
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
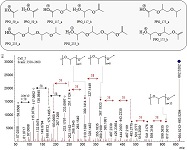
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
The impact of biochar-entrapped microorganisms on enzymatic activity and the cleanup of petroleum hydrocarbons in polluted soil
Vol 4, Issue 2, 2023
Download PDF
Abstract
The high-temperature pyrolysis oxidation process was utilized to produce reed biochar, which was then employed as a carrier for immobilizing the predominant petroleum hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria. The study investigated the effects of this biochar-bound microbial immobilization on the remediation efficacy and enzymatic activity of soil contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons. The findings indicated that after 40 days of treatment with reed biochar-immobilized microorganisms, the soil's petroleum hydrocarbon removal rate reached 55.01%, markedly surpassing the removal rates of biochar (45.82%) and the untreated control group (24.83%). Additionally, it was observed that the biochar-immobilized microorganisms significantly enhanced the activities of soil enzymes such as dehydrogenase, catalase, urease, and polyphenol oxidase. The application of biochar-bound microbial immobilization technology not only boosts the cleanup efficiency of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil but also substantially elevates the soil's biological enzyme activity.
Keywords
References
- Wang L. Impact of petroleum hydrocarbon development on environment and Countermeasures. Qingdao: Ocean University of China; 2009.
- Liu W, Luo Y, Teng Y, et al. Ecological risk assessment and bioremediation of petroleum contaminated soil II Study on physical and chemical properties and microbial ecological changes of oil contaminated soil. Journal of soil. 2007; 4(5): 848-853.
- Qiao X, Li F, Zhang Y, et al. Effects of freezing and thawing on enzyme activity and water-soluble carbon in oil contaminated soil. Journal of Agricultural Environmental Sciences. 2008; 4(3): 914-919.
- Zhan Yan Harm of soil petroleum hydrocarbon pollution in China and its control countermeasures [J]. Environmental pollution and prevention, 2008,30 (3): 91-93
- Alegbeleye OO, Opeolu BO, Jackson VA. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: A Critical Review of Environmental Occurrence and Bioremediation. Environmental Management. 2017; 60(4): 758-783. doi: 10.1007/s00267-017-0896-2
- Zhang B, Zhang L, Zhang X. Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil by petroleum-degrading bacteria immobilized on biochar. RSC Advances. 2019; 9(60): 35304-35311. doi: 10.1039/c9ra06726d
- Cao Z. Study on bioremediation effect and toxicity change of petroleum contaminated soil. Xi’an: Xi’an University of architecture and technology; 2017.
- Xin L. Experimental study on step-by-step Fenton chemical oxidation of heavily petroleum contaminated soil. Xi’an: Xi’an University of architecture and technology; 2000.
- Tang J. Diversity analysis of heavy metal resistant actinomycetes in soil of sewage irrigation area in the northern suburbs of Xi’an. Xianyang: Northwest University of agriculture and forestry science and technology. 2009.
- Lu G, Wang S, Guo G, et al. Effect of peat intensification on bioremediation effect of aged oil sludge [J]. Journal of environmental engineering technology. 2011; 1(5): 389-395.
- Yang Q, Wu M, Nie M, et al. Bioremediation technology and microbial ecological effect of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil. Environmental Science. 2015; 36(5): 1856-1863.
- Xie W, Li R, Li X, et al. Different responses to soil petroleum contamination in monocultured and mixed plant systems. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 2018; 161: 763-768. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.06.053
- Zhang X, Bai X, Xu N, et al. Study on Influencing Factors of oil contaminated soil remediation by immobilized microorganisms. Journal of environmental engineering. 2013; 7(3): 1156-1162.
- Zhang X, Geng C, Fang M, et al. Application of immobilized microorganisms in bioremediation of oil contaminated soil. Journal of Petroleum (petroleum processing). 2008; 4:409-414.
- Xu Y, Lu M. Bioremediation of crude oil-contaminated soil: Comparison of different biostimulation and bioaugmentation treatments. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2010; 183(1-3): 395-401. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.07.038
- Wang X, Chao Q, Xu X, et al. Laboratory simulation study on bioremediation of petroleum contaminated soil. Journal of environmental engineering. 2012; 6(5): 1663-1668.
- Wang Y, Li F, Rong X, et al. Remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil by combined application of biomass materials and nutrients. Journal of Agricultural Environmental Sciences. 2018; 37(2): 232-238.
- Zhu W, Tang J. Remediation effect of wheat straw biochar on petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil. Journal of agricultural resources and environment. 2014; 31(3): 259-264.
- Wang Y. Study on the mechanism and effect of Combined Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil by biochar immobilized microorganisms and plants. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University; 2017.
- Ruan Z. Screening and identification of oil degrading strains and preliminary study on their oil degradation characteristics. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. 2006.
- Guan Y. Soil enzymes and their research methods. Beijing: Agricultural Press; 1986.
- Zhou L. Soil enzymology. Beijing: Science Press; 1989.
- Wang J, Zhang Z, Su Y, et al. Study on rhizosphere effect of phytoremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil. Journal of petrochemical colleges and universities. 2008; 21(6): 36-40.
- Wu W, Zhang X, Shan B, et al. Effects of different disposal methods on physical, chemical and biological properties of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil. Journal of Petroleum (petroleum processing). 2010; 26(5): 831-834.
- Gao F, Yang F, Wu X, et al. Effects of biochar application on organic matter content and enzyme activity in rhizosphere soil of Chinese cabbage. Soil bulletin. 2019; 50(1): 103-108.
- Graham DW, Smith VH, Law KP. Effects of nitrogen and phosphoroussupply on hexadecane biodegradation in soil systems. Water,Air,and Soil Pollution. 1999; 111(1/4): 1-18.
- Zhang X, Zhang S, Zhang H, et al. Effects of immobilized microorganisms on biological characteristics of oil contaminated soil. Journal of Petroleum (petroleum processing). 2015; 31(1): 112-118.
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2023 Lifang Shi, Meixia Lin, Fayun Li, Ming Gao, Wei Wang, Chunliang Zhou
License URL: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China



