
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
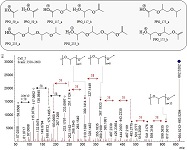
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
The distribution characteristics of heavy metal contamination in the central segment of Xiaonan River, Shenyang
Vol 4, Issue 1, 2023
Download PDF
Abstract
The middle segment of Xiaonan River, which feeds into the Puhe River, was chosen for research. Samples including its water, river bottom mud, river bank soil, and nearby vegetation were collected from six monitoring sites. These samples were analyzed by ICP-OES to determine heavy metal distribution. The results showed that main contamination of heavy metals in the Xiaonan River are Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn. Notably, Cr and Zn are in high levels, and Cr surpassed the limit of third-grade standard, indicating severe contamination. By using the potential ecological risk index method, Cd showed a high coefficient, severely damaging the surface water and riparian soil. The migration patterns of Cr and Zn were different. Cr tended to accumulate more in riverbank soils, while Zn showed higher concentrations in river bottom mud. Plants of nearby vegetation showed minimal absorption and transfer capabilities for Cd, while Ni transferred most. By applying the ecological risk index, potential pollution sources were inferred to assess each metal's distribution, so to offer a basis from its origin, and to protect the ecological health of the Puhe River Basin.
Keywords
References
- Li Yunchao, ji Hua, wen Zhiyu, et al Residue dynamics and safety risk assessment of three plant growth regulators in main fruits and vegetables in Beijing Tianjin Hebei region [J]. Journal of food safety and quality inspection, 2017, 8 (8): 3011-3017
- Lixiaogang, baiqiaohui, pang Jingyu, et al Grain size analysis and heavy metal pollution assessment of river surface sediments in Danjiang River Basin [J]. Jiangxi Agricultural Journal, 2019, 31 (4): 93-98
- Wangcunlong, pangxugui, yangliyuan, et al Ecological hazard assessment of heavy metals in soil: taking a typical gold mine area as an example [J]. Geochemistry, 2013, 42 (6): 557-566
- Arnaudguilhem Carine, Larroque Marion, Sgarbura Olivia, et al. Toward a comprehensive study for multielemental quantitative LA-ICP MS bioimaging in soft tissues[J]. Talanta, 2020, 222(3):121537.
- Wang Yu Remediation of heavy metal pollution in soil was accelerated [n]. Farmer daily, april 8, 2014 (002)
- Yu Zhengsheng Response of soil bacterial community to heavy metal chromium pollution and its reduction mechanism in Lanzhou section of the Yellow River [d]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019
- Zhouxuhua Study on water pollution control technology of urban polluted river [J]. Low carbon world, 2021, 11 (2): 36-37
- Xiazhenyan Response analysis of diatom markers under heavy metal pollution in Le'an River [d]. Nanchang: Nanchang Institute of engineering, 2019
- Guoyuxi Research and design on solid-liquid separation of contaminated soil by pressure filtration [d]. Shenyang: Shenyang University, 2018
- Cheng Yan, wang Ya, zhou Yongzhang, et al Pollution status and sources of heavy metals and metalloids in groundwater system of Zhuhai City [J]. Bulletin of mineral and rock geochemistry, 2019, 38 (3): 595-603
- Zhaoshuai, wang Ji, caixiongfei, et al A review on the speciation, biological impact analysis and remediation technology of soil lead pollutants [J]. Modern chemical industry, 2020, 40 (12): 8-12, 18
- Feng Zhenmin A soil remediation agent for heavy metal pollution and its preparation method [p]. CN108192638B, 2021.
- Wangxiaoyin, luojiangyan, zhangbei, et al Determination of acid soluble heavy metals and total heavy metals in Chinese patent medicines containing four heavy metals [J]. Chinese herbal medicine, 2009, 32 (4): 631-633
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2023 Yinglian Lan, Ying Ma, Jing Gao, Peng Zhou, Chuang Song, Yanlong Li
License URL: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China



