
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
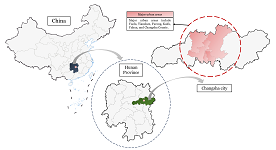
As China's pillar industry, the property market has suffered a considerable impact in recent years, with a decline in turnover and many developers at risk of bankruptcy. As one of the most concerned factors for stakeholders, housing prices need to be predicted more objectively and accurately to minimize decision-making errors by developers and consumers. Many prediction models in recent years have been unfriendly to consumers due to technical difficulties, high data demand, and varying factors affecting house prices in different regions. A uniform model across the country cannot capture local differences accurately, so this study compares and analyses the fitting effects of multiple machine learning models using February 2024 new building data in Changsha as an example, aiming to provide consumers with a simple and practical reference for prediction methods. The modeling exploration applies several regression techniques based on machine learning algorithms, such as Stepwise regression, Robust regression, Lasso regression, Ridge regression, Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression, Extreme Gradient Boosted regression (XGBoost), and Random Forest (RF) regression. These algorithms are used to construct forecasting models, and the best-performing model is selected by conducting a comparative analysis of the forecasting errors obtained between these models. The research found that machine learning is a practical approach to property price prediction, with least squares regression and Lasso regression providing relatively more convincing results.
Dialect diversity, element agglomeration and city size—Empirical Test Based on satellite lighting data
Vol 4, Issue 1, 2023
Download PDF
Abstract
Since the reform and opening up, China's urbanization has developed rapidly Behind the rapid urbanization is the imbalance and insufficiency of urban development From the perspective of social and cultural diversity, this paper explores the impact of the diversity of dialect types on urban scale The diversity of dialects leads to the division of trust, hinders the cross regional flow of factors, affects the agglomeration effect of factors, and then affects the expansion of urban scale Using the diversity index of regional dialect types and 2016 nppviirs urban night light index, this paper empirically studies the impact of dialect diversity on urban scale The measurement results show that: Dialect diversity has a significant negative impact on urban scale On average, the addition of one dialect category will lead to a 4.5% decline in the size of the city measured by the night light index 55%. A series of robustness tests and causal identification show that the estimation result in this paper is the causal relationship of robustnessfurther empirical research shows that dialect diversity mainly affects the expansion of urban scale by hindering the flow and agglomeration of labor, capital and technological factorsthe Enlightenment of this study: To build a diversified and inclusive modern city, we need to weigh the costs and benefits of cultural diversity and unity, break cultural barriers, eliminate cultural prejudices, improve social trust, and give full play to the complementary effects brought by multiculturalism
Keywords
References
- Chen L, Yang K, Wu J. Empirical Research on the evolution of China's urban system. Jiangsu Social Sciences. 2007; 1.
- Duan R. Research on China's urban scale and its influencing factors -- Empirical Evidence from 284 prefecture level and above cities. financial research. 2013; 9.
- Sun B, Jin X, Lin J. China's new urbanization pattern towards coordinated development of large, medium and small cities -- Evolution and influencing factors of China's urban scale distribution since 1952. Geographical research. 2019; 1.
- Liu Y, Xu X, Xiao Z. Inverted U-shaped model of labor force flow across dialects. Economic research. 2015; 10.
- Lin J, Zhao Z. Invisible barriers to balanced development: dialects, institutions and technology diffusion. Economic research. 2017; 9.
- Ding C, Ji Z, Lei Y, Liang Z. Dialect diversity and market integration: from the perspective of urban circle. Economic research. 2018; 11.
- Xu X, Liu Y, Xiao Z. Dialects and economic growth. Journal of economics. 2015; 2.
- Ruan J, Wang L. Language differences and market system development. Management world. 2017; 4.
- Li G, Cao J, Shao S. Language diversity and regional differences in China's opening up. world economy. 2017; 3.
- Dai Y, Xiao J, Pan Y. Can "local accent" reduce the agency cost of the company? -- Research from the perspective of dialect. Economic research. 2016; 12.
- Huang J, Liu C. Dialect and social trust. financial research. 2017; 7.
- Pendakur K, Pendakur R. Language as Both Human Capital and Ethnicity. International Migration Review. 2002; 36(1): 147-177. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-7379.2002.tb00075.x
- Chen Z, Lu M, Xu L. Returns to dialect. China Economic Review. 2014; 30: 27-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chieco.2014.05.006
- Wei X, Chen S, Li J. Dialect skills and entrepreneurial choices of floating population. China Population Science. 2016; 6.
- Chen J, Huang J. China's industry, city and region from the perspective of Agglomeration -- a summary of the latest progress of domestic spatial economics. Journal of Zhejiang University. 2008; 4.
- Li Q, Meng L. Dialects, Putonghua and regional mobility of Chinese labor force. Journal of economics. 2014; 4.
- Lu M, Chen Z. Market integration and industrial agglomeration in China's regional economic development. Shanghai People's publishing house; 2006.
- Doll CNH, Muller JP, Morley JG. Mapping regional economic activity from night-time light satellite imagery. Ecological Economics. 2006; 57(1): 75-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2005.03.007
- Elvidge CD, Cinzano P, Pettit DR, et al. The Nightsat mission concept. International Journal of Remote Sensing. 2007; 28(12): 2645-2670. doi: 10.1080/01431160600981525
- Chen X, Nordhaus WD. Using luminosity data as a proxy for economic statistics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2011; 108(21): 8589-8594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1017031108
- Yang M, Wang S, Zhou Y, Wang L. Remote sensing estimation method of urbanization level based on DMSP / OLS image. Remote sensing information. 2011; 4.
- Wu J, Liu H, Peng J, Ma L. The hierarchical structure and spatial pattern of China's urban system -- An Empirical Study Based on DMSP/OLS night light data. Journal of geography. 2014; 6.
- Levin N, Zhang Q. A global analysis of factors controlling VIIRS nighttime light levels from densely populated areas. Remote Sensing of Environment. 2017; 190: 366-382. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.01.006
- Yang M, Cai Z, Zhang K. The measurement of China's urban scale and the source of its spatial competition -- a study based on global night light data. Finance and trade economics. 2017; 3.
- Yang R, Luo H, Zhou S, et al. Reconstruction and analysis of spatial formation process of Chengdu Chongqing urban agglomeration driven by night light data. Journal of Earth Information Science. 2017; 5.
- Li W, Sun B, Liu Q, Zhang T. Characteristics and influencing factors of China's urban spatial structure. Geographical Sciences. 2018; 6.
- Wu B. Formation and division of Chinese cultural areas. Academic monthly. 1996; 3.
- Fan Y. Inflection point and transformation of China's urban development: from the perspective of dynamic mechanism. Economic aspect. 2019; 8.
- Zhao R, Shen C. Capital flow, industrial agglomeration and Industrial Structure Upgrading -- Empirical Analysis Based on panel data of 16 central cities in the Yangtze River Delta. Exploration of economic problems. 2019; 6.
- You R, Zhou Z. Dialects and Chinese culture. Fudan Journal. 1985; 3.
- Conley TG, Hansen CB, Rossi PE. Plausibly Exogenous. The Review of Economics and Statistics. 2012; 94(1): 260-272. doi: 10.1162/REST_a_00139
- Chen J, Huang J. China's industry, city and region from the perspective of Agglomeration -- a summary of the latest progress of domestic spatial economics. Journal of Zhejiang University. 2008; 4.
- Xu Y, Yin X, Yin X. Labor mobility and wage changes of Chinese urban residents. population and economy. 2019; 4.
- Lu M, Chen Z. Market integration and industrial agglomeration in China's regional economic development. Shanghai People's publishing house; 2006.
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2023 Congming Ding, Xueyang Huang, Min Zhou

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).

Prof. Mehmet Cetin
Kastamonu University,
Turkey
Polish Scientific Bibliography

