
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
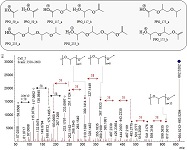
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
Issue release: 30 June 2023
This summary outlines a significant challenge in ecological risk assessment of contaminated sites: quantitatively evaluating the ecological effects of combined heavy metal pollution in real-world soil. The study proposes a novel quantitative ecological assessment approach that integrates both broad (“top-down”) and detailed (“bottom-up”) knowledge. This approach involves three key steps: identifying effective biomarkers, pinpointing dominant pollutants, and assessing the combined effects of various exposure types and contaminants. To validate this approach, researchers examined an abandoned electronic waste site in Jiangsu Province using soil microcosms with earthworms. By analyzing biomarkers such as malondialdehyde (MDA), metallothionein (MT), catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and reduced glutathione (GSH), they found that earthworms accumulated heavy metals in the order of Cd > Cu > Zn > Ni > Pb > Cr. Principal component analysis (PCA) identified GSH, CAT, and MDA as effective biomarkers, with Cd and Zn as the primary contaminants. The study revealed significant linear relationships between biomarker changes and specific heavy metal concentrations in soil (e.g., GSH with total Cd and DTPA-extractable Zn, MDA with DTPA-extractable Cd, and CAT with total Zn and bioaccumulated Zn). The sensitivity of the biomarkers to heavy metal contamination was ranked as GSH > CAT > MDA. Furthermore, the study highlighted complex interactions among different heavy metals, exposure types (e.g., soil vs. bioaccumulated), and biomarkers, emphasizing the need for comprehensive assessments in contaminated site evaluations.
Issue release: 30 June 2023
The weathering of mining wastes with a high content of metallic sulfides is involved in the release and mobility of heavy metals, being one of the main risk factors for the environment and public health. In this work, two types of manure were used to evaluate their effect on the mobile or bioavailable chemical fractions of Cu in a soil contaminated with mining waste. An experiment was conducted using a soil artificially contaminated with 25% mining waste from Zimapán, to which increasing doses of composted cow and pig manure (0, 3, 6, 12 and 24%) were added. The pseudo-total Cu concentration was determined by atomic absorption spectrophotometry after acid digestion, while the Cu chemical fractions were determined from sequential extractions. The results obtained showed a high pseudo-total Cu concentration in the mining residues and low in the soil and in both types of manure. In the treatments with greater application of pig manure, there was a decrease in the concentration of soluble-interchangeable Cu and an increase in the concentration of Cu strongly bound to the organic fraction. While with cow manure there were higher concentrations of soluble-interchangeable Cu and an increase in the fraction of Cu weakly bound to the organic fraction.
Issue release: 30 June 2023
The middle segment of Xiaonan River, which feeds into the Puhe River, was chosen for research. Samples including its water, river bottom mud, river bank soil, and nearby vegetation were collected from six monitoring sites. These samples were analyzed by ICP-OES to determine heavy metal distribution. The results showed that main contamination of heavy metals in the Xiaonan River are Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn. Notably, Cr and Zn are in high levels, and Cr surpassed the limit of third-grade standard, indicating severe contamination. By using the potential ecological risk index method, Cd showed a high coefficient, severely damaging the surface water and riparian soil. The migration patterns of Cr and Zn were different. Cr tended to accumulate more in riverbank soils, while Zn showed higher concentrations in river bottom mud. Plants of nearby vegetation showed minimal absorption and transfer capabilities for Cd, while Ni transferred most. By applying the ecological risk index, potential pollution sources were inferred to assess each metal's distribution, so to offer a basis from its origin, and to protect the ecological health of the Puhe River Basin.
Issue release: 30 June 2023
The study aimed to assess the quality and sanitation of direct drinking water from terminal devices collected from various places such as communities, schools, and homes in Yantai City. This research was to support regulations, enhance authorized supervision, and inform consumer choices. 232 samples were randomly gathered in aforementioned places between June to November, 2019. The test of aerobic plate count, Coliforms, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa followed the standard operating procedure provided by Chinese National Food Contamination and Harmful Factors Risk Monitoring Manual in 2019. Findings showed that 84.05% of the samples had aerobic plate counts as main contamination, with Coliforms and Pseudomonas aeruginosa was respectively 3.02% and 7.33%. These results revealed that aerobic plate count was the main contaminant in high-quality drinking water, while Pseudomonas aeruginosa was the main pathogenic bacteria. Overall, 9.48% of the samples exceeded the standard. Family settings had the highest non-compliance rate at 12.68%, followed by schools at 8.97%, and communities at 7.23% by comparing different sources, yet these differences were not statistically significant (χ2 = 1.36, P > 0.05). There was no clear seasonal variation regularity of the detection rate. However, there was clear variation in monthly non-compliance rates. The highest was at 15.00% in November, followed by June at 13.89%, September at 11.76%, October at 6.25%, August at 5.88%, and July at 5.00%. Yet these differences were not statistically significant, either (χ2 = 4.47, P > 0.05). It was notable that some samples exhibited multiple contamination by various indicators. In summary, the study showed widespread contamination of direct drinking water by aerobic plate count, Coliforms and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, with aerobic plate count being the most prevalent issue.
Issue release: 30 June 2023
Science curricula emphasize the need to involve students in civil society issues related to science, highlighting the primacy of learning about the science-technology-society-environment relationship. The objective of this work is to know the students' learning when they get involved in the attempt to solve the problem related to the pollution of the stream near their school. The research methodology is qualitative, interpretative and based on participant observation. Twenty-one students from two 8th grade classes with an alternative curriculum, living in a rural environment in southwestern Portugal, participated in the study. Data were collected through the teacher's diary, written documents and interviews with the students (conducted at the final of the study). The results reveal that the positive experiences provided by the radio club gave them confidence and encouraged them to engage in community activism related to the pollution of the local stream. This activism takes the form of a puppet show about sewage treatment. Also, the results show us that activism leads students to the identification of the science and technology issues that are at the root of the pollution of the creek, expanding their knowledge about the problem and discussing different perspectives for its solution. In addition, young people recognize that knowledge enables them to inform other members of the community and realize that they have the right to become involved in socio-scientific issues that affect their quality of life.
Issue release: 30 June 2023
Urban impervious surface rainfall runoff pollution is a significant component of non-point source pollution, with pollutants accumulating on these surfaces during dry periods being the primary source of contaminants in rainfall runoff. Using the first ten rainfall events of 2015 as a case study, impervious surfaces such as the roofs of teaching buildings, campus roads, and nearby main traffic roads within the university campus in southeastern Beijing were selected for field sampling and analysis of natural rainfall and rainfall runoff pollution. The findings indicate that the initial rainfall runoff pollution following winter is severe, with water quality falling below Class V. Subsequently, the pollution levels decrease; however, the severity of water pollution varies at different sampling locations. Notably, ammonia nitrogen concentrations are higher near building toilet exhaust outlets, and the presence of pervious surface facilities can mitigate runoff pollution. Based on the analysis and research findings, several recommendations for controlling and managing urban rainfall runoff pollution are proposed.
Issue release: 30 June 2023
Water transport has emerged as one of the most significant modes of transportation globally, owing to its high carrying capacity, low transport costs, and minimal energy consumption. As a critical hub for land-water transfer, ports experience frequent interactions between ships and land, leading to substantial discharges of domestic sewage and oily wastewater, as well as suspended pollutants from construction activities. Consequently, water pollution in port areas has become increasingly severe. To implement sustainable development strategies and promote green port initiatives, it is essential to research and address water pollution in these areas. This paper first summarizes the sources and impacts of the main water pollutants associated with port construction and operations. It then discusses the spatial and temporal distribution patterns of these pollutants. Finally, based on a literature review, the author highlights the current state of water pollution in port areas, advocates for the introduction of ecological engineering solutions for wastewater treatment, compares the differences in water pollution prevention plans between domestic and international ports, and identifies the shortcomings and gaps in existing research and prevention efforts related to water pollution in port areas.
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China




 Open Access
Open Access