
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
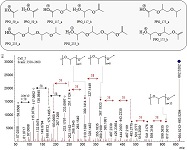
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
Issue release: 30 June 2024
The main objective of the study was to characterize raw (RFA), water-washed (WFA) and iron-modified (Fe-WFA) Botswana coal fly ash to determine the physical and chemical properties as well as investigate its potential use as adsorbents for the removal of arsenic(III) ((As(III)) from fortified water. Scanning electron microscopy with an energy dispersive spectrometer (SEM-EDS) showed particles with irregular size and shape for all the materials and porous iron oxide flakes for Fe-WFA. The SEM-EDS, X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) showed the main constituents of RFA, WFA and Fe-WFA to be SiO2, Fe2O3, Al2O3 and CaO. The XPS further showed the surface composition of Fe-WFA with higher Fe content at 19.7% compared to 0.8% and 1.2% for RFA and WFA respectively. The XRF and XRD results confirmed the successful modification of WFA with iron by showing the Fe2O3 composition increasing from 12.6% of WFA to 25.5% for Fe-WFA. The inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) results showed continuous reduction of metal concentrations for WFA and Fe-WFA from the first to the sixth wash. The adsorption of As(III) on the adsorbents followed the Freundlich adsorption model. The maximum adsorption capacities of 0.85, 0.02 and 2.26 mgg−1 were obtained for RFA, WFA and Fe-WFA respectively.
Issue release: 30 June 2024
Context: At present, nanotechnology can be used in multiple areas of action which, due to its nature, can be implemented with great versatility, given that many advances in nanotechnology base their studies on how to optimize daily and industrial processes and how to favor the environment. In addition, the manipulation of matter at this level allows the creation of solutions with greater scientific, social and economic impact. For the purposes of this research, laboratory results will be shown using cellulosic nanomaterials for the adsorption of emerging antibiotic-type contaminants. Method: This research was carried out at laboratory level, where cellulose was modified by chemical methods to obtain nanocellulose by oxidation. A characterization of the material obtained by spectroscopy techniques was carried out, and the adsorption of emerging anti-biotic contaminants such as ciprofloxacin. Results: Cellulosic nanomaterials have the potential to be used in tertiary water treatment for the removal of emerging contaminants such as ciprofloxacin. The results show that the cellulosic nanomaterial adsorbs ciprofloxacin by 27%. Conclusions: Nanocellulose membranes have potential for use in a water purification system; those made only with cellulose showed a lower percentage of contaminant adsorption than membranes with nanocellulose.
Issue release: 30 June 2024
Objective: To present a systematic review of studies that evaluate the impact caused by urban solid waste generated in the Oaxacan Mixtec region. Results: The analysis of the research results consulted in the following databases: Red de Revistas Científicas de América Latina y el Caribe (Redalyc), Scientific Electronic Library Online (Scielo), Dialnet, EBSCO and Consorcio Nacional de Recursos de Información Científica y Tecnológica (CONRICYT), show that pollution is a problem that has been gradually increasing globally, which has led to the presence of foreign organisms and substances that interfere with and damage the health of people, natural resources and the ecological balance; It is worth mentioning that the impact on communities caused by the inadequate generation and management of solid waste significantly alters the ecosystem of the areas surrounding the disposal sites. It is important to note that there is legislation in this area that specifically classifies the different disposal sites and entrusts the municipalities with the integral management of urban solid waste, but this legislation is not correctly applied despite the fact that this problem has become very important in the last two decades in governmental spheres. Conclusions: Mexico faces the challenge of resolving environmental problems in order to reach a level of sustainability and sustainability in the medium term. The generation rates of urban solid waste continue to increase because we live in a society that has drastically modified its consumption habits. The degradation of the environment and natural resources for the Oaxacan Mixtec region is classified in ranges from unstable-critical to critical, causing pressure on natural resources, which is why we must have an adequate management and disposal of municipal solid waste, to achieve this it is necessary to have the support of society, governments and society in general, this synergy is necessary to reduce the extraction of resources used to produce them obtaining economic, social and environmental benefits in the long term for the region.
Issue release: 30 June 2024
The bay of Santiago de Cuba is the second in importance and contamination in the country. Aggressive waste discharges with organic and inorganic materials, heavy metals, masonry residues, grease, oils and hydrocarbons, among others, are discharged into the bay. A systematic review of databases, publications, web pages and other documents was carried out in order to find out more about contamination. Eighty-five percent of the main reports refer to organic matter contamination and waste characterization, followed by hydrocarbon contamination (15%). This makes the work related to sustainable management in the bay insufficient.
Issue release: 30 June 2024
Biochar is the product of biomass decomposition, whose physicochemical characteristics are associated with its origin and the combustion method used. Among these properties, the surface area, the formation of macro and micropores, and the presence of functional groups stand out. Due to these characteristics, biochar becomes an alternative material with high adsorption capacity of toxic compounds present in contaminated wastewater. This work provides information on the generation mechanisms of biochar and how they interfere in its physicochemical characteristics. It also describes the parameters involved in the pollutant removal processes and mentions the treatments under which biochar can be subjected to improve its adsorption capacity. Finally, the possible uses or the appropriate final disposal of biochar in order to contribute to the circular economy strategy are indicated.
Issue release: 30 June 2024
Despite the scientific consensus on the need to limit global warming, the urgency for the autonomous provision of energy resources has led many States to authorize projects that apply non-conventional fossil fuel extraction techniques, such as horizontal drilling and high-volume hydraulic fracturing of shale. Although few studies present conclusive evidence, these techniques are accused of causing dangers to the environment and to the health of the people who work and live in fracking areas, so that the States are faced with the dilemma of extending their energy autonomy for a few years, squeezing their natural gas and oil reserves to the end, or seeking a balance with the planet by moving towards more sustainable energy sources. Based on the review of studies that present evidence of physical and chemical contamination and other impacts on the environment in areas where the fracking technique has been developed, a panorama of risks for people living near extraction platforms and the dangers of developing fracking projects in tropical climate zones is presented.
Issue release: 30 June 2024
In this study, based on an existing analytical solution for the two-dimensional transport of contaminants in a saturated soil layer, for the pulse source, the R program code was developed. The simulation is used to obtain the profiles of contaminant concentration, for a steady groundwater velocity, as a function of distance from the source and time. The problem is analytically solved by leveraging the similarity between the Gaussian (normal) distribution and contaminant concentration distribution, the development of the analytical model (i.e., solution of partial differential equation) by using this similarity is explained step by step since it may be of interest to researchers. Contaminant propagation is modeled using R software, which helps to understand how contaminants migrate through a saturated soil layer. This approach aids in comprehending the mechanisms and spatial dynamics of contaminant dispersion, facilitating the prediction and management of soil and groundwater contamination. The provided R code can be altered for different parameters and time intervals.
Issue release: 30 June 2024
This paper addresses air quality in Bulgaria, a pressing environmental issue with monitoring data indicating persistent challenges in urban areas due to pollutants like PM10 and NO2. Bulgaria’s government operates a comprehensive air quality monitoring network, offering real-time data to track pollutants across multiple regions. Scientific research in this area focuses on identifying pollution sources, assessing public health impacts, and developing models for pollution control. Efforts to improve air quality include implementing stricter regulations, investing in green technologies, and conducting public awareness campaigns. Future research emphasizes sustainable urban planning, the adoption of renewable energy, and advanced monitoring technologies to strengthen air quality management in Bulgaria.
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China




 Open Access
Open Access