
Water overexploitation in agriculture can be caused by inefficient irrigation practices and infrastructure, leading to reduced crop yields and land degradation. The proper use of land and water resource are essential to achieve long-term agricultural sustainability. This issue highlights works on sustainable agricultural water productivity, eco-farming policies and agricultural inputs on farming for certain regions. There is also a review on the strategies to optimize resource utilization for urban agricultural systems. These works provide a better outlook on the individual and collaborative interactions within an urban city to address water and resource utilization, to support a more resilient agricultural ecosystem.
Issue release: 31 March 2025
In order to track changes in developments and the degree of insecticide resistance, some common insecticides used to control T. absoluta in Egyptian fields were examined for seasonal variations in resistance. Tests were designed and tested for a few years at various field sample and greenhouse locations. Ten pesticides were selected for testing, and insects were sampled from eight agricultural fields for the laboratory bioassay. The identification and measurement of resistance in various field populations, seasons, and greenhouses revealed that insects were highly vulnerable to the IGR insecticide tested and only mildly susceptible to OP, Py, carbamate, and nicotinoids. Kalubia and Menufia showed more resistance in terms of both distribution and intensity than Dakahlia, Sharkia, and Giza, which showed lower resistance levels, possibly due to less effective insecticide applications. However, lufenuron was the most effective insecticide, followed by chlorfenapyr (IGRs), methoxyfenzoid, chlorfluazuron, indoxacarb, imidacloprid, cypermethrin, and chlorpyrifos. Dimethoate and spinoteram were the least effective insecticides.
Issue release: 31 March 2025
This article explores how hydroponics can help the State of Qatar implement sustainable agricultural policy in the face of the nation’s climatic and environmental problems, including a lack of arable land and water. Because it uses nutrient solutions to grow plants without soil, hydroponics is a cutting-edge substitute for conventional agriculture. It reduces water consumption and increases production efficiency. The article discusses how Qatar is adopting hydroponics within the framework of its National Vision 2023, which seeks to achieve food security by promoting innovation and sustainability in the agricultural sector. It also focuses on the environmental and economic benefits of hydroponics, such as reducing dependence on food imports and improving the use of natural resources by analysing available data. The article reviews the challenges of applying hydroponics in the State of Qatar, including the high initial cost and lack of public awareness. The article concludes that the demand for hydroponics in Qatar is rising due to a number of causes. Given Qatar’s harsh climate, hydroponics is a cutting-edge and environmentally friendly farming technique that enables year-round growing. Hydroponics is an effective method for growing crops, including fruits and vegetables, on a small amount of arable land and water.
Issue release: 31 March 2025
Growing depletion of groundwater resources is a global threat and intensified under improper water valuation systems. Here, we proposed an irrigation water valuation framework based on the opportunity cost concept (IWVF), to better differentiate the value of surface water, renewable, and nonrenewable groundwater. In this study, a 10-years dataset was used in Marvdasht-Kharameh irrigation networks (MKINs) in southern Iran, where groundwater depletion overshoots the sustainable level with an annual average rate of 1.42 m y−1. Irrigation water use, net incomes and losses, and economic water productivities (EWP) were estimated under the common and newly developed valuation methods. The reflections of adopting IWVF on EWPs were assessed under current condition and the proposed WP improvement scenarios, including removing irrigation efficiency gaps, changing the cropping calendar, and application of different levels of deficit irrigation. Results showed that the value of irrigation water supply ($436.91 million) exceeds gross income through crop production ($139.01 million) under current condition, which results in a net loss of $297.9 million in the study area. Hence, economic WP loss will be −0.33 $ m−3, meaning that consuming a unit of blue water causes $0.33 income loss under current condition. Applying WP improvement scenarios can reduce value of irrigation water by 27%, and gross income by 5.3%. Accordingly, common WP can increase by 6.6% from 1.81 to 1.93 kg m−3. However, the negative sign of EWP loss under management scenarios (−0.22 $ m−3) indicates that crop production in the study area is not viable due to its considerable environmental damages. Hence, current irrigation system should be revisited when sustainable agriculture is considered. The proposed water valuation method can help decision makers to better assess the consequences of WP improvement strategies, if the true value of different water resources is ignored.
Issue release: 31 March 2025
The key factors affecting domestic rice production in Preah Vihear Province, Cambodia, are investigated in this study. Cambodia’s economy depends largely on rice, which is both a main food and a major export. It helps Cambodia’s economy and food security. However, rice production is difficult due to lack of water, small farms, and geographical problems. Preah Vihear province is a key rice-producing region with hills and small farms. It helps increase income and sell rice to other countries with unique and famous rice seeds. To analyze the factors affecting domestic rice production in Preah Vihear, a statistical model known as ordinary least squares (OLS) will be used to examine the relationship between various input variables (costs) and rice yield. Data were gathered from a sample of 51 rice-farming households across five villages in Preah Vihear province. Additionally, both regression models indicated that herbicide costs were the most significant factor affecting rice yield, demonstrating high significance at the 5% level. This was closely followed by the price for renting rice harvesters and the total land area for rice production (ton). This study provides crucial information that can be used to develop targeted strategies to increase rice production and enhance the livelihoods of rural farmers. This will also empower stakeholders in the agricultural sector to propose campaigns that promote sustainable rice cultivation in local communities.
Issue release: 31 March 2025
Cities serve as principal economic hubs within the nation, characterized by unique socio-economic conditions and potential that present advantages as well as challenges for future economic advancement. The swift urbanization process is associated with the increasing demand for safety and sustainable development, especially in major cities like Ho Chi Minh City in Vietnam. Notably, sustainable urban agriculture, which is an integral component of the increasing movements towards locally sourced food, is a significant concern and is prioritized in the city’s comprehensive planning. This review paper presents models of agricultural development, emphasizing the synthesis, analysis, and evaluation of diverse resources—both their individual effects and their collaborative interactions with urban development—alongside the principal benefits and challenges in optimizing and utilizing these resources for optimal effectiveness. Additionally, this paper also suggests strategies to optimize resource utilization and foster the establishment of a sustainable, adaptable, and efficient urban agricultural system.

Prof. Zhengjun Qiu
Zhejiang University, China

Cheng Sun
Academician of World Academy of Productivity Science; Executive Chairman, World Confederation of Productivity Science China Chapter, China
Indexing & Archiving
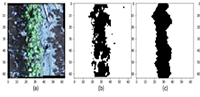
In the realm of modern agriculture, the integration of cutting-edge technologies is revolutionizing the way we approach sustainable farming practices. A recent study published in Advances in Modern Agriculture titled "Classification of cotton water stress using convolutional neural networks and UAV-based RGB imagery" has garnered significant attention for its innovative approach to precision irrigation management. Conducted by researchers from Institute of Data Science and the AgriLife Research and Extension Center of Texas A&M University (authors's information is below). This study introduces a novel method for classifying cotton water stress using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), offering a powerful solution for optimizing water use in agriculture.
Modern agricultural technology is evolving rapidly, with scientists collaborating with leading agricultural enterprises to develop intelligent management practices. These practices utilize advanced systems that provide tailored fertilization and treatment options for large-scale land management.
This journal values human initiative and intelligence, and the employment of AI technologies to write papers that replace the human mind is expressly prohibited. When there is a suspicious submission that uses AI tools to quickly piece together and generate research results, the editorial board of the journal will reject the article, and all journals under the publisher's umbrella will prohibit all authors from submitting their articles.
Readers and authors are asked to exercise caution and strictly adhere to the journal's policy regarding the usage of Artificial Intelligence Generated Content (AIGC) tools.
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.


 Open Access
Open Access

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
