
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
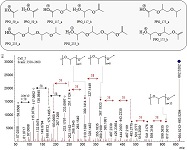
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
Systematic review of pollutants in Santiago de Cuba Bay
Vol 5, Issue 1, 2024
Download PDF
Abstract
The bay of Santiago de Cuba is the second in importance and contamination in the country. Aggressive waste discharges with organic and inorganic materials, heavy metals, masonry residues, grease, oils and hydrocarbons, among others, are discharged into the bay. A systematic review of databases, publications, web pages and other documents was carried out in order to find out more about contamination. Eighty-five percent of the main reports refer to organic matter contamination and waste characterization, followed by hydrocarbon contamination (15%). This makes the work related to sustainable management in the bay insufficient.
Keywords
References
- Planos Gutiérrez E, Rivero Vega R, Guevara Velazco V. Climate Change Impact and Adaptation Measures in Cuba. Available online: http://www.redciencia.cu/geobiblio/paper/2012_Planos_Impacto%20y%20Adaptacion, %20Libro.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Villasol A. Preliminary report on water pollution in the bay of Santiago de Cuba. Partial Report. Item 02 Contamination of waters in the port of Santiago de Cuba; 1979; Unpublished work.
- Valdés M, Regadera R. Monitoring of the environmental quality of the ecosystem of the bay of Santiago de Cuba (Partial Report). Havana, Cuba; 2012; Unpublished work.
- Putney AD, Vela C. Project RLA97G31. Establishment of a program for the consolidation of the Mesoamerican Biological Corridor (MBC). Available online: https://erc.undp.org/evaluation/documents/download/3112 (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Chabalina L, Beltran J. Marine pollution in bays and coastal areas of Cuba and the Greater Caribbean (Report 1). Center for Engineering and Environmental Management of Bays and Coasts; 2008; Unpublished work.
- Chabalina L, Beltran, J. Marine pollution in bays and coastal areas of Cuba and the Wider Caribbean (Report 2). Center for Engineering and Environmental Management of Bays and Coasts; 2012; Unpublished work.
- Álvarez I, Gómez L. Goals for an ICZM initiative in the inner lobe of the bay of Santiago de Cuba. Ciencia en su PC. 2009; 70-93.
- Gómez L, Larduet Y, Abrahantes N. Contamination and biodiversity in aquatic ecosystems. The phytoplankton of the bay of Santiago de Cuba. Rev. Invest. Mar. 2011; 22(3): 191-197.
- Abalos A, Marañón A., Fernández JM, et al. Characterization of wastewater from the edible oil refining plant ERASOL. CENIC Rev. Ciencias Biológicas. 2007; 38(3): 220-223.
- Poveda I, Morales M, Rizo M. Influence of the enterprise as an economic agent of sustainable development in the coastal area of the bay of Santiago de Cuba. Ciencia en su PC. 2009; 94-103.
- Arias Lafargue T. Characterization of some of the main pollutant sources in the bay of Santiago de Cuba and their consequences on the environment. Tecnología Química. 2008; XXVIII(2): 79-89.
- Poveda I. The dimensions of development in polluting state-owned enterprises in the bay of Santiago de Cuba. Ciencia en su PC. 2014; 86-94.
- Regadera R, Gómez Y, Beltrán J. Control of the environmental quality of the marine ecosystem of the bay of Santiago de Cuba (Research-Development and Technological Innovation Project). Center for Engineering and Environmental Management of Bays and Coasts (Cimab); 2014; Unpublished wok.
- Regadera R, Gómez L, Gómez Y. Monitoring of the environmental quality of the ecosystem of the bay of Santiago de Cuba (Partial report). Havana, Cuba; 2009; Unpublished work.
- Regadera R, Valdés M. Monitoring of the environmental quality of the ecosystem of the bay of Santiago de Cuba (Executive Abstract). Havana, Cuba; 2012; Unpublished work.
- Geocuba-Serpo. Environmental Impact Study to the Multipurpose Terminal Project Puerto Santiago de Cuba. Environmental Baseline; 2015; Unpublished work.
- Ministry of Science, Technology and Environment (Citma). National Environmental Strategy 2016/2020. Available online: https://www.cubahora.cu/uploads/documento/2019/05/21/estrategia-ambiental- nacional-2016-2020.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Milanés C, Pacheco A. Coastal settlements in the bay of Santiago de Cuba: studies of their urban vulnerability. Rev. Arquitectura y Urbanismo, XXXII(3), 18-26. https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/3768/376839863005.pdf
- Téllez, D. Contingency plan against oil spills, a sound practice in integrated coastal zone management [Master’s thesis]. Universidad de Oriente, Center for Multidisciplinary Studies of Coastal Zones; 2003; Unpublished work.
- Fernández MA, Rodríguez D, García I, et al. Behavior of organic pollution in the bay of Santiago de Cuba. Ciencia en su PC. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/1813/181338814003.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Nápoles, J., Ábalos, A., Pérez, N., Marañón, A. and Díaz, E. (2007). Environmental impact of the oil industry in Santiago de Cuba. Characterization. Tecnología Química. 2007; XXVII(2): 83-91.
- Bermúdez J. Bioremediation of hydrocarbon contaminated soils from the use of an allochthonous bacterial consortium in the coastal area of Punta Majagua. Cienfuegos, Cuba [Master’s thesis]. Martha Abreu Central University of Las Villas; 2012.
- Mesa L, Falcón J. Evaluation of the degree of oil contamination in waters of the bay of Santiago de Cuba. Rev. Boliviana de Química. 2017; 34(2): 56-64.
- Rodríguez D, Santana MA, Creagh B. Contamination by fats and oils in bathing areas of the bay of Santiago de Cuba. Part # 1: Chemical determination. Science in your CP. 2016; 77-88.
- Santana MA, Rodríguez D, Díaz M, et al. Evaluation of hydrocarbon contamination of the bay of Santiago de Cuba. Rev. Cubana Química. 2015; 554-560.
- Cuba. National Office of Standardization. Statistical Yearbook of Santiago de Cuba. National Office of Statistics and Information (ONEI); 2014.
- González A, Reyes, O. Evaluation of the environmental impact of industrial atmospheric pollution in the bay of Santiago de Cuba. Revista Cubana de Quimica. 2005; XVII(3): 43.
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2024 Alina de la Caridad Morell-Bayard, Alberto de las Mercedes Beyris-Mazar, Pedro Siboney Bergues-Garrido, Axel Campos-Castro, Jainer Costa-Acosta

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China



