
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
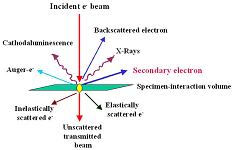
Separation and detection technologies are core components of analytical science, aimed at qualitative and quantitative analysis of samples. They can isolate target components from complex mixtures and accurately measure their concentrations, supporting fields such as environmental monitoring, food safety, and pharmaceutical analysis.
Issue release: 31 December 2022
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are organic chemicals capable of persisting in the environment, being transported over long distances, bioaccumulating and biomagnifying in ecosystems. The harmful effects of these compounds on the environment and the health of living beings are of concern. In particular, humans can come into contact with POPs when consuming contaminated food of animal origin with a high fat content. In the Dominican Republic these compounds have been widely used and generated. However, the levels of POP exposure to which the population is exposed are unknown. Therefore, the objective of this study was to determine the presence of 34 POPs in five main brands of nationally produced cow’s milk. The samples were prepared using the QuEChERS extraction method and the analytical technique used was GC/MS. The results obtained indicated that no POPs were present in the samples. The results obtained indicated that there is no presence of the POPs evaluated in any of the cow’s milk samples, which suggests that their consumption does not represent a threat to the health of consumers. In addition, this study contributes to the knowledge on the evaluation of POPs in the Dominican Republic.
Issue release: 31 December 2022
Gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) were prepared by reducing HAuCl4 with sodium citrate. The sensitivity and selectivity of the gold amalgam catalytic degradation system for rhodamine B (RhB) in mercury detection were assessed using fluorescence and ultraviolet-visible absorption spectroscopy. This experiment aims to stimulate students' interest in scientific research and foster their exploratory spirit. It also enhances their comprehensive experimental skills and initiative, deepens their understanding and application of nanoparticle preparation, characterization, catalytic reactions, and metal ion analysis methods, and cultivates their innovative thinking and scientific mindset.
Issue release: 31 December 2022
Microplastic pollution has emerged as a significant global environmental issue, raising considerable concern. To assess the biological impacts of microplastics, precise quantification within organisms is essential. Fluorescence intensity is a common method for measuring microplastics, but biological sample digestion—a crucial pre-treatment step—can potentially degrade the microplastics, affecting fluorescence readings and causing discrepancies between measured and actual values. This study investigates six widely used digestive agents: KOH, naoh, H2O2, HNO3, HNO3: hcl, and HNO3: HClO4. The effects of these digestion methods on microplastic fluorescence intensity and surface morphology were evaluated to determine the most effective protocol. The results indicate that KOH digestion (100 g·L-1, 60℃) has the least impact on fluorescence intensity and preserves the microplastics' surface morphology, whereas the other five methods caused varying degrees of fluorescence reduction and surface damage (such as aggregation, bubbles, scratches, and depressions). Furthermore, the KOH digestion method achieved a recovery rate of ≥96.3%±0.5% when used to extract microplastics from biological samples, demonstrating its suitability for analyzing fluorescent microplastics in such samples.
Issue release: 31 December 2022
Several analytical techniques, including High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Spectrophotometry, were developed to quantify the chitosan content in water-soluble fertilizers, with a focus on optimizing the hydrolysis conditions for chitosan. The results showed that the optimal hydrolysis was found to occur using a 1+1 hydrochloric acid solution at 100°C for 24 hours. For HPLC, using 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone (PMP) as the derivatizing agent, the method exhibited a linear range of 1-200 mg/L, a detection limit of 0.07 mg/L, and a spiked recovery rate of 95%-101%. Spectrophotometry, on the other hand, had a linear range of 0-100 μg, a detection limit of 0.47 μg, and a recovery rate of 94%. The two methods demonstrated good agreement in their determination of chitosan content in water-soluble fertilizer samples, satisfying the analytical requirements for chitosan in such fertilizers. HPLC proved to be more efficient with fewer interference factors. Additionally, the use of methyl fluorene chloroformate (FMOC-Cl) as a derivatizing agent for chitosan hydrolysate, followed by detection with HPLC, yielded results that were essentially consistent with the previous two methods. However, the HPLC and spectrophotometry methods established in this study were not suitable for determining chitosan content in water-soluble fertilizers that contain nitrates.
Issue release: 31 December 2022
A method has been developed to analyze 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in shellfish samples. The procedure involves ultrasonic extraction, separation using florisil and MIP-PAHs columns, concentration through vacuum evaporation and nitrogen blowing, and detection via HPLC-VWD/FLD. The pre-treatment method was optimized, and at spiked levels of 0.5, 1.5, and 2 μg/kg, the average recoveries of the 16 PAHs ranged from 58.1% to 89.6%, 60.6% to 88.1%, and 72.3% to 98.0%, with relative standard deviations (RSDs) of 0.23% to 11%, 1.3% to 13%, and 1.5% to 14%, respectively, in Mytilus coruscus. The detection limit for the PAHs was 0.5 μg/kg. This method was also applied to analyze 16 PAHs in Ostrea gigas, Meretrix meretrix, and Sinonovacula constricta.
Issue release: 31 December 2022
This review examines key analytical methods for determining the nutritional value of forage and feedstuffs, focusing on the fibrous fraction's variability and its impact on animal nutrition. Traditional and modern techniques, including the widely used detergent system and enzymatic-gravimetric methods, are evaluated for their accuracy, reproducibility, and practicality. Despite improvements, challenges remain due to methodological variations and the high costs of advanced techniques. The review highlights the need for further research to enhance analytical methods, ensuring precise estimation of cell wall constituents for optimal diet formulation in animal production.
Issue release: 31 December 2022
With the mass production and application of carbon nanomaterials, effective detection and characterization methods in various media are crucial. This paper reviews commonly used techniques for analyzing carbon nanomaterials, starting with their separation and enrichment methods, including extraction and fractionation technologies. It then covers characterization techniques such as electron microscopy, spectroscopy, thermal analysis, electrochemical analysis, isotope labeling, imaging, fluorescence spectroscopy, laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, scanning Raman microscopy, and quantitative analysis methods. The paper also introduces new carbon nanomaterials and specialized characterization methods, concluding with a discussion on future trends and prospects in the field.
Issue release: 31 December 2022
Supramolecular chemistry involves non-covalent interactions and specific molecular recognition of molecules/analytes by host molecules or supramolecules. These events are present in synthesis, catalysis, chiral separations, design of sensors, cell signaling processes and drug transport by carriers. The typical behavior of supramolecules is derived from their ability to build well-structured self-assembled and self-organized entities. Cavitands are a particular group of supramolecules possessing a cavity capable to include a variety of compounds thanks to host-guest non-covalent interactions developed among cavitands and analytes. Some typical cavitands are crown ethers, calixarenes, cucurbiturils, porphyrins and cyclodextrins. The two latter families are natural product cavitands that are generally considered models for molecular recognition of cations and organic and inorganic guest molecules, being attractive host molecules from the sustainability point of view. The natural cyclodextrins (α, β and γ-cd) are obtained with reasonable cost by enzymatic treatment of starch under adequate temperature conditions. They are profusely used in pharmaceutical, food and cosmetic industries due to their very low toxicity and side effects. This review is focused on the relevance andapplications of cyclodextrins in pharmaceuticaltechnology for their ability to increase solubility and stabilize drug molecules, thereby enhancing their bioavailability. The association of cyclodextrins with diverse nanostructured materials, i.e., carbon nanotubes, magnetic nanoparticles, silica and molecularly imprinted polymers, allows to synergize the properties of cyclodextrins and these nanostructured materials to reach highly specific molecular recognition of analytes. The exploitation of these benefits for analytical sample pre-treatment and chiral chromatographic separations are described. The use of cyclodextrins as mobile phases additives in hplc provides interesting results for green and sustainable chromatographic separations. Polymers incorporating cyclodextrins show exceptional adsorption properties for retaining toxic compounds and persistent organic pollutants from soils and water samples, allowing satisfactory recoveries of these environmental samples according to the stockholm convection principles.
1.jpg)
Prof. Sivanesan Subramanian
Anna University, India


 Open Access
Open Access



.jpg)
