
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
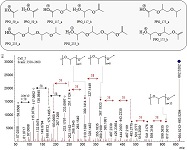
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
Utilization of complex networks for analyzing PM2.5 air pollution in various regions
Vol 1, Issue 1, 2020
Download PDF
Abstract
The complex network approach was employed to investigate PM2.5 levels in air pollution. Relevant PM2.5 data were analyzed for correlation, leading to the establishment of a complex network across various regions in China. By examining factors such as degree, community structure, and motifs, the findings indicated that this method effectively identifies the major polluted cities in China. Furthermore, cities experiencing clustered air pollution should be addressed collectively, reflecting the actual conditions. Given the dynamic nature of air movement, this research offers valuable insights for analyzing the aggregation of polluted cities.
Keywords
References
- Kampa M, Castanas E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environmental Pollution. 2008; 151(2): 362-367. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.012
- Bove MC, Brotto P, Cassola F, et al. An integrated PM2.5 source apportionment study: Positive Matrix Factorisation vs. the chemical transport model CAMx. Atmospheric Environment. 2014; 94: 274-286. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.05.039
- Wang F, Chen DS, Cheng SY, et al. Identification of regional atmospheric PM10, transport pathways using HYSPLIT, MM5-CMAQ and synopticpressure pattern analysis. Environmental Modelling &Software. 2010; 25(8): 927-934.
- Yang X, Feng L, Wei P. Atmospheric particulate matter PM2.5 and its hazards. Preface science. 2012; 6(21): 22-30.
- Rodriguez S, Querol X, Alastuey A, et al. Comparative PM10-PM2.5 source contribution study at rural, urban and industrial sites during pmepisodes in Eastern Spain. Science of the Total Environment. 2004; 328(1-3): 1-26.
- Elangasinghe MA, Singhal N, Dirks KN, et al. Complex time series analysis of PM10 and PM2.5 for a coastal site using artificial neural network modelling and k-means clustering. Atmospheric Environment. 2014; 94: 106-116. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.04.051
- Zhu T, Wu L, Bi X, et al. Study on Optimization Technology of atmospheric particulate source apportionment receptor model. China Environmental Science. 2010; 30(7): 865-870.
- Yang H, Zou X, Wang H, et al. Research progress and Prospect of PM2.5 in atmospheric environment. Journal of Meteorology and environment. 2012; 28(3): 77-82.
- Sun Y, Zhuang G, Wang Y, et al. The air-borne particulate pollution in Beijing—concentration, composition, distribution and sources. Atmospheric Environment. 2004; 38(35): 5991-6004. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.07.009
- Yu X, Li X, Deng Z, et al. Aerosol optical characteristics during haze in Beijing. Environmental Science. 2012; 33(4): 1057-1062.
- Song Y, Tang X, Fang C, et al. Relationship between visibility decline and particulate pollution in Beijing. Journal of environmental science. 2003; 23(4): 468-471.
- Su F, Gao Q, Zhang Z, et al. Transport channel of foreign pollutants in Beijing boundary layer. Environmental science research. 2004; 17(1): 26-29.
- Fan X, Wang L, Xu H, et al. Characterizing air quality data from complex network perspective. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2015; 23(4): 3621-3631. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5596-y
- Gu C, Coomans CP, Hu K, et al. Lack of exercise leads to significant and reversible loss of scale invariance in both aged and young mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2015; 112(8): 2320-2324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1424706112
- Yang T, Gu C, Yang H. Long-Range Correlations in Sentence Series from A Story of the Stone. PLOS ONE. 2016; 11(9): e0162423. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162423
- Qiu L, Yang T, Yin Y, et al. Multifractals embedded in short time series: An unbiased estimation of probability moment. Physical Review E. 2016; 94(6). doi: 10.1103/physreve.94.062201
- Yang Y, Gu C, Xiao Q, et al. Evolution of scaling behaviors embedded in sentence series from A Story of the Stone. PLOS ONE. 2017; 12(2): e0171776. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171776
- Xiao Q. Application of network in correlation analysis of stock market. China management science. 2016; 24(SI): 470-474.
- Xiao Q. Application of network in correlation analysis of stock market. In: Proceedings of the 18th China Annual Conference on management science; 2016. pp. 476-480.
- Wang Y, Yang H, Yan J, et al. Complex network approach to relations between universities in China. Chinese Science Bulletin. 2012; 57(10): 875-882. doi: 10.1360/972011-1538
- Liu Shan, peng Lin, wenyanping, et al. Pollution characteristics of organic carbon and elemental carbon in PM2.5 in Taiyuan. Environmental Science, 2015, 36 (2): 396-401
- Wang L. Air quality data analysis based on complex network theory [Marster’s thesis]. Jiangsu University; 2017.
- Zhang Z, Wang Z. Research on urban PM2.5 diffusion network model. China environmental monitoring. 2014(6): 129-132.
- Xue An, Geng E. China PM2.5 regional division based on complex network. Journal of applied basic and Engineering Sciences. 2015(SI): 68-78.
- Ma Y, Gao G. Research on Beijing Tianjin Hebei haze pollution network based on node importance evaluation. Journal of environmental science. 2018; 38(6): 2287-2296.
- Kruskal JB. On the shortest spanning subtree of a graph and the traveling salesman problem. Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society. 1956; 7(1): 48-50. doi: 10.1090/s0002-9939-1956-0078686-7
- Yang Y, Yang H. Complex network-based time series analysis. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications. 2008; 387(5-6): 1381-1386. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2007.10.055
- Wang J, Yang H. Complex network-based analysis of air temperature data in China. Modern Physics Letters B. 2009; 23(14): 1781-1789. doi: 10.1142/s0217984909019946
- Xu X, Zhang J, Small M. Superfamily phenomena and motifs of networks induced from time series. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2008; 105(50): 19601-19605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806082105
- Newman MEJ. The Structure and Function of Complex Networks. SIAM Review. 2003; 45(2): 167-256. doi: 10.1137/s003614450342480
- Fortunato S. Community detection in graphs. Physics Reports. 2010; 486(3-5): 75-174. doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2009.11.002
- Ravasz E, Barabási AL. Hierarchical organization in complex networks. Physical Review E. 2003; 67(2). doi: 10.1103/physreve.67.026112
- Shen-Orr SS, Milo R, Mangan S, et al. Network motifs in the transcriptional regulation network of Escherichia coli. Nature Genetics. 2002; 31(1): 64-68. doi: 10.1038/ng881
- Austin RB, David FG, Jure L. Supplementary materials for higher-order organization of complex network. Science. 2016; 353(6295): 163-166.
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2020 Qin Xiao, Yunting Lu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China



