
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
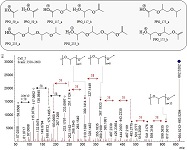
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
The present state of lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn) contamination in agricultural soil as revealed by meta-analytic findings
Vol 4, Issue 2, 2023
Download PDF
Abstract
Agricultural soil serves as the fundamental resource for grain production, with its quality being integral to both the national economy and the well-being of the population. As economic and societal development progresses, the levels of lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn) in farmland soil are on the rise. Currently, research into the total quantities and speciation distribution of Pb and Zn in agricultural soil, as well as their influencing factors, is fragmented, and there is a gap in comprehensive understanding regarding the transformation mechanisms and pollution status of various forms of these heavy metals. To gain a clearer picture of the heavy metal pollution in soil, as well as the distribution and transformation dynamics of different forms, this study conducts an integrated analysis of the pollution levels, speciation distribution, and influencing factors of Pb and Zn in Chinese farmland soil. Additionally, it assesses the ecological risk of heavy metals using principal component analysis and the geoaccumulation index. The findings indicate that the average concentrations of Pb and Zn are 4045 mg/kg and 10699 mg/kg, respectively. The residual form of Pb is most predominant in the Northwest, while the exchangeable form is most prevalent in the Southwest. The residual form of Zn constitutes over 50% of its presence. The analysis reveals that pH is the primary factor influencing the speciation distribution of heavy metals. The combined results of the geoaccumulation index and the potential ecological risk index (RI) suggest that Pb levels at the study site exceed those of Zn, though both are classified as posing a slight risk. A holistic analysis of soil environmental factors reveals that the speciation distribution of heavy metals reaches an equilibrium state through the interaction of multiple factors.
Keywords
References
- Ouyang, D. Effects of long-term fertilization on farmland soil fertility and chemical behavior of heavy metals. Changsha: Hunan Normal University; 2015.
- Li M, Wang Y, Hao Y, et al. Research Progress on soil heavy metal pollution under wheat maize rotation system in North China. Shandong Agricultural Science. 2018; 50(12): 144-151.
- Tóth G, Hermann T, Da Silva MR, et al. Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environment International. 2016; 88: 299-309. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2015.12.017
- Wang X. Spatial distribution and influencing factors of heavy metals in soils of Beijing sewage irrigation area in Tianjin. Tianjin: Tianjin Normal University; 2012.
- Zhou Z. Heavy metal pollution and control of vegetables in China. Research trends of resource ecological environment network. 1999; 10(3): 21-27.
- Faitondjiev L, Stanislavova L, Tchuldjian H, et al. Toxic elements in soils of the region of Kremikovtzi. Pochvoznanie Agrokhimiya I Ekologiya. 2000; 35:3-9.
- Pagnanelli F, Moscardini E, Giuliano V, et al. Sequential extraction of heavy metals in river sediments of an abandoned pyrite mining area: pollution detection and affinity series. Environmental Pollution. 2004; 132(2): 189-201. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2004.05.002
- Arain MB, Kazi TG, Jamali MK, et al. Speciation of heavy metals in sediment by conventional, ultrasound and microwave assisted single extraction methods: A comparison with modified sequential extraction procedure. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2008; 154(1-3): 998-1006. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.004
- Pueyo M, Mateu J, Rigol A, et al. Use of the modified BCR three-step sequential extraction procedure for the study of trace element dynamics in contaminated soils. Environmental Pollution. 2008; 152(2): 330-341. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.020
- Tessier A, Campbell PGC, Bisson M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry. 1979; 51(7): 844-851. doi: 10.1021/ac50043a017
- Huang Y. Analysis of heavy metal pollution sources in farmland soils at different scales. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University; 2018.
- Lei L. Current situation and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil: a case study of Jinghuiqu Irrigation Area in Shaanxi. Yang Ling: Northwest University of agriculture and forestry science and technology. 2015.
- Net S, Sempéré R, Delmont A, et al. Occurrence, Fate, Behavior and Ecotoxicological State of Phthalates in Different Environmental Matrices. Environmental Science & Technology. 2015; 49(7): 4019-4035. doi: 10.1021/es505233b
- Quevauviller Ph, Rauret G, Griepink B. Single and Sequential Extraction in Sediments and Soils. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry. 1993; 51(1-4): 231-235. doi: 10.1080/03067319308027629
- Gambrell RP. Trace and Toxic Metals in Wetlands-A Review. Journal of Environmental Quality. 1994; 23(5): 883-891. doi: 10.2134/jeq1994.00472425002300050005x
- Shao T, Liu Z, Huang K, et al. Study on occurrence forms and bioavailability of heavy metals in oil contaminated soil. China Environmental Science. 2000; 20(1): 57-60.
- Zheng Z. Study on spatial variation of soil nutrients in longmatun karst depression of Tiandeng County. Nanning: Guangxi Normal University; 2011.
- Fan S, Gan Z, Li M, et al. Progress in soil heavy metal pollution assessment methods. Chinese agronomy bulletin. 2010; 26(17): 310-315.
- Xu Z, Ni S, Tuo X, et al. Calculation of Heavy Metal Toxicity Coefficient in potential ecological hazard index method. Environmental Science and technology. 2008; 31(2): 112-115.
- GB. 15618-2018, ministry of ecological environment Soil environmental quality standard soil pollution risk control standard for agricultural land. GB; 2018.
- Guo JH, Liu XJ, Zhang Y, et al. Significant Acidification in Major Chinese Croplands. Science. 2010; 327(5968): 1008-1010. doi: 10.1126/science.1182570
- Ning Y, Zhang X, Li B, et al. Distribution of Cd and Cu Fractions in Chinese Soils and Their Relationships with Soil pH: A Meta-Analysis. Sustainability. 2019; 11(2): 337. doi: 10.3390/su11020337
- Ni Z, Shi Y, Xie G, et al. Chemical forms of cadmium, copper, lead and mercury in Typical Farmland Soils in Hangzhou and their pollution risk assessment. Zhejiang agricultural science. 2017; 58(10): 1785-1788.
- Zhou Y, Yang Z, Wang Q, et al. Potential ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in farmland soil crop system in xiong'an New Area. Environmental Science. 2021; 42(4): 2003-2015.
- Cai K, Zhang Q, Wu Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and control factors of heavy metals in farmland soil of Hebei plain. Journal of ecotoxicology. 2017; 12(2): 155-168.
- Guo TZ, Delaune RD, Patrick WH Jr. The influence of sediment redox chemistry on chemically active forms of arsenic, cadmium, chromium, and zinc in estuarine sediment. Environment International. 1997; 23(3): 305-316.
- Marschner H, Romheld V, Cakmak I. Root-induced changes of nutrient availability in the rhizosphere. Journal of Plant Nutrition. 1987; 10(9): 1175-1184. doi: 10.1080/01904168709363645
- Chen Y, Ji H, Zhu X, et al. Speciation analysis and potential risk assessment of heavy metals in soils around Detiangou gold mine and qifengcha gold mine in Beijing. Journal of Agricultural Environmental Sciences. 2012; 31(11): 2142-2151.
- Chinese Encyclopedia of Agriculture Editorial Board. Editorial Department of China Agricultural encyclopedia Encyclopedia of Chinese agriculture. Beijing: Agricultural Press; 1996.
- Xu M, Wu M, Wu H, et al. Stabilization Characteristics of exogenous lead in soil and its response to soil properties. Journal of Agricultural Environmental Sciences. 2012; 31(9): 1702-1709.
- Appel C, Ma L. Concentration, pH, and Surface Charge Effects on Cadmium and Lead Sorption in Three Tropical Soils. Journal of Environmental Quality. 2002; 31(2): 581-589. doi: 10.2134/jeq2002.5810
- Bolan NS, Adriano DC, Duraisamy P, et al. Immobilization and phytoavailability of cadmium in variable charge soils. Ⅲ. Effect of biosolid compost addition. Plant and Soil. 2003; 25(1): 231-241.
- Wang X, Fu W, Zhang L, et al. Speciation distribution characteristics and influencing factors of heavy metal Zn in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Earth and environment. 2011; 39(1): 85-90.
- Cui Y, Li X, Dong J, et al. Distribution and transformation of chemical forms of heavy metals in soils of Yantai gold mine area and surrounding towns in Shandong Province. Geophysical and geochemical exploration. 2013; 37(6): 1100-1106.
- Fang Y, Zhang X, Liu J, et al. Speciation and bioavailability of heavy metals in agricultural soils in Tonglushan mining area, hubei Province. Earth and environment. 2017; 45(6): 634-642.
- Ma YB, Uren NC. Effect of aging on the availability of zinc added to a calcareous clay soil. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems. 2006; 76(1): 11-18. doi: 10.1007/s10705-006-9036-8
- Jing S, Tian J, Luke MCC, et al. Small scale spatial heterogeneity of soil organic matter components in primitive broad-leaved Korean pine forest in Changbai Mountain. Journal of ecology. 2016; 36(20): 6445-6456.
- Tipping E, Lofts S, Lawlor AJ. Modelling the chemical speciation of trace metals in the surface waters of the Humber system. Science of the Total Environment. 1998; 210/211: 63-77.
- Badea SL, Lundstedt S, Liljelind P, et al. The influence of soil composition on the leachability of selected hydrophobic organic compounds (hocs) from soils using a batch leaching test. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2013; 254/255: 26-35.
- Xu M, Zeng X, Zhou S. Fertilization and remediation of heavy metal pollution in soil. Beijing: Science Press; 2014.
- Chen F, Dong Y, An Q, et al. Change of heavy metal content in soil under long-term fertilizer location test. Soi. 2005; 37(3): 308-311.
- Liu Jing, Lv J, Xu M, et al. Effects of long-term Different Fertilization on Cu and Cd contents and activation rates in red soil [J]. Journal of ecological environment. 2009;18(3): 914-919.
- Liu S, Zhao Y, Sun Y, et al. Effects of 25 year long-term fertilization on the status of heavy metals in non calcareous fluvo aquic soil. Journal of soil and water conservation. 2005; 19(1): 164-167.
- Ren S, Shao Y, Wang Z. Analysis of heavy metal content in commercial organic fertilizer produced from livestock and poultry waste. Journal of Agricultural Environmental Sciences. 2005; 24(S1): 216-218.
- Cao D, Bai Y, Li W. Effects of different fertilization treatments on soil quality and cadmium uptake by wheat. Modern agricultural science and technology. 2020; (9): 1-2.
- Hao H, Chen W, Lv Y, et al. Content analysis of heavy metals in organic fertilizers and evaluation of their accumulation in soil and vegetables. Hunan Agricultural Science. 2018; (12): 50-54.
- Shen L, Bai L, Zeng X, et al. Effects of Fertilization on nitrate accumulation and ph in Protected Vegetable Soil. Journal of Agricultural Environmental Sciences. 2012; 31(7): 1350-1356.
- Wang Ying, Han X, Sun S, et al. Effect of long-term fertilization on heavy metals in brown soil and its environmental quality assessment. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University. 2008; 39(4): 442-446.
- Huang C, Xu J. Pedology [m]. Version 3 Beijing: China Agriculture Press; 2010.
- Huang PM. Future prospects for soil chemistry. Madison, WI, USA: Soil Science Society of America; 1998.
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2023 Yinzhong Ning
License URL: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China



