
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
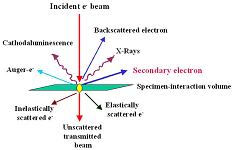
The highlight of this issue is the development of an electrochemical DNA biosensor based on graphene oxide/gold nanoparticles, capable of simultaneously detecting E. coli and Salmonella DNA. This sensor integrates logic gate functionality, showcasing its potential applications in food safety.
Issue release: 30 June 2023
High concentrations of heavy metals in urban watersheds can offer harmful effects to human health and have contributed to environmental contamination. The present work aims to evaluate the total concentration of Zn (zinc), Mg (magnesium), lead (Pb), Cr (chromium), manganese (Mn) and Ni (nickel) analyzed according to FAAS—Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, in samples of the aquatic macrophyte Egeria densa present in the urban stretch of the Cascavel River watershed, Guarapuava, PR; and specific objectives to identify the potential sources of contamination by heavy metals and to obtain physical parameters of the water. The elements zinc, magnesium, manganese and lead showed higher potential emissions upstream, a fact associated with the proximity of the industrial zone of Guarapuava. It is likely that the increase in electrical conductivity values at the upstream points is related to the discharge of domestic effluents. The decrease of conductivity and total dissolved solids in the sample points occurs downstream, corresponding to the lower topography of the study area and the end of the urban stretch of the Cascavel River basin. Despite the concentrations of heavy metals being considered critical, the plant showed efficiency in bioaccumulation of these chemical elements, being an effective tool for research and environmental assessment, and aquatic macrophytes can be the basis for biomonitoring studies of urban environments impacted by heavy metals.
Issue release: 30 June 2023
In this study, water-soluble copper-doped carbon nanodots (Cu-CDs) with high fluorescence quantum yield were synthesized using a one-step hydrothermal process with citric acid and ethylenediamine as precursors and copper sulfate as the dopant. A novel fluorescence-based method for detecting anthrax biomarkers was developed, leveraging the strong chelation of 2,6-pyridinedicarboxylic acid (DPA) with the carbon nanodots. Under optimal conditions, the fluorescence quenching rate of Cu-CDs with DPA exhibited excellent linearity in the concentration ranges of 5–100 nmol/L (r² = 0.9941) and 150–400 nmol/L (r² = 0.9976), with a detection limit of 2.3 nmol/L. The method's low cost, high specificity, sensitivity, and simplicity suggest promising potential for anthrax biomarker detection.
Issue release: 30 June 2023
In this study, Graphene oxide/gold nanoparticles composite membrane electrodes (GCE/GO/AuNPs) were fabricated using drop coating and electrodeposition techniques. By analyzing changes in the probe's surface configuration before and after binding with target DNA, the electrochemical signal varies, enabling the intelligent detection of E. coli and Salmonella DNA. Take the target as the input signal, and Σ|ΔI| and |ΔIMB/ΔIFC| constructs “and” and “XOR” DNA molecular logic gates for output, and proposes a new semi adder model that can be used for logic operations. Square wave voltammetry (SWV) was used to detect the current change value Σ|ΔI| of the two labeled probes, which was consistent with E. The logarithmic values of the concentrations of coli DNA and Sal DNA showed a good linear relationship in the range of 1.0 × 10−13 to 1.0 × 10−8 mol·L−1, and the detection limits (S/N = 3) were respectively 3.2 × 10−14 mol·L–1 and 1.7 × 10−14 mol·L−1.
Issue release: 30 June 2023
The present study has as objective the analysis and characterization of a sample of an Ecuadorian feldspar, by means of XRD, SEM and TGA techniques, for the microstructural analysis of mineral phase and chemical composition. Qualitative and quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis by Rietveld refinement revealed that this feldspar is composed of 33.31% Albite, 15.70% Quartz and a large percentage by weight of 50.99% amorphous material. To validate these results, the uncertainty of the measurement was investigated and calculated by statistical analysis of standard deviation, giving as results an uncertainty error of ±0.87 wt%, ±0.23 wt% and ±0.89 wt% respectively for the percentages by weight of the minerals found in this analysis. The result by SEM shows the presence of Albite in the feldspar exhibiting laminar twinning and characterized by randomly dispersed spherical quartz and plagioclase inclusions.
Issue release: 30 June 2023
Objective: To assess the quality of whole wheat products, a method for determining alkylresorcinols (ARs)—markers of whole wheat, black wheat, and other cereal products—was developed. Methods: The study focused on wheat and black wheat, using factorial design to evaluate the impact of extraction solvents (acetone, alcohol, and ethyl acetate), extraction techniques (ultrasonic extraction for 30 or 60 minutes, and shaking overnight at room temperature), and sample forms (granules or flour) on AR determination. AR detection conditions were optimized by comparing chromatographic settings and fluorescence scanning wavelengths. The method's effectiveness was validated by measuring AR content in various commercially available cereals. Results: Considering reagent toxicity and efficiency, the optimal procedure involved ultrasonically extracting comminuted samples with ethanol for 30 minutes, then analyzing with a Waters CORTES-C18 column using an ethanol: acetonitrile (30:70, v:v) mobile phase. Fluorescence detection was performed at an excitation wavelength of 272 nm and an emission wavelength of 296 nm. The method had a linear range of 0.050–10.0 µg/mL with an R² ≥ 0.9999. Precision experiments showed an RSD of less than 5%, and spiked recovery rates ranged from 94.5% to 104%. The total AR content was 47.9–54.3 mg/100 g in commercially available wheat and 53.6–60.9 mg/100 g in black wheat. Conclusion: The liquid-fluorescence method established in this study effectively and rapidly separates ARs from wheat and black wheat, offering advantages of simplicity, high sensitivity, and accuracy.
Issue release: 30 June 2023
As knowledge and civilization advance, forensic science and technology are continuously evolving. Chromatography, a key analytical method known for its simplicity, speed, and high sensitivity, is extensively utilized worldwide for detecting toxic substances and drugs in forensic investigations. This paper offers a thorough analysis of chromatographic techniques from three key angles: the historical development of chromatography, its classification based on phase states, chromatographic separation mechanisms and stationary phase characteristics, and its various applications. Additionally, the paper forecasts future trends in chromatographic analysis technology, aiming to inspire new directions for the advancement and research of other forensic science technologies.
1.jpg)
Prof. Sivanesan Subramanian
Anna University, India


 Open Access
Open Access



.jpg)
