
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
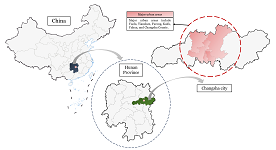
As China's pillar industry, the property market has suffered a considerable impact in recent years, with a decline in turnover and many developers at risk of bankruptcy. As one of the most concerned factors for stakeholders, housing prices need to be predicted more objectively and accurately to minimize decision-making errors by developers and consumers. Many prediction models in recent years have been unfriendly to consumers due to technical difficulties, high data demand, and varying factors affecting house prices in different regions. A uniform model across the country cannot capture local differences accurately, so this study compares and analyses the fitting effects of multiple machine learning models using February 2024 new building data in Changsha as an example, aiming to provide consumers with a simple and practical reference for prediction methods. The modeling exploration applies several regression techniques based on machine learning algorithms, such as Stepwise regression, Robust regression, Lasso regression, Ridge regression, Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression, Extreme Gradient Boosted regression (XGBoost), and Random Forest (RF) regression. These algorithms are used to construct forecasting models, and the best-performing model is selected by conducting a comparative analysis of the forecasting errors obtained between these models. The research found that machine learning is a practical approach to property price prediction, with least squares regression and Lasso regression providing relatively more convincing results.
Issue release: 31 December 2023
Biodiversity has brought rich material products and non-material benefits to mankind, and is an important support for the sustainable development of human society. Although people realize the importance of improving biodiversity under the pressure of rapid disappearance of biodiversity, few people have fully explored the parametric design of biodiversity in urban landscapes. Therefore, this article briefly describes the development process of urban landscape biodiversity, taking examples of different types and different scales at home and abroad as examples, comparing its parameterized evaluation and design models, and analyzing the parametric design in the urban landscape and the biodiversity target organic ways and means of combination. On this basis, the approach of urban landscape design for biodiversity is explored, its development trend and main problems are prospected, and the corresponding enlightenment for the future development of urban biodiversity and practical reference are provided.
Issue release: 31 December 2023
Taking the urban plants of Yiyang as the research object, the field investigation of Yiyang plants was carried out by using the method of combining route investigation and quadrat investigation, the current situation of plant diversity level in Yiyang City was analyzed, and the planning content and construction strategy of plant diversity protection in Yiyang City were studied, in order to provide reference for the effective protection of plant diversity in Yiyang City. The results showed that there were 145 families, 481 genera and 955 species of vascular plants in Yiyang urban planning area; there are 232 species of garden plant resources in the central urban area, belonging to 62 families. 105 genera; the overall level of plant diversity in Yiyang City is general. Urban landscaping relies too much on exotic species, and the utilization rate of native plants in urban gardens is low.
Issue release: 31 December 2023
The integrated green development of the Yangtze River Delta is a long-term major strategy. The rural ecological status is the basis for the healthy development of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. This study focuses on the expansion of demand for rural vegetation biodiversity conservation and ecosystem service functions in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. A total of 256 plant communities in 28 villages were investigated, and the composition of family, genera and species and life forms were analyzed respectively; through clustering, 47 community types and 8 vegetation types were divided, and the composition and distribution characteristics of plant community were analyzed; and then it analyzed the species biodiversity and compared the characteristics of rural transformation in the Yangtze River Delta with the vegetation characteristics of urban areas and natural areas. Finally, specific countermeasures for biodiversity conservation and reconstruction of the Yangtze River Delta rural vegetation was proposed in terms of species protection, habitat maintenance, plant community conservation, and ecological aesthetics guidance.
Issue release: 31 December 2023
The present study evaluated the effect of silvicultural treatments on the diversity and structure of species in temperate forest ecosystems in the Municipality of Pueblo Nuevo in the State of Durango, Mexico; it was carried out to know if forest use modifies the diversity, mixture of species, spatial distribution, and dimensional differentiation of individuals in these ecosystems. The evaluation was carried out by comparing 10 plots with management history, which were measured before the application of the treatment and five years later. The diversity indices of Shannon, Simpson and Margalef were compared, as well as indices of structure of mixture of species, spatial distribution, and dimensional differentiation. According to the silvicultural treatments applied, the values of the indices do not present significant differences in their evaluations (p > 0.05), which indicates that forest use does not modify the diversity and structure of species of the tree stratum of this plant community.
Issue release: 31 December 2023
This paper explores the relationship between the spatial scale and biodiversity protection level and thinks that under the specifi c urban-region scale, landscape diversity is the key level to the macroscopic protection of biodiversity. Based on the systematicness and the otherness of urban–regional environment and the biologic fl ow and process, the protection pattern of biodiversity within urban–regional scale should be established. The author holds that seeking the “optimal landscape pattern” is one of the core missions of biodiversity protection planning. Based on that, the paper summarizes the two types of city space and their biodiversity planning and design in two ways: first, the “Urban-rural landscape pattern optimization approach” specific to the space of city matrix, which includes “agglomeration segregation”, “landscape”, “green infrastructure”, three models and five pattern optimization strategies; second, the “Nature reserve approach” specific to the space of natural matrix, which includes “reserve circle” and “protected area network” two modes and six reserve design principles.
Issue release: 31 December 2023
Issue release: 31 December 2023
From the evidence obtained in the 2017 Chilean population census pyramid for the country scale, the question arises whether the population structure by age is replicated homogeneously at the subnational level or, on the contrary, it presents heterogeneous local characteristics based on age groups. For each of the third-level subnational units (n = 346), the standard deviation of the different age classes was compared in relation to the national population pyramid. With these differences, the k-means method was used to identify eight groups of communes, and four demographic indicators were calculated. The results allow to affirm that the population structure by age and sex at the communal level presents heterogeneous characteristics. The analysis of territorial patterns identified groups of the aging population, households with active aging, transition to aging, adult population, men in terminal productive age, men in initial age, households with children under 15 years and households with children over 15 years.
Issue release: 31 December 2023
This paper scrutinizes the way diversity is understood in urban zones and cities. It seeks to demonstrate that diversity is a consequence of the fragmentation of social interactions drawn from the blurring of the other in order to root out liberal subject, the one that holds political and social equality. In this sense, we propose looking once again at the city and public space from the perspective of its distances and social separation, as well as the recognition of social absences in what is called “plurality” that, nowadays, demands an interdisciplinary dialogue and creatively crafted methodological frames.
Issue release: 31 December 2023
Since the reform and opening up, China's urbanization has developed rapidly Behind the rapid urbanization is the imbalance and insufficiency of urban development From the perspective of social and cultural diversity, this paper explores the impact of the diversity of dialect types on urban scale The diversity of dialects leads to the division of trust, hinders the cross regional flow of factors, affects the agglomeration effect of factors, and then affects the expansion of urban scale Using the diversity index of regional dialect types and 2016 nppviirs urban night light index, this paper empirically studies the impact of dialect diversity on urban scale The measurement results show that: Dialect diversity has a significant negative impact on urban scale On average, the addition of one dialect category will lead to a 4.5% decline in the size of the city measured by the night light index 55%. A series of robustness tests and causal identification show that the estimation result in this paper is the causal relationship of robustnessfurther empirical research shows that dialect diversity mainly affects the expansion of urban scale by hindering the flow and agglomeration of labor, capital and technological factorsthe Enlightenment of this study: To build a diversified and inclusive modern city, we need to weigh the costs and benefits of cultural diversity and unity, break cultural barriers, eliminate cultural prejudices, improve social trust, and give full play to the complementary effects brought by multiculturalism

Prof. Mehmet Cetin
Kastamonu University,
Turkey
Polish Scientific Bibliography


 Open Access
Open Access