
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
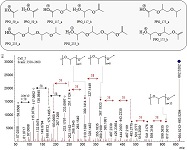
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
Issue release: 31 December 2023
Biochar offers several advantages, including high carbon content, a large specific surface area, a well-developed pore structure, and excellent adsorption capabilities. It is extensively utilized in improving soil quality, remediating environmental pollution, and contributing to carbon sequestration and emission reduction. However, practical challenges such as the low bulk density of biochar, difficulties in solid-liquid separation, and the need to enhance its long-term effectiveness and stability persist. To address these issues, biochar composites with improved remediation efficiency for polluted environments have been developed by combining biochar with metal materials, photocatalysts, and clay minerals, garnering significant attention. This systematic review examines the preparation methods and applications of biochar-based composite materials in environmental pollution control, analyzes the mechanisms for removing organic pollutants, and discusses future research and development trends for biochar materials, aiming to provide new insights for the creation and practical use of high-efficiency biochar composites.
Issue release: 31 December 2023
The high-temperature pyrolysis oxidation process was utilized to produce reed biochar, which was then employed as a carrier for immobilizing the predominant petroleum hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria. The study investigated the effects of this biochar-bound microbial immobilization on the remediation efficacy and enzymatic activity of soil contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons. The findings indicated that after 40 days of treatment with reed biochar-immobilized microorganisms, the soil's petroleum hydrocarbon removal rate reached 55.01%, markedly surpassing the removal rates of biochar (45.82%) and the untreated control group (24.83%). Additionally, it was observed that the biochar-immobilized microorganisms significantly enhanced the activities of soil enzymes such as dehydrogenase, catalase, urease, and polyphenol oxidase. The application of biochar-bound microbial immobilization technology not only boosts the cleanup efficiency of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil but also substantially elevates the soil's biological enzyme activity.
Issue release: 31 December 2023
Agricultural soil serves as the fundamental resource for grain production, with its quality being integral to both the national economy and the well-being of the population. As economic and societal development progresses, the levels of lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn) in farmland soil are on the rise. Currently, research into the total quantities and speciation distribution of Pb and Zn in agricultural soil, as well as their influencing factors, is fragmented, and there is a gap in comprehensive understanding regarding the transformation mechanisms and pollution status of various forms of these heavy metals. To gain a clearer picture of the heavy metal pollution in soil, as well as the distribution and transformation dynamics of different forms, this study conducts an integrated analysis of the pollution levels, speciation distribution, and influencing factors of Pb and Zn in Chinese farmland soil. Additionally, it assesses the ecological risk of heavy metals using principal component analysis and the geoaccumulation index. The findings indicate that the average concentrations of Pb and Zn are 4045 mg/kg and 10699 mg/kg, respectively. The residual form of Pb is most predominant in the Northwest, while the exchangeable form is most prevalent in the Southwest. The residual form of Zn constitutes over 50% of its presence. The analysis reveals that pH is the primary factor influencing the speciation distribution of heavy metals. The combined results of the geoaccumulation index and the potential ecological risk index (RI) suggest that Pb levels at the study site exceed those of Zn, though both are classified as posing a slight risk. A holistic analysis of soil environmental factors reveals that the speciation distribution of heavy metals reaches an equilibrium state through the interaction of multiple factors.
Issue release: 31 December 2023
The objective of this paper is to discuss the approach of journalism to the use of pesticides as a situation that generates environmental injustice. To make such a reflection, we rely on the series of Zero Hora reports published in December 2016 on the contamination of Ceasa products, in Porto Alegre, by pesticides banned in Rio Grande do Sul (Brazil) or used above the limit set by law. We start from Acselrad’s conception of environmental justice. This is a notion that refers to socio-political dynamics since it includes conflicts arising from the violation of the rights of human communities due to unsustainable use of the environment. To assess the impact of injustices in the media, we resorted to the assumptions of Environmental Journalism, a perspective that defends the mobilizing function of journalism based on a complex view of the phenomena (Girardi et al.) from a descriptive and qualitative analysis (Martins). Among the results, it is noted that the series does not incorporate a systemic view of the problem, ignoring the impacts of pesticides on the entire production chain and ecosystems.
Issue release: 31 December 2023
In Mexico, an agricultural soil poor in nitrogen (N) contaminated by a hydrocarbon derivative such as automotive residual oil (ARA), with a relatively high concentration of 100,000 ppm, is an environmental problem, but also because it drastically affects soil properties associated with the mineralization of organic matter and loss of fertility, since it exceeds the maximum accepted limit of 4400 ppm of the Mexican standard called, NOM-138-SEMARNAT-2012 (NOM-138). An alternative solution is to treat it with ecological actions to eliminate the ARA and recover fertility. Therefore, the objectives of this research were: i) bioremediation of soil contaminated by 100,000 ppm of ARA ii) phytoremediation using Sorghum vulgare with Aspergillus inger and Penicillium chrysogenum to decrease ARA to a value below 4400 ppm of NOM-138. For this purpose, soil recovery was performed using the variable-response: disappearance of ARA by Soxhlet at the beginning and after bioremediation and at the end of phytoremediation with S. vulgare with phenology and biomass to seedling. All experimental data were validated by ANOVA/Tukey HSD P < 0.05%. The results indicated that bioremediation and phytoremediation of soil contaminated by 100,000 ppm of ARA, decreased it to 3400 ppm, a value lower than the maximum established by NOM-138, sufficient for soil recovery in agricultural production, in 120 days, a relatively short period of time.
Issue release: 31 December 2023
To address the issue of cadmium (CD) contamination in the Enshi Mountain vegetable-growing soil, a pot experiment was conducted to assess the impact of various passivators (including biochar, hydroxyapatite, lime powder, fly ash, and a blend of organic passivators) on the passivation of Cd in the test soil, as well as on the yield, quality, and Cd content of Chinese cabbage. The findings revealed that while lime powder treatment hindered the growth of Chinese cabbage, all other treatments enhanced the fresh weight and height of the plants, with the fly ash treatment increasing the fresh weight of Chinese cabbage by 109.72%. Hydroxyapatite, lime powder, and the mixed passivator raised the soil pH by 25.18%, 36.61%, and 28.21% respectively. None of the treatments significantly affected the activities of soil urease, cellulase, and sugarcane enzyme, but biochar and mixed passivator treatments significantly boosted phosphatase activity by 52.85% and 69.82%, respectively, while lime powder treatment significantly suppressed it. All five passivator treatments decreased the Cd content in Chinese cabbage, with biochar, hydroxyapatite, lime powder, and mixed passivator treatments showing significant suppression, with lime powder being the most effective at reducing Cd by 73.80%. None of the treatments significantly impacted the quality of Chinese cabbage. Biochar and mixed passivator treatments lowered the total Cd content in the soil by 27.21% and 46.98% respectively, while lime powder and mixed passivator treatments reduced soil ion-exchangeable Cd by 67% and 47.35% respectively. The application of these five passivators was effective in reducing the Cd content in Chinese cabbage. Specifically, the mixed passivator treatment not only maintained the yield and quality of Chinese cabbage but also enhanced soil enzyme activity and decreased the proportion of total and effective Cd (ionic and water-soluble) in the soil.
Issue release: 31 December 2023
To uncover the pollution characteristics of the main rivers flowing into Erhai Lake, a study was conducted from January 2014 to December 2016, monitoring the water quality and quantity of 27 major rivers using total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N), and chemical oxygen demand (CODcr) as pollution indicators. Additionally, this study combined an analysis of precipitation data during the same period with water quality monitoring data from the lake area, detailing the water quantity and quality characteristics of the rivers entering the lake, estimating the pollution load entering the lake, and assessing the impact of this pollution load on the lake's water quality. The results indicate that: a) from 2014 to 2016, the total water inflow from the 27 main rivers into the lake ranged from 287 million to 474 million m³, with the inflow during the flood season accounting for 79.17%, 74.90%, and 61.96% of the annual total, respectively. The water inflow into the lake was positively correlated with the basin's precipitation; b) over time, pollutant concentrations exhibited a fluctuating trend, initially increasing and then decreasing throughout the year. Generally, water quality during the rainy season was good, and the spatial variation in pollutant concentrations was less pronounced than the temporal variation, with a significant negative correlation between pollutant concentrations and basin rainfall; c) the pollution load entering Erhai Lake initially decreased, then increased, and subsequently decreased again over the year. The pollution load was primarily influenced by water volume, with contribution rates ranked as north bank > west bank > southeast bank. The total nitrogen input from the rivers was positively correlated with the total nitrogen concentration in the lake area, while total phosphorus input was positively correlated with the total phosphorus concentration in the lake area, indicating that these rivers are significant sources of nitrogen and phosphorus for Erhai Lake.
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China




 Open Access
Open Access