
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
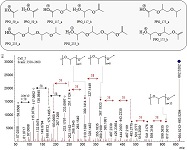
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
Issue release: 31 December 2020
A hybrid model approach is proposed to address the limitations of traditional physical and empirical models in simulating smoke diffusion and depicting gas pollution. This method integrates the semi-Lagrangian method for smoke modeling, with the k-d tree algorithm enhancing computational efficiency. To enhance smoke simulation details, a fluctuating wind field generated by the linear filter method is incorporated into the external force term to refine smoke particle trajectories. The rendering process employs a bidirectional projection function combined with actual smoke textures to mitigate the issue of particle visibility and to significantly enhance the visual fidelity of smoke diffusion. Additionally, an optimized Gaussian plume model is utilized to bridge the gap between physical and empirical models, while a pollution attenuation formula and refined Perlin noise are applied to enrich the global gas pollution details and to increase the realism of pollution dynamics. The method also incorporates an improved time axis algorithm to overcome the issue of static gas pollution color, enabling the depiction of dynamic and gradual pollution changes. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of this approach in generating realistic and dynamic gas pollution scenes in real-time.
Issue release: 31 December 2020
Human fecal contamination poses a significant public health concern in water sources, yet standard indicator microorganisms for detecting such contamination fail to pinpoint the exact source. The genus Bifidobacterium, particularly species like B. adolescentis and B. dentium, has been suggested as a potential marker for identifying human fecal pollution, though this proposal has yet to be tested in tropical settings. This study aimed to assess the presence of bifidobacteria in a water sample from the Mesolandia swamp in the Colombian Caribbean, as well as in 260 human fecal samples and 94 samples from domestic animals in a nearby settlement. DNA was extracted from each sample and subjected to PCR amplification with gender-specific primers targeting the 16S rRNA gene, followed by DGGE (Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis) separation. DGGE bands were then excised, re-amplified, sequenced, and compared to the GenBank database. The DGGE profiling revealed the presence of eight Bifidobacteria species in the water sample, matching those found in human feces. The proposed markers B. adolescentis and B. dentium were also detected in domestic animal feces. Despite the efforts, the study was unable to identify a unique Bifidobacteria species that could serve as a reliable marker for human fecal contamination in tropical environments under the evaluated conditions. Nevertheless, the methodology employed provided a more precise approximation to the source of fecal contamination than traditional cultural methods, as identical DNA sequences were found in both water and fecal samples.
Issue release: 31 December 2020
A proper evaluation of the health risks and economic burden incurred by urban residents due to air pollution is crucial for regional air pollution management, the formulation and execution of environmental policies, and the promotion of public health in China. Utilizing data on PM2.5 concentration and population density from 338 Chinese cities between 2015 and 2017, this study employs the Exposure-Response model to estimate the premature mortality and disease incidence linked to PM2.5 exposure. It also assesses the direct economic losses associated with PM2.5 pollution using the Value of Statistical Life (VSL) and Cost of Illness (COI) approaches. The findings indicate that: 1) Between 2015 and 2017, there was a slight improvement in PM2.5 concentration levels, yet the overall spatial distribution of pollution remained largely unchanged. The most polluted areas were concentrated in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and adjacent cities; 2) PM2.5 pollution has resulted in substantial reductions in both health and economic losses. Specifically, the number of residents affected by severe health issues due to pollution decreased by 23.9%, and the total economic loss for residents decreased by 24.24%, from 1824.96 billion yuan in 2015 to 1382.64 billion yuan in 2017; 3) The rising urbanization rate has intensified the health impacts and economic costs of PM2.5 pollution, particularly in cities with both high pollution levels and high urbanization rates, such as Beijing and Tianjin. Moving forward, it is imperative to implement tailored measures to enhance PM2.5 monitoring and control in key cities, thereby effectively safeguarding the health of urban residents.
Issue release: 31 December 2020
Objective: The study aims to investigate the impact of atmospheric nitrogen dioxide (NO2) levels on pediatric outpatient consultations for respiratory illnesses in the Yuexiu District of Guangzhou, China. Methods: Data on atmospheric NO2 levels, weather conditions, and outpatient visits for respiratory diseases were gathered from a children’s hospital in Guangzhou’s Yuexiu District over the period of 2014 to 2016. Spearman rank correlation analysis and time-series analysis employing a generalized additive model were utilized to examine the association and lagged effects between NO2 concentrations and concurrent pediatric respiratory outpatient visits. Results: The annual mean NO2 concentrations in Yuexiu District during 2014, 2015, and 2016 were 6130, 6046, and 6081 μg/m3, respectively, and the number of days exceeding national standard values was 70, 64, and 62, respectively. The time-series analysis revealed a significant impact of NO2 on respiratory outpatient visits from day 0 to day 7, with the most pronounced effect observed on lag day 0 (lag0). An excess risk (ER) of 145% (95% CI: 93%–198%) was observed on lag day 0 (lag0). The highest cumulative lag effect and ER of 307% (95% CI: 204%–410%) were found on lag days 0 to 6 (lag06 d). Conclusion: The rise in NO2 levels in Guangzhou’s Yuexiu District between 2014 and 2016 was associated with an increase in pediatric respiratory disease outpatient visits.
Issue release: 31 December 2020
The complex network approach was employed to investigate PM2.5 levels in air pollution. Relevant PM2.5 data were analyzed for correlation, leading to the establishment of a complex network across various regions in China. By examining factors such as degree, community structure, and motifs, the findings indicated that this method effectively identifies the major polluted cities in China. Furthermore, cities experiencing clustered air pollution should be addressed collectively, reflecting the actual conditions. Given the dynamic nature of air movement, this research offers valuable insights for analyzing the aggregation of polluted cities.
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China




 Open Access
Open Access