
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
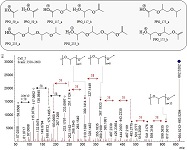
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
A bibliometric analysis of research trends in air pollution and environmental impacts
Vol 6, Issue 1, 2025
Download PDF
Abstract
This study presents an extended bibliometric analysis to identify the research landscape, trends, and influential aspects in the field of air pollution and environmental impacts. This study aims to explore the existing gaps and emerging trends in the research landscape on air pollution and its environmental impacts by analyzing publication records, author analysis, country analysis, keywords analysis and thematic maps. The findings expose the increasing interest in air pollution and its environmental impacts worldwide, growing research output, key contributors, and influential knowledge hubs that are in the process of shaping this field of study. Bibliometric techniques, like keyword co-occurrence and thematic mapping, unravel the intellectual structure and evolving focal areas within this research domain. The main findings reveal a number of highly frequent keywords that describe the interdisciplinary nature of air pollution and environmental impact studies. Thematic mapping highlights the following major themes: “air”, “climate” and “pollution”, while emerging themes in research involve “emission”, “biomass” and “factors”, etc. The study gives useful insights for future studies and informed decision-making in the industry with a better understanding of the status quo in air pollution and its environmental impacts research. Future research efforts are recommended to be directed toward more interdisciplinary approaches, strengthened regional studies in developing countries, and the promotion of international collaborations in order to meet air pollution and its environmental consequence challenges effectively on a global scale.
Keywords
References
- World Health Organization. Ambient (outdoor) air pollution. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-quality-and-health (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Sofia D, Gioiella F, Lotrecchiano N, et al. Mitigation strategies for reducing air pollution. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2020; 27(16): 19226–19235. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08647-x
- Nandasena S, Wickremasinghe A, Sathiakumar N. Air pollution and public health in developing countries: Is Sri Lanka different? Journal of the College of Community Physicians of Sri Lanka. 2012; 17(1): 15. doi: 10.4038/jccpsl.v17i1.4932
- World Health Organization. Air pollution. Available online: https://www.who.int/india/health-topics/air-pollution (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Ecosystems and air quality. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/eco-research/ecosystems-and-air-quality (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Bruce N, Perez-Padilla R, Albalak R. Indoor air pollution in developing countries: A major environmental and public health challenge. Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 2000; 78: 1078–1092.
- Fahmy YM, Fornasiero P, Zinoviev S, et al. Air pollution control technologies compendium. International Center for Science and High Technology, United Nations Industrial Development Organization; 2007.
- Smith P, Martino D, Cai Z, et al. Greenhouse gas mitigation in agriculture. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2007; 363(1492): 789-813. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2007.2184
- Chen F, Zhang W, Mfarrej MFB, et al. Breathing in danger: Understanding the multifaceted impact of air pollution on health impacts. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 2024; 280: 116532. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116532
- Manisalidis I, Stavropoulou E, Stavropoulos A, et al. Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review. Frontiers in Public Health. 2020; 8. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00014
- World Health Organization. World Health Statistics. World Health Organization; 2021.
- Landrigan P, Fuller R, Acosta N, et al. The Lancet Commission on pollution and health. The Lancet. 2017; 391. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32345-0
- Lelieveld J, Pozzer A, Pöschl U, et al. Loss of life expectancy from air pollution compared to other risk factors: a worldwide perspective. Cardiovascular Research. 2020; 116(11): 1910-1917. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa025
- Fehresti-Sani M, GholamAzad M, GholamAzad MA. Assessing the effect of industrial products on air pollution in Iran: a novel NDEA approach considering undesirable outputs. Environment, Development and Sustainability. 2024. doi: 10.1007/s10668-024-04868-z
- Ghorani-Azam A, Riahi-Zanjani B, Balali-Mood M. Effects of air pollution on human health and practical measures for prevention in Iran. Journal of Research in Medical Sciences. 2016; 21. doi: 10.4103/1735-1995.189646
- Passas I. Bibliometric Analysis: The Main Steps. Encyclopedia. 2024; 4(2): 1014–1025. doi: 10.3390/encyclopedia4020065
- Öztürk O, Kocaman R, Kanbach DK. How to design bibliometric research: an overview and a framework proposal. Review of Managerial Science. 2024; 18(11): 3333–3361. doi: 10.1007/s11846-024-00738-0
- Donthu N, Kumar S, Mukherjee D, et al. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research. 2021; 133: 285–296. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
- Wen S, Tan Q, Baheti R, et al. Bibliometric analysis of global research on air pollution and cardiovascular diseases: 2012–2022. Heliyon. 2024; 10(12): e32840. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32840
- Sun J, Zhou Z, Huang J, et al. A Bibliometric Analysis of the Impacts of Air Pollution on Children. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(4): 1277. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17041277
- Ansari A, Quaff AR. Bibliometric Analysis on Global Research Trends in Air Pollution Prediction Research Using Machine Learning from 1991–2023 Using Scopus Database. Aerosol Science and Engineering. 2024; 8(3): 288–306. doi: 10.1007/s41810-024-00221-z
- Villacura L, Sánchez LF, Catalán F, et al. An overview of air pollution research in Chile: Bibliometric analysis and scoping review, challenger and future directions. Heliyon. 2024; 10(3): e25431. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25431
- Feng T, Sun Y, Shi Y, et al. Air pollution control policies and impacts: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2024; 191: 114071. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.114071
- Zupic I, Čater T. Bibliometric Methods in Management and Organization. Organizational Research Methods. 2014; 18(3): 429–472. doi: 10.1177/1094428114562629
- Xie H, Zhang Y, Wu Z, et al. A Bibliometric Analysis on Land Degradation: Current Status, Development, and Future Directions. Land. 2020; 9(1): 28. doi: 10.3390/land9010028
- Dissanayake H, Popescu C, Iddagoda A. A Bibliometric Analysis of Financial Technology: Unveiling the Research Landscape. FinTech. 2023; 2(3): 527–542. doi: 10.3390/fintech2030030
- Springmann M, Wiebe K, Mason-D’Croz D, et al. Health and nutritional aspects of sustainable diet strategies and their association with environmental impacts: A global modelling analysis with country-level detail. Lancet Planetary Health. 2018; 2(9): e451–e461. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2542-5196(18)30206-7
- Martins F, Felgueiras C, Smitkova M, et al. Analysis of Fossil Fuel Energy Consumption and Environmental Impacts in European Countries. Energies. 2019; 12(6): 964. doi: 10.3390/en12060964
- Cheng C, Ren X, Wang Z, et al. Heterogeneous impacts of renewable energy and environmental patents on CO2 emission: Evidence from the BRIICS. Science of The Total Environment. 2019; 668: 1328–1338. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.063
- Bhuvaneshwari S, Hettiarachchi H, Meegoda JN. Crop Residue Burning in India: Policy Challenges and Potential Solutions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(5): 832. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16050832
- Eckelman MJ, Sherman J. Environmental Impacts of the U.S. Health Care System and Effects on Public Health. Ahmad S, ed. PLOS ONE. 2016; 11(6): e0157014. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157014
- Bacoş IB, Gabor MR. Air Quality Indices—Case Study: Environmental Sustainability Pillar and Romania’s Positioning in the European and Global Context. Acta Marisiensis Seria Technologica. 2021; 18(1): 22–27. doi: 10.2478/amset-2021-0004
- Al Nadhairi R, Al Kalbani M, Al Khazami S, et al. Air quality and health risk assessment during Middle Eastern dust storms: a study of particulate matter. Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health. 2024. doi: 10.1007/s11869-024-01662-8
- Ben B, Yang X, Shao P, et al. Assessment of COVID-19 lockdown measures on air quality over the Sichuan Basin, China: insights from multiple observations. Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health. 2024. doi: 10.1007/s11869-024-01671-7
- Hadj Sassi MS, Chaari Fourati L. Comprehensive survey on air quality monitoring systems based on emerging computing and communication technologies. Computer Networks. 2022; 209: 108904. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2022.108904
- Elbestar M, Aly SG, Ghannam R. Advances in Air Quality Monitoring: A Comprehensive Review of Algorithms for Imaging and Sensing Technologies. Advanced Sensor Research. 2024; 3(11). doi: 10.1002/adsr.202300207
- Rani Hemamalini R, Vinodhini R, Shanthini B, et al. Air quality monitoring and forecasting using smart drones and recurrent neural network for sustainable development in Chennai city. Sustainable Cities and Society. 2022; 85: 104077. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2022.104077
- Lovett GM, Tear TH, Evers DC, et al. Effects of Air Pollution on Ecosystems and Biological Diversity in the Eastern United States. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2009; 1162(1): 99–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04153.x
- Kumar JIN. Impact of pollution on aquatic biodiversity. Ecology, Environment and Conservation. 1997; 3: 209–217.
- Viedra GGZ, Sukojo BM. Analysis of The Effect of Deforestation Rates on Air Pollution Concentration and Land Surface Temperature Using Landsat-8 Imagery with Google Earth Engine (Case Study: East Kalimantan Province, 2019-2020). IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 2023; 1127(1): 012032. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/1127/1/012032
- Rahman RA, White B, Ma C. The effect of growth, deforestation, forest fires, and volcanoes on Indonesian regional air quality. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2024; 457: 142311. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.142311
- Liang L, Gong P. Urban and air pollution: a multi-city study of long-term effects of urban landscape patterns on air quality trends. Scientific Reports. 2020; 10(1). doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74524-9
- Sicard P, Agathokleous E, Anenberg SC, et al. Trends in urban air pollution over the last two decades: A global perspective. Science of The Total Environment. 2023; 858: 160064. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160064
- Kumar A, Omidvarborna H, Shandilya KK. Air Pollution and Climate Change. Research Anthology on Environmental and Societal Impacts of Climate Change. 2022: 1066–1102. doi: 10.4018/978-1-6684-3686-8.ch053
- Stanisci I, Sarno G, Curzio O, et al. Air Pollution and Climate Change: A Pilot Study to Investigate Citizens’ Perception. Environments. 2024; 11(9): 190. doi: 10.3390/environments11090190
- Hilly JJ, Singh KR, Jagals P, et al. Review of scientific research on air quality and environmental health risk and impact for PICTS. Science of The Total Environment. 2024; 942: 173628. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173628
- Craig L, Brook JR, Chiotti Q, et al. Air Pollution and Public Health: A Guidance Document for Risk Managers. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part A. 2008; 71(9–10): 588–698. doi: 10.1080/15287390801997732
- Van den Brekel L, Lenters V, Mackenbach JD, et al. (2024). Ethnic and socioeconomic inequalities in air pollution exposure: A cross-sectional analysis of nationwide individual-level data from the Netherlands. Lancet Planetary Health. 2024; 8: e18–e29. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(23)00258-9
- Pinho-Gomes AC, Roaf E, Fuller G, et al. Air pollution and climate change. Lancet Planetary Health. 2023; 7: e727–e728. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(23)00189-4
- Rabie S. Air Pollution and Climate Change. The Lancet Planetary Health. 2022; 7(9): e727-e728.
- Tran HM, Tsai FJ, Lee YL, et al. The impact of air pollution on respiratory diseases in an era of climate change: A review of the current evidence. Science of The Total Environment. 2023; 898: 166340. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166340
- Boogaard H, Patton AP, Atkinson RW, et al. Long-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution and selected health outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environment International. 2022; 164: 107262. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107262
- Déciga-Alcaraz A, Tlazolteotl Gómez de León C, Morales Montor J, et al. Effects of solvent extracted organic matter from outdoor air pollution on human type II pneumocytes: Molecular and proteomic analysis. Environmental Pollution. 2023; 337: 122551. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2023.122551
- Ai H, Tan X. A Literature Review of the Effects of Energy on Pollution and Health. Energy RESEARCH LETTERS. 2021; 2(4). doi: 10.46557/001c.28135
- Harizanova-Bartos H, Stoyanova Z. Impact of agriculture on air pollution. In: Proceedings of the CBU International Conference Proceedings; 2018. pp. 1071–1076.
- Dong D, Wang J. Air pollution as a substantial threat to the improvement of agricultural total factor productivity: Global evidence. Environment International. 2023; 173: 107842. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2023.107842
- Pandya S, Gadekallu TR, Maddikunta PKR, et al. A Study of the Impacts of Air Pollution on the Agricultural Community and Yield Crops (Indian Context). Sustainability. 2022; 14(20): 13098. doi: 10.3390/su142013098
- Dominski FH, Lorenzetti Branco JH, Buonanno G, et al. Effects of air pollution on health: A mapping review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Environmental Research. 2021; 201: 111487. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111487
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2025 Author(s)
License URL: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China



