
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
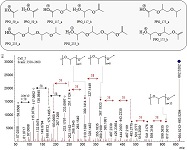
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
Temporal analysis of atmospheric nitrogen dioxide pollution and pediatric outpatient visits for respiratory illnesses in Yuexiu District, Guangzhou, China
Vol 1, Issue 1, 2020
Download PDF
Abstract
Objective: The study aims to investigate the impact of atmospheric nitrogen dioxide (NO2) levels on pediatric outpatient consultations for respiratory illnesses in the Yuexiu District of Guangzhou, China. Methods: Data on atmospheric NO2 levels, weather conditions, and outpatient visits for respiratory diseases were gathered from a children’s hospital in Guangzhou’s Yuexiu District over the period of 2014 to 2016. Spearman rank correlation analysis and time-series analysis employing a generalized additive model were utilized to examine the association and lagged effects between NO2 concentrations and concurrent pediatric respiratory outpatient visits. Results: The annual mean NO2 concentrations in Yuexiu District during 2014, 2015, and 2016 were 6130, 6046, and 6081 μg/m3, respectively, and the number of days exceeding national standard values was 70, 64, and 62, respectively. The time-series analysis revealed a significant impact of NO2 on respiratory outpatient visits from day 0 to day 7, with the most pronounced effect observed on lag day 0 (lag0). An excess risk (ER) of 145% (95% CI: 93%–198%) was observed on lag day 0 (lag0). The highest cumulative lag effect and ER of 307% (95% CI: 204%–410%) were found on lag days 0 to 6 (lag06 d). Conclusion: The rise in NO2 levels in Guangzhou’s Yuexiu District between 2014 and 2016 was associated with an increase in pediatric respiratory disease outpatient visits.
Keywords
References
- Zhang ZQ, Wang SH, Wu ZL, et al. Effects of air pollutants on outpatient and emergency number of respiratory diseases in Yanqing District of Beijing. Chin J Dis Control Prev. 2019; 23(7): 822-827,834.
- Zhang YY, Liu ZW, Li WL, et al. Air pollution influence on symptoms and respiratory system diseases in pupils in Weifang city. J Environ Hyg. 2017; 7(4): 274-278,290.
- Qin H, Sun J, Wang Q, et al. Study on ambient air pollution and respiratory diseases in children. China maternal and child health care. 2010; 25(34): 5048-5049
- Zhu Y, Yang XN, Li YB. Relationship between air pollution and children respiratory diseases in a certain area in Shenyang. J Environ Health. 2008; 25(7): 575-578.
- Zhang JY, Meng HY, Zhang GB, et al. Relationship between air pollution and daily respiratory system disease mortality in Chaoyang district, beijing: a time-series analysis. J Environ Health. 2011; 28(9): 788-791.
- Greenberg N, Carel RS, Derazne E, et al. Different effects of People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. Ambient air quality standard: GB 3095 2012. Beijing: China Environment Science Press; 2016.
- General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. Ambient air quality standard: GB 3095-2012. Beijing: China Environment Science Press; 2016.
- Lu F, Li Y, Li C, et al. Application of time series analysis in the field of air pollution and health and its R software implementation. China health statistics. 2018; 35(4): 622-625.
- Franck U, Leitte AM, Suppan P. Multifactorial airborne exposures and respiratory hospital admissions—The example of Santiago de Chile. Science of The Total Environment. 2015; 502: 114-121. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.08.093
- Liu F, Zhao Y, Liu YQ, et al. Asthma and asthma related symptoms in 23,326 Chinese children in relation to indoor and outdoor environmental factors: The Seven Northeastern Cities (SNEC) Study. Science of The Total Environment. 2014; 497-498: 10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.07.096
- Zhu YD, Wei JR, Huang L, et al. Comparison of respiratory diseases and symptoms among school-age children in areas with different levels of air pollution. J Peking Univ (Health Sci). 2015; 47(3): 395-399.
- Xiong YX, Zou YF, Zheng J, et al. Effects of haze on children’s respiratory symptoms in Guangzhou. J Environ Health. 2016; 33(1): 48-51.
- Wu YZ, Zhang JL, Zhao XG, et al. Relationship between ambient air pollution and children’s respiratory health in China. J Environ Health. 2009; 26(6): 471-477.
- Qin M, Gao Y, Gu PQ, et al. Acute effects of air pollutants on respiratory diseases in Fengxian District, Shanghai. J Environ Occup Med. 2018; 35(6): 521-525.
- Zhang W, Zhen G, Chen D, et al. Influence of air pollutants on outpatient volume of respiratory diseases in Shunyi District of Beijing. China health statistics. 2017; 34(2): 275-279.
- Wang Y, Yang S, Zhang J, et al. Correlation between air pollution in Zhengzhou and daily outpatient volume of respiratory system in children’s Hospital. Journal of environmental hygiene. 2019; 9(6): 583-588.
- Liu XB, Yang L, Hong QQ, et al. Time-series analysis on association between air pollutants and hospital outpatients for respiratoty diseases in a district, Harbin in 2015. J Environ Hyg. 2017; 7(4): 279-283.
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2020 Chuangwei Weng, Li Chen, Jue Zeng, Jiaming Lu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China



