
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
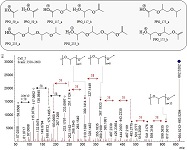
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
Study of waste management treatment facilities using advanced Membrane Bio Reactor (MBR) technology
Vol 6, Issue 2, 2025
Download PDF
Abstract
Sewage treatment plays a crucial role in sustainable urban and industrial development. This study focuses on the generation and treatment of sewage from residential, institutional, commercial, and industrial sources, distinguishing between grey water and black water. While grey water is relatively easier to treat, conventional practices in India merge both streams for processing. This research evaluates the application of advanced Membrane Bio Reactor (MBR) technology in a Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) at an industrial township in Andhra Pradesh, India, to achieve Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD). The study demonstrates the significant efficiency of MBR technology in removing contaminants, with Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) reduced from 350 mg/L to 20 mg/L, Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) from 650 mg/L to 50 mg/L, and Total Suspended Solids (TSS) from 150 mg/L to 4 mg/L. Additionally, oil and grease levels decreased from 19 mg/L to 4 mg/L, and total nitrogen dropped from 45 mg/L to 10 mg/L. These results affirm the effectiveness of MBR in producing high-quality treated water suitable for irrigation and toilet flushing. The research involved systematic sampling of influent and effluent wastewater over a set period, employing analytical methods like spectrophotometry and chromatography. Key operational parameters such as flux rate, transmembrane pressure (TMP), sludge retention time (SRT), and hydraulic retention time (HRT) were monitored to optimize efficiency. Comparative analysis with conventional treatment methods highlights MBR’s advantages, including superior pollutant removal, reduced footprint, and lower energy consumption. Real-time sensors and lab-scale MBR setups were used for continuous data collection and statistical analysis, confirming MBR’s effectiveness in sustainable wastewater treatment.
Keywords
References
- Sharma VK, Rajesh L. Safety Management at Tummalapalle Mill. In: Proceedings of the 35th DAE Safety & Occupational Heath Professional Meet-2018; 2018.
- Sharma VK, Rajesh L. Case study of air quality at Tummalapalle Mill and effective actions for improvement. In: Proceedings of the DAE Safety & Occupational Health Professional Meet; 2019.
- Rout VK, Setia G, Kaur S, et al. Membrane Bioreactors. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-58331-5_3 (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Jijingi HE, Yazdi SK, Abakar YA, et al. Evaluation of membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology for industrial wastewater treatment and its application in developing countries: A review. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering. 2024; 10: 100886. doi: 10.1016/j.cscee.2024.100886
- Jiang J, Sohn W, Almuntashiri A, et al. Feasibility study of powdered activated carbon membrane bioreactor (PAC-MBR) for source-separated urine treatment: A comparison with MBR. Desalination. 2024; 580: 117544. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2024.117544
- Tang Y, Sasaki K, Ihara M, et al. Evaluation of virus removal in membrane bioreactor (MBR) and conventional activated sludge (CAS) processes based on long-term monitoring at two wastewater treatment plants. Water Research. 2024; 253: 121197. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2024.121197
- Mofatto PMB, Cosenza A, Di Trapani D, et al. Reducing wasted sewage sludge from wastewater treatment: Comparison of two membrane bioreactor pilot plants. Journal of Water Process Engineering. 2024; 58: 104847. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2024.104847
- Cutrupi F, Cadonna M, Postinghel M, et al. SARS-CoV-2 removal in municipal wastewater treatment plants: Focus on conventional activated sludge, membrane bioreactor and anaerobic digestion. Science of The Total Environment. 2024; 906: 167434. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167434
- Mardalisa, Wang R, Sabar MA, et al. Different fates between extracellular and intracellular antimicrobial resistome in full-scale activated sludge and membrane bioreactor processes. Water Research. 2025; 274: 123155. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2025.123155
- Mburu J, Njogu P, Kinyua R, et al. Process Performance and Nutrient Removal in Fish Processing Wastewater Using a Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Unit for Reuse for Irrigation. Global Research in Environment and Sustainability. 2024; 2(8): 11-18. doi: 10.63002/gres.28.609
- Ikarashi T, Bandaranayake US, Watari T, et al. Unique gel-like colony forming bacterium Novosphingobium pituita sp. nov., isolated from a membrane bioreactor (MBR) treating sewage. Heliyon. 2024; 10(19): e38795. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38795
- Sharma VK, Namboori VR, Tunga CR, et al. Technical modification of alkali leaching circuit to improve slurry throughput into the autoclave. Suranaree Journal of Science and Technology. 2023; 30(4): 010247(1-7). doi: 10.55766/sujst-2023-04-e0998
- Sharma VK, Thamida SK, Reddy BNK. Engineering study of water jacket system in place of a spiral heat exchanger at mining and mineral ore processing industry. European Chemical Bulletin. 2023; 12(7): 1507-1512.
- Reddy TCS, RNV, RLK. Technical modifications of alkali leaching circuit to improve slurry throughput into the autoclave. In: Proceedings of the 74th Annual Session of Indian Institute of Chemical Engineers; 27-30 December 2021; Odisha, India.
- Pyssa J. Technical and technological aspects of sewage waste management after amendments in legislation in Poland. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 2019; 214: 012016. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/214/1/012016
- Rajesh NV, Sarkar S, Rao MS. Effectiveness of autoclave agitator in alkali leaching based ore processing plant. In: Proceedings of the 77th ATM IIM; 2023.
- Sharma KS, Sriharsha P, Kannan JD, et al. Trial of Pilot Scale Nanofiltration Unit for Improvement of Precipitation Circuit at Tummalapalle Mill. Current Natural Sciences and Engineering. 2025; 2(1): 528-543. doi: 10.63015/7n-2453.2.1
- Rahman T, Roy H, Islam M, et al. The Advancement in Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Technology toward Sustainable Industrial Wastewater Management. Membranes. 2023; 13. doi: 10.3390/membranes13020181
- Sreenivas T, Rao KA, Rao MM, et al. Autoclave Leaching of Refractory Uranium Minerals. In: Proceedings of the XI International Seminar on Mineral Processing Technology (MPT-2010); December 2010; Jamshedpur, India.
- Sriharsha P, Rao LK, SS. Process intensification in post alkali leached liquor precipitation circuit using re-dissolution of sodium diuranate slurry. In: Proceedings of the 77th ATM IIM; 2023.
- Suri AK, Sreenivas T, Anand Rao K, et al. Process development studies for the recovery of uranium and sodium sulphate from a low-grade dolostone hosted stratabound type uranium ore deposit. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy. 2014; 123(2): 104-115. doi: 10.1179/1743285514y.0000000054
- Sarkar S, Kannan JD. A view on advanced separation techniques used in various uranium processing plant of Uranium Corporation of India Limited (UCIL). In DAE-BRNS (editor). SESTEC-2022. Institute of Chemical Technology (ICT); 2022.
- Hu Y, Cai X, Du R, et al. A review on anaerobic membrane bioreactors for enhanced valorization of urban organic wastes: Achievements, limitations, energy balance and future perspectives. The Science of the total environment. 2022; 153284. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153284
- Thamida SK, RBNK, SVK. Detailed calculations for rainwater recharge system, considering the storm water runoff and geological formation. Pure Earth Foundation, Delhi; 2023.
- Reddy BNK, Thamida SK, Sharma VK. Case Study on Advanced Separation Techniques Used in Alkali Leaching based Mineral Processing Plant. AIJR Publisher; 2024.
- Kharraz J, Khanzada N, Farid M, et al. Membrane distillation bioreactor (MDBR) for wastewater treatment, water reuse, and resource recovery: A review. Journal of Water Process Engineering. 2022. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102687
- Sharma VK. Evaluation of Air Pre-Heater System on Vis-Breaker Heaters. In: Proceedings of the National Conference on Emerging Trends & Innovations in Chemical Engineering; 2008.
- Khan N, Singh S, López Maldonado, et al. Emerging membrane technology and hybrid treatment systems for the removal of micropollutants from wastewater. Desalination. 2023. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2023.116873
- Ni L, Wang P, Westerhoff P, et al. Mechanisms and Strategies of Advanced Oxidation Processes for Membrane Fouling Control in MBRs: Membrane-Foulant Removal versus Mixed-Liquor Improvement. Environmental science & technology. 2024. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.4c02659
- Ashok SS, Kumar T, Bhalla K. Integrated Greywater Management Systems: A Design Proposal for Efficient and Decentralised Greywater Sewage Treatment. Procedia CIRP. 2018; 69: 609-614. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2017.11.098
- Rani N, SVK. Instrumental Analysis of Corrosion on Stainless Steel. Chemtechnik’09; 2009.
- Tiwari R, SVK. Pump Efficiency Evaluation & Overview of Catalytic Cracking Unit. Pansophy’08; 2008.
- Krzeminski P, van der Graaf JHJM, van Lier JB. Specific energy consumption of membrane bioreactor (MBR) for sewage treatment. Water Science and Technology. 2012; 65(2): 380-392. doi: 10.2166/wst.2012.861
- Brepols C, Drensla K, Janot A, et al. Energetic refurbishment of an existing large-scale MBR. Water Practice and Technology. 2020; 15(1): 182-187. doi: 10.2166/wpt.2020.009
- Rao MS. Management of alkali leaching based uranium tailings at Tummalapalle. In: IAEA website (editor). UPC. UMREG Presentations; 2019.
- Sharma VK, Thamida SK, Reddy BNK. Carbonation and modeling study for process liquor in batch mode using flue gas in the mining and mineral processing industry. Chemical Papers. 2024; 78(7): 4189-4199. doi: 10.1007/s11696-024-03379-5
- Namdeti R, Lakkimsetty NR, Rao GB, et al. Membrane Bioreactors: Integration of Biological Processes with Membrane Technology for Wastewater Treatment. Journal of Membrane Science and Research. 2025; 11(2).
- Uddin M, Islam MK, Dev S. Investigation of the performance of the combined moving bed bioreactor-membrane bioreactor (MBBR-MBR) for textile wastewater treatment. Heliyon. 2024; 10(10): e31358. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31358
- Bilici Z, Hasnaoui A, Chikhi M, et al. Treatment of landfill leachate wastewater by chemical coagulation‐flocculation, electro‐membrane bioreactor, and anaerobic hybrid system. Water Environment Research. 2025; 97(2). doi: 10.1002/wer.70026
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2025 Author(s)
License URL: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China



