet’s diameter, the longer the range and the greater the increase in the velocity of the water droplets. The larger the aspect ratio, the shorter the range and the greater the average diameter and velocity of the droplets. The elliptical nozzle has the lowest droplet velocity increase as droplet diameter increases. The impacting kinetic energy and growth range of water droplets per unit volume at the same position decrease as the pressure increases. Along the radial direction, the droplet velocity and diameter are logarithmic, while the droplet kinetic energy and diameter are exponential and linear functions. The relationship between the shape coefficient, outlet diameter, aspect ratio, and droplet distribution characteristics of the shaped nozzle can be simulated using the fitting coefficients of the three droplet distribution prediction models, all of which are above 0.9.
Based on the panel data from 2000 to 2018, the super efficiency SBM-DEA model is used to calculate the agricultural green development efficiency of 11 provinces and cities in the Yangtze River economic belt, and then the Tobit econometric model is used to empirically test the impact of Internet technology popularization on the agricultural green development of the Yangtze River economic belt. The results show that: (1) on the whole, the efficiency of agricultural green development in the Yangtze River Economic Belt showed a downward trend in fluctuations from 2000 to 2018; in terms of regions, the efficiency of agricultural green development in various regions of the Yangtze River Economic Belt varies greatly, showing a spatial pattern of “downstream > upstream > midstream”. (2) The popularization of Internet technology has significantly promoted the green development of agriculture in the Yangtze River Economic Belt; at the same time, there is a significant positive correlation between rural human capital and the green development of agriculture in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, while the level of agricultural mechanization, the degree of capital deepening, the level of urbanization, and agricultural economic growth inhibit the improvement of the green development of agriculture in the Yangtze River Economic Belt to a certain extent. Therefore, the local governments of the Yangtze River Economic Belt should actively promote the popularization of Internet technology, enhance the Internet awareness of farmers, and give better play to the enabling role of Internet technology in the green development of agriculture in the Yangtze River Economic Belt.
The research was conducted in Jipijapa, in the town of Andil. The objective was to evaluate the physiological and morphological behavior of arabica coffee in the nursery stage with the application of biostimulants: starlite, humega, micorriza, and evergreen, compared to urea. A completely randomized experimental design was applied, using a factorial arrangement of repetitions in time for the morphological variables, and Tukey’s test was applied based on the statistical differences found. The results obtained at the physiological level established a significant difference (p < 0.05) in the variables dry matter, moisture, and nitrogen (N), with starlite and evergreen biostimulants being the best in DM and humega and evergreen in N content. There was a better response to chlorophyll (Cl) assimilation by all biostimulants, surpassing urea in general, with micorriza and starlite being the best, establishing a high positive correlation between N and chlorophyll. In terms of morphological development, Urea showed a better response, and at the biostimulant level, humega and micorriza showed better results, all between 90 and 120 days.
Alginic acid products are widely used in all fields, and the main source of alginic acid is seaweed. Alginic acid varies in various varieties of seaweed, plant parts, season to season, and the temperature of the water in which it is grown. The content of alginic acid also varies from manufacturer to manufacturer, as it depends on the process of extraction. No full-proof method for quantification is available. As alginic acid became a point of concern for regulators, a robust method for quantifying alginic acid became a prime requirement. As seaweed is only considered a source of alginic acid, essential amino acids, and nonessential amino acids, other sources need to be identified to overcome future needs and maintain biodiversity. The author succeeds in identifying another source of alginic acid, nutrients, and amino acids, i.e., Chromolaena odorata leaf extract, which contains about 5 to 6% alginic acid and 30 to 40% amino acids and proteins. A novel RP-HPLC method was found to be simple, suitable, and robust for the determination of alginic acid content in seaweed extract, its formulations, and also in phytoextracts (Chromolaena odorata leaf extract). The alginic acid content in seaweed and the formulated product quantified shows 10.05 ± 0.1% and 1.0 ± 0.03%, respectively, and is in close agreement with the declared content. Various authors have used gravimetric, colorimetric, titrimetric, and HPLC methods, each with their own limitations. The novel method is simple in terms of sensitivity, eco-friendly mobile phase, regular HPLC column and detector, lowest retention time (rapid analysis), and no internal standard required.
In order to maximize agricultural yields and reduce environmental effect, modern agriculture must overcome new obstacles in the integration of ecological and molecular approaches. Synthetic fertilizer doses per unit area have been greatly raised to produce larger yields, but this has resulted in pollution, health problems, and a loss of soil fertility, making it one of the biggest issues in agricultural production. Research has focused on developing new biotechnologies to increase production without the use of synthetic fertilizers, which has sparked interest in beneficial soil microorganisms that can encourage plant growth and, in certain situations, guard against pathogen infections of plant tissue. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) have intricate interactions with the biotic environment of microorganisms and plants, and they use many methods of action to support plant growth. These methods fall into three categories: 1) phytostimulation; 2) biocontrol; and 3) biofertilization. When crops are injected with PGRP, it significantly lowers the usage of synthetic fertilizers and their detrimental effects on the soil, boosts crop yields, and benefits the economy of the producer as well as the supply of food for the general public. The advantages that CVPGRs provide to agricultural activities are the main topic of this review, which also covers the fundamental elements of the relationship between CVPGRs and plant species.
Transgenic technology promises to eradicate hunger and poverty worldwide, among other sustainable development goals, and as a result, its acceptance is increasing. However, there are perspectives that highlight the challenges raised by such expansion. This paper is a reflection on a study effort on the bioethical consequences of using transgenic technology in agriculture in Colombia. The goal is to prove that this adoption poses a bioethical danger. The paper, on the one hand, addresses the problem that arises from confronting arguments for and against the adoption of this technology, while also noting the absolute importance of the economic aspect in the provision of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and the general difficulties of Colombian national regulations regarding GMO control and surveillance. Finally, it discusses the bioethical implications of adoption, beginning with the illusion of a transformational technology and progressing via the political will of the government to its eventual delivery to consumers.

Prof. Zhengjun Qiu
Zhejiang University, China

Cheng Sun
Academician of World Academy of Productivity Science; Executive Chairman, World Confederation of Productivity Science China Chapter, China
Indexing & Archiving
In the realm of modern agriculture, the integration of cutting-edge technologies is revolutionizing the way we approach sustainable farming practices. A recent study published in Advances in Modern Agriculture titled "Classification of cotton water stress using convolutional neural networks and UAV-based RGB imagery" has garnered significant attention for its innovative approach to precision irrigation management. Conducted by researchers from Institute of Data Science and the AgriLife Research and Extension Center of Texas A&M University (authors's information is below). This study introduces a novel method for classifying cotton water stress using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), offering a powerful solution for optimizing water use in agriculture.
Modern agricultural technology is evolving rapidly, with scientists collaborating with leading agricultural enterprises to develop intelligent management practices. These practices utilize advanced systems that provide tailored fertilization and treatment options for large-scale land management.
This journal values human initiative and intelligence, and the employment of AI technologies to write papers that replace the human mind is expressly prohibited. When there is a suspicious submission that uses AI tools to quickly piece together and generate research results, the editorial board of the journal will reject the article, and all journals under the publisher's umbrella will prohibit all authors from submitting their articles.
Readers and authors are asked to exercise caution and strictly adhere to the journal's policy regarding the usage of Artificial Intelligence Generated Content (AIGC) tools.
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.


 Open Access
Open Access

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
