
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
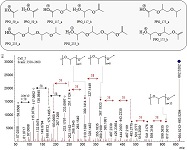
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
Tourist activities is one of the management tools used to identify the carrying capacity of beach and level of natural resources impacted by human activities, and it’s highly essential in revenue generation to the national blue economy. However, if its activities is not adequately controlled, it can disrupt the balance of coastal ecosystem and defeat the purpose of environmental services provision. This study assesses the beach quality status and beach users’ activities along the Lagos coastline, Southwest Nigeria. The survey was conducted during the summer holiday period in the peak of dry season (November 2021–February 2022) at six beaches (Atican, Alpha, Elegushi, Narval, Oniru and Takwa). A total number 600 people were interviewed, and secondary information was noted from the beach managers’ files, including the log book kept in the security post and vendor interviews with food and snack merchants and entertainers. Visitors were chosen at random (using a randomised complete design) to participate in interviews via a combination of passive and active questionnaires from a sample size of 100 visitors at each beach. The heterogeneity of tourists’ activities varied and significantly differed across the beaches. T-test values for all the activities were significance (p < 0.05) with the exception of religious and sporting activities. Recreation, clubbing, picnic, family retreat activities scored above 5% in all beaches, given exceptional note to Narval beach that had the highest activities of the tourists in religious group (70%). The Canonical Correspondence Analysis (CCA) ordination bi-plot diagram state that all activities, ages, and number of visitors were identified as the constrained variables. The activities Eigen scores were religious activity (0.79), picnic (0.58), family retreat (0.52), and site viewing (0.38). Religious activity had highest score of 70% with a strong relationship on the tourists of groups of above 50years at the Narval beach. This is in agreement with the cultural activities that accompanied tourism with peculiarity to life style and location. The ascending order of activities at the Oniru beach are: site viewing 9%, family retreat 25% and Picnic 45%. Whereas, the profound activities on recreation from other study area are: 40%, 35%, 30% and 20% at Takwa beach, Elegushi beach, Atican beach and Alpha beach respectively.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
This work used multivariable analysis to correlate groundwater high aluminum content in the area of the Liquid Effluent Treatment Center—CETREL of the Camaçari Industrial Pole, with natural environmental factors: geology, hydrogeology, precipitation, soil and vegetation; and anthropic: equipments of treatment and disposal of industrial waste from CETREL. This company made available data from 99 monitoring wells, period 2006–2016, with aluminum content above (0.2mg/L) the limit established by the Ministry of Health Ordinance Nº 888, 5 April 2021. Previous studies have indicated that there is no correlation of aluminum in groundwater of the Camaçari Industrial Pole with other metallic contaminants; also, that aluminum in the studied region is disseminated in the geological matrix, clayey soils, and poor and leached Cerrado soils. The Kruskal-Wallis test indicated significant correlation of high aluminum content with the treatment/disposal areas, geology, soil and vegetation; and no correlation with precipitation and hydrogeology. The four environmental factors indicating the highest average aluminum content (±C95%), in descending order, are: Clayey Soils, Organic Sludge Farm I, Marizal Formation, and Herbaceous-Subshrub Vegetation. The multivariable analysis indicated that, the most influential factors on the high aluminum content in groundwater of the CETREL region, are all ultimately associated with the leaching of aluminum present in the solid matrix. As CETREL processes are not correlated with aluminum residues, the results were an important information for the company environmental managers.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
From the point of view of the systemic approach in sustainable rural development programs, all components should be considered concerning each other, but one of the most important components is the environmental index in development programs. Considering that the lack of attention to the environmental components in the development plans of many projects has failed and many challenges have been created in the environmental components. The current research aims to evaluate the role of environmental components in the sustainable development of rural areas. For this purpose, a questionnaire was compiled and using Cochran’s formula, a sample size of 100 copies of the questionnaire was completed from household heads, and in addition, 20 copies of the questionnaire were completed to survey the relevant officials. SPSS software was used to classify and analyze data and information, and the AHP model was used to examine the relationship between variables and prioritize them. The studied area was located in the north of Tehran-Mashhad asphalt road and about 50 km east of Garmsar city. The results of the study indicate that there is a significant relationship between the environmental components and the sustainable development of the rural areas of the studied area, which requires the special attention of the officials in this sector. It has the most importance in this region. At the end, suggestions for better planning and sustainable development are given.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
Addressing environmental concerns with sustainable nanomaterial is a vital step towards innovative and eco-friendly techniques that address important global issues like pollution, water contamination, and resource depletion. This eco-friendly approach offers a sustainable alternative to conventional methods and this study aims to showcase the applications of biogenic silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) synthesized using green synthesis techniques with aqueous leaf extracts from five Alpinia varieties; Alpinia purpurata, Alpinia caerulea, Alpinia zerumbet ‘variegata’, Alpinia calcurata and Alpinia zerumbet. The AgNPs were synthesized using water extracts (WE) and silver nitrate at the optimum conditions. Characterization of AgNPs using UV-Vis spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), confirmed their successful formation and morphology. Spherical A.zerumbet_AgNPs between 28–68 nm in size were observed. The photocatalytic activity was tested by degrading methyl Orange (MO) dye under solar irradiation and the use NaBH4 with AgNPs significantly increased the degradation of MO. P-nitrophenol catalysis using AgNP and NaBH4 resulted promising results. Cytotoxicity of AgNPs using Artemia salina was evaluated and 100% viability was seen. The antibacterial activity was conducted using Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, unlike the WEs, all AgNPs showed antibacterial activity. This study revealed that the AgNPs synthesized using Alpinia leaves has diverse functional properties, presenting a promising avenue for future research and practical applications in environmental pollution.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
The textile industry, being a giant consumer of water and chemicals, uses synthetic dyes on a wide scale because of their low cost and wide color gamut. In contrast, synthetic dyes have shown great environmental hazards. A notable feature of textile dyes is their resistance to biodegradation, which contributes to long-lasting pollution in water, soil, and the atmosphere. The water body ecosystems are contaminated with dye-laden wastewater resulting from textile manufacturing. Photosynthetic activity is prevented, hence decreasing oxygen levels in water and drastically affecting aquatic life. Moreover, improper sludge disposal containing dyes leads to the degradation of soil quality, impacting plant health and microbial activities. Such pollutants can exhibit bioaccumulation in organisms, enhancing toxicity via the food chain and presenting serious health risks to humans, including carcinogenic effects and genetic malfunction. The paper reviews new developments related to ecologically friendly dyes, advanced wastewater treatments, and circular economies involving dye recycling and waterless dyeing techniques that are key to reducing the environmental impact of these dyes. Also needed is rigid enforcement of regulations coupled with the wider diffusion of sustainable technologies to minimize environmental damage in the textile industry and protect natural ecosystems and human health.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
Japan has 111 active volcanoes, supplying a great amount of magnetically-enhanced fly ashes. Such fly ashes likely mask anthropogenic magnetic signals; therefore, only a few magnetic biomonitoring studies have been reported in active volcanic regions, including Japan. The environmental magnetic results are reported for the materials deposited on Sasa Kurilensis, also known as dwarf bamboo, in the vicinity of the industrialized Muroran city center in Japan. The dust on the ten leaves at 105 sites was wiped off with a commercial wipe sheet, and their rock magnetic properties were analyzed. Room- and low-temperature magnetic analyses indicate that the major magnetic mineral in the dust is partially oxidized magnetite, ranging from single to pseudo single domain size, and the magnetic mineralogy on the leaves’ surface remains consistent throughout the study area. Much higher saturation isothermal remanent magnetization intensities are observed in the city’s eastern parts. The dominant wind directions in Muroran city are northwest, indicating that the steel companies in the city center are the major source of the fine-grained magnetic minerals on the dwarf bamboo leaves. These results indicate that using the leaves of dwarf bamboo for magnetic biomonitoring can be a non-destructive and rapid method to study the spatial distribution of atmospheric particulate matter from local industrial activities, even in active volcanic areas.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
This study investigates the seasonal dynamics of trace metal concentrations and hydrological parameters in the Balu River, Bangladesh, to inform sustainable water management practices and support efforts to meet environmental standards. Water level, discharge, rainfall, and groundwater data were collected from February to August 2019, alongside sediment samples analyzed for Zn, Pb, Cu, Cr, and Cd concentrations. Statistical analyses, including correlation studies, time series modeling, and Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests, revealed significant seasonal variations. Water levels and discharge rates increased dramatically during the wet season, with upstream levels rising by 862.68% and downstream by 752.92%. Trace metal concentrations showed diverse responses: Cd increased by 554.52%, Zn by 11.86%, while Pb, Cu, and Cr decreased by 44.15%, 5.16%, and 32.72% respectively. Strong correlations were observed between certain metals, particularly in wet periods, with notable relationships between Cr-Cu (r = 0.870) and Zn-Cr (r = 0.742). The integrated analysis of hydrological parameters and metal concentrations, using Gower coefficient and partial correlation analyses, suggests complex interactions between seasonal changes and pollutant dynamics. These findings highlight the need for season-specific water management strategies and more frequent monitoring to better understand and mitigate the environmental impacts of trace metal pollution in the Balu River system. The study contributes valuable insights into the interplay between hydrological conditions and trace metal behavior, essential for developing effective pollution control measures and achieving sustainable river management in Bangladesh.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
The article reviews the existing methodology and results of monitoring the quality of surface waters in Georgia. It also discusses improving the existing monitoring network and its approximation to the EU Water Framework Directive. The monitoring results are related to water quality indicators (chemical analysis) and pollution assessment. Georgia stands out worldwide for its biological and landscape diversity, features of an ecologically clean natural environment, water resources and a history of agricultural development of several thousand years. Despite this, the indicators of chemical and biological pollution of water bodies are still high. In Georgia, the quality of water bodies is monitored in several dozen locations (points). The monitoring results are the subject of constant attention and discussion. The importance of water quality monitoring is increasing even more against climate change trends when the demand for both water resources and their quality is constantly growing.
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China




 Open Access
Open Access