
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.

Issue release: 31 December, 2020
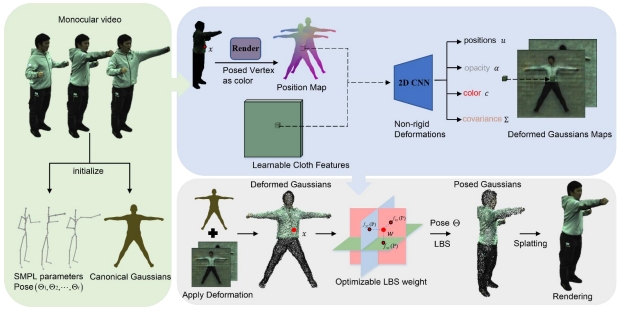
The metaverse is a digital landscape that participants can use to build their own virtual environments, and the Augmented reality (AR) technique has a certain degree of power, convincing your brain that those elements really exist in your environment.
Issue release: 31 December, 2020
The mobile augmented reality (M-AR) besides being a booming computer technology is an innovative tool that can support the pedagogical process in university classrooms, that is why the present research aims to show a methodological proposal for its implementation, in order to facilitate the learning of spatial reasoning of students, through the visualization and manipulation of three-dimensional virtual objects, promoting the motivation of learning knowledge and topics of the course of industrial design and technical drawing for the career of industrial engineering. A collection of geometric figures has been elaborated with the help of technological tools such as 2D and 3D modeling software, computer-aided design software and augmented reality application software. An updated methodology is proposed, available to any teacher, oriented to the stimulation of mental processes related to spatial reasoning of students, which integrates technological tools in the didactics of the dihedral system and the different graphic projections.
Issue release: 31 December, 2020
This research inquiries about the flexibility of two augmented reality storytelling apps, as well as eight specific variables of this cognitive characteristic of creativity from the Creapp 6–12 questionnaire. The study concludes that they meet all the specific variables of flexibility, used in convergent and divergent mode activities: they stimulate critical and divergent thinking, accessibility and adaptation to different levels of difficulty, including variety of codes, allow the interrelation of disparate elements, build different stories, manipulate and exchange elements, change and reformulate the story.
Issue release: 31 December, 2020
The introduction of information and communication technology (ICT) into the classroom has led to a new learning scenario based on educational innovation, in which mobile devices are used for teaching. In this study, the views of upper middle class students in a private educational institution in Mexico on the implementation of augmented reality teaching strategy based on metaverse mobile application are analyzed. The study is descriptive and survey based. Data retrieval is conducted using a clearly designed digital questionnaire. From August to December 2018, 192 first semester students who participated in the basic mathematics course participated in the course. The results show that compared with the previous academic year, the school recognition index has improved, and the affinity for the use of reality in the classroom has improved. When using the strategies mediated by these tools, the view of learning change is favorable. Therefore, it can be inferred that the application of augmented reality in mathematics teaching is of great help to students’ performance.

Prof. Zhigeng Pan
Professor, Hangzhou International Innovation Institute (H3I), Beihang University, China

Prof. Jianrong Tan
Academician, Chinese Academy of Engineering, China
Conference Time
December 15-18, 2025
Conference Venue
Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Center (HKCEC)
...
Metaverse Scientist Forum No.3 was successfully held on April 22, 2025, from 19:00 to 20:30 (Beijing Time)...
We received the Scopus notification on April 19th, confirming that the journal has been successfully indexed by Scopus...
We are pleased to announce that we have updated the requirements for manuscript figures in the submission guidelines. Manuscripts submitted after April 15, 2025 are required to strictly adhere to the change. These updates are aimed at ensuring the highest quality of visual content in our publications and enhancing the overall readability and impact of your research. For more details, please find it in sumissions...


 Open Access
Open Access




.jpg)
.jpg)

