
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
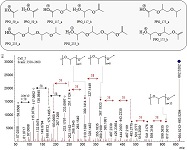
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
This issue focuses on research related to water pollution. Key research explores spatial microplastic accumulation at aquatic interfaces, advanced MBR treatment efficacy, and coagulant-based pollutant removal. These studies align with frontiers in pollution tracking and innovative remediation, offering vital insights for sustainable management from source to sink.
Issue release: 30 June 2025
Microplastics are a major form of anthropogenic pollution, and over time, the sediment at the bottom of aquatic environments becomes the sink for the denser of these particles. By mapping and analyzing sediment from lake and estuary systems, this study aimed to find spatial relationships between water and sediment dynamics at stream-to-slack-water transitions and resulting microplastic sediment accumulation characteristics. Sediment was collected along transects extending from the stream mouth to open water depositional environments at four unique study sites. After a series of separations from collected sediment, microplastics were weighed to map longitudinal variations in plastic concentration. At all study sites, the highest concentrations of microplastics (up to 14% dry weight) in sediment were found to focus in spatial hotspots peaking 600–700 m down gradient from the transition to a low-energy environment in intertidal freshwater estuary systems, and 150 m downstream in a lake system, all being associated with environments of clay-dominated sediment deposition. The dominant types of plastics identified were cellophane and polydimethylsiloxane. We hypothesize these spatial hotspots of microplastic accumulation may result from the unique diversity of density ranges for microplastic sediment, ranging from just above 1 g/cm3, but below the 2.7 g/cm3 common for natural mineral sediment, thus creating plastic depositional locations that are spatially offset from those of common mineral grains.
Issue release: 30 June 2025
Sewage treatment plays a crucial role in sustainable urban and industrial development. This study focuses on the generation and treatment of sewage from residential, institutional, commercial, and industrial sources, distinguishing between grey water and black water. While grey water is relatively easier to treat, conventional practices in India merge both streams for processing. This research evaluates the application of advanced Membrane Bio Reactor (MBR) technology in a Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) at an industrial township in Andhra Pradesh, India, to achieve Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD). The study demonstrates the significant efficiency of MBR technology in removing contaminants, with Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) reduced from 350 mg/L to 20 mg/L, Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) from 650 mg/L to 50 mg/L, and Total Suspended Solids (TSS) from 150 mg/L to 4 mg/L. Additionally, oil and grease levels decreased from 19 mg/L to 4 mg/L, and total nitrogen dropped from 45 mg/L to 10 mg/L. These results affirm the effectiveness of MBR in producing high-quality treated water suitable for irrigation and toilet flushing. The research involved systematic sampling of influent and effluent wastewater over a set period, employing analytical methods like spectrophotometry and chromatography. Key operational parameters such as flux rate, transmembrane pressure (TMP), sludge retention time (SRT), and hydraulic retention time (HRT) were monitored to optimize efficiency. Comparative analysis with conventional treatment methods highlights MBR’s advantages, including superior pollutant removal, reduced footprint, and lower energy consumption. Real-time sensors and lab-scale MBR setups were used for continuous data collection and statistical analysis, confirming MBR’s effectiveness in sustainable wastewater treatment.
Issue release: 30 June 2025
Issue release: 30 June 2025
The Godavari River flows year-round, being a perennial watercourse, providing a steady water supply. However, rising pollution threatens its water quality. Without regular pollution control, it may face a decline similar to the River Nandini, which vanished in the 1940s along with its surrounding forest. Thus, this study investigated the specific gravity and surface tension of various water samples collected near the Victoria Bridge on the Godavari River to assess the impact of different contaminants. Samples analyzed include pure water, polluted water, saline water, water with detergent, slightly muddy water, and slightly ashy water, which might contain gold particles or gold dust in it. The findings reveal that saline water exhibited the highest specific gravity (1.025 g/cm3), while pure water maintained a specific gravity of 1.000 g/cm3. At point 1, the surface tension ranged from 31 to 42 mN/m. For point 2, it fell between 49 and 55 mN/m. Point 3 showed a range of 49 to 60 mN/m, while at point 4, it varied from 49 to 57 mN/m. Lastly, point 5 exhibited surface tension values between 49 and 56 mN/m at Victoria Bridge. Surface tension measurements ranged from 55 to 70 mN/m at all five points—point 1 through point 5 each displayed values within this consistent interval at Tapovan Bridge and a point near Dasak Bridge. Thus, surface tension measurements indicated that contaminants such as detergents and organic pollutants significantly reduce water’s surface tension, affecting the transport and fate of pollutants. The average suspended particle mass (mg) was found to be about 13.4 (mg). These results emphasize the importance of continuous monitoring and remediation efforts to maintain water quality, especially under extreme climatic conditions.
Issue release: 30 June 2025
Methane, a potent greenhouse gas, has gained prominence due to its significant contribution to global climate change. Beyond its climate impact, this review recognizes methane’s dual role in influencing local and regional air quality, underscoring its growing concern in the context of contemporary environmental issues. The paper aims to provide an overview of methane sources, geographic distribution, long-term health effects, interactions with other pollutants, and the pivotal role of integrated monitoring systems in effective pollution control strategies. The review delves into the primary sources of methane emissions, including anthropogenic and natural processes. Geographically, it identifies high-risk areas, with substantial emissions concentrated in North America, Europe, and Asia. Prolonged exposure to elevated methane levels in urban and industrial settings is associated with respiratory, cardiovascular, and neurological health issues. Furthermore, methane’s interaction with other pollutants leads to the formation of secondary organic aerosols and ground-level ozone, exacerbating air quality challenges. Efficient pollution control hinges on integrating satellite and ground-based data into monitoring systems, ensuring accurate and timely information. Managing methane emissions presents a complex dilemma, impacting both local air quality and global climate. Addressing this dual challenge necessitates a comprehensive approach encompassing legislative reforms, technological advancements, increased public awareness, and international collaboration. A swift response is imperative to mitigate the adverse effects of methane emissions on the environment and human health.
Issue release: 30 June 2025
The Yamuna River, a lifeline for millions in India, has been severely polluted over the decades. From 2014–2024, substantial research has been conducted to analyze the extent of its degradation, pollution sources, and mitigation efforts. This review synthesizes studies from this decade, focusing on chemical, biological, and physical parameters of pollution, industrial and municipal waste contributions, agricultural runoff, and policy interventions. Despite increased awareness and remedial measures, the river remains critically polluted, demanding urgent and sustainable solutions. Also, incomplete data has been collected over the years. The focus of researchers has been primarily on Delhi-NCR regions, mainly because industrial and agricultural activities are more prominent in these regions, neglecting the entire stretch of the River Yamuna which is very important to understand the overall health of the river and to analyze the areas that are contributing mostly to its polluted water.
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China




 Open Access
Open Access