
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
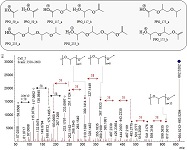
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
Noise contamination and automobile traffic along the Mexican frontier
Vol 2, Issue 1, 2021
Download PDF
Abstract
Objective: The aim was to establish a correlation between the noise levels at major road intersections and the volume of vehicles passing through these areas. Method: A non-invasive electronic vehicle sound level meter was used for one-week periods; noise levels were assessed on a daily basis throughout the week, utilizing type I integrating sound level meters. Results: An annual average daily traffic volume of 2739 vehicles was recorded; an estimated noise level of 77.6 decibels for 12-hour spans was observed; peak noise levels reached 98.5 decibels, with the lowest recorded level at 58.3 decibels. Constraints: The fieldwork was conducted over a period shorter than one year, which may limit the comprehensiveness of the findings. Main findings: The city's noise levels surpass the World Health Organization's recommended threshold of 65 decibels, indicating that the city is experiencing noise pollution as a result of vehicular traffic.
Keywords
References
- Kim KH, Ho DX, Brown RJC, et al. Some insights into the relationship between urban air pollution and noise levels. Science of The Total Environment. 2012; 424: 271-279. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.02.066
- Hunashal RB, Patil YB. Assessment of Noise Pollution Indices in the City of Kolhapur, India. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2012; 37: 448-457. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.03.310
- Mehdi MR, Kim M, Seong JC, Arsalan MH. Spatio-temporal patterns of road traffic noise pollution in Karachi, Pakistan. Environment International. 2011; 37(1): 97-104. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2010.08.003
- World Health Organization [WHO]. Burden of disease from environmental noise. Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/_data/assets/pdf_file/0008/136466/e94888.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2020).
- Chang TY, Lin HC, Yang WT, et al. A modified Nordic prediction model of road traffic noise in a Taiwanese city with significant motorcycle traffic. Science of the Total Environment. 2012; 432: 375-381. doi: 10.1016Zj.scitotenv.2012.06.016
- Zhang M, Kang J, Jiao F. A social survey on the noise impact in open-plan working environments in China. Science of the Total Environment. 2012; 438: 517-526. doi: 10.1016Zj.scitotenv.2012.08.082
- Hunashal RB, Patil YB. Assessment of Noise Pollution Indices in the City of Kolhapur, India. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2012; 37: 448-457. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.03.310
- Iglesias-Merchant C, Diaz-Balteiro L. Noise pollution mapping approach and accuracy on landscape scales. Science of total, environment. 2013; 449: 115-125. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.01.063
- Paviotti M, Vogiatzis K. On the outdoor annoyance from scooter and motorcycle noise in the urban environment. Science of total environment. 2012; 430: 223-230. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.05.010
- Zamorano B, Peña F, Parr V, Vargas JI. Social perception of urban noise. Ojeando la Agenda. 2014; 32: 2-21.
- Fyhri A, Aasvang GM. Noise, sleep and poor health: Modeling the relationship between road traffic noise and cardiovascular problems. Science of The Total Environment. 2010; 408(21): 4935-4942. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.06.057
- Gündogdu O, G6kdag M, Yüksel F. A traffic noise prediction method based on vehicle composition using genetic algorithms. Applied Acoustics. 2005; 66(7): 799-809. doi: 10.1016Zj.apacoust.2004.11.003
- Li B, Tao S, Dawson RW, et al. A GIS based road traffic noise prediction model. Applied Acoustics. 2002; 63(6): 679-691. doi: 10.1016/S0003-682X(01)00066-4
- Guedes ICM, Bertoli SR, Zannin PHT. Influence of urban shapes on environmental noise: A case study in Aracaju — Brazil. Science of The Total Environment. 2011; 412-413: 66-76. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.10.018
- Laszlo HE, McRobie ES, Stansfeld SA, et al. Annoyance and other reaction measures to changes in noise exposure—A review. Science of The Total Environment. 2012; 551-562. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.06.112
- Szeremeta B, Zannin PHT. Analysis and evaluation of soundscapes in public parks through interviews and measurement of noise. Science of the Total Environment. 2009; 407(24): 6143-6149. doi: 10.1 016/j.scitotenv.2009.08.039
- Vlachokostas C, Achillas C, Michailidou AV, Moussiopoulos V. Measuring combined exposure to environmental pressures in urban areas: An air quality and noise pollution assessment approach. Environment International. 2012; 39(1): 8-18. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2011.09.007
- Paunović K, Jakovljević B, Belojević G. Predictors of noise annoyance in noisy and quiet urban streets. Science of e Total Environment. 2009; 407(12): 3707-3711. doi: 10.1016/j.scit otenv.2009.02.033
- Ögren M, Molnár P, Barregard L. Road traffic noise abatement scenarios in Gothenburg 2015–2035. Environmental Research. 2018; 164: 516-521. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2018.03.011
- Secretaría de Comunicaciones y Transportes [SCT]. Demand modeling for toll roads (Manual No. SCT-NIS-0420). Steer Davies and TransDirección General de Desarrollo Carretero. Available online: http://www.sct.gob.mx/normatecaNew/manual-de-modelacion-para-carreteras-de-cuota/ (accessed on 2 May 2020).
- Mendoza A, Abarca E, Mayoral EF, Quintero FL. Recommendations for updating some elements of the geometric design of highways. Querétaro: IMT-SCT. Available online: http://www.imt.mx/archivos/Publicaciones/PublicacionTecnica/pt244.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2020).
- Reyes RC, Cárdenas J. Traffic engineering: fundamentals and applications (Spanish), 8th ed. Mexico: Alfaomega; 2007.
- International Standards Organization [ISO]. Acoustics-Description, measurement and assessment of environmental noise. Part 1: Basic quantities and assessment procedures, ISO 1996-1:2016. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/59765.html (accessed on 2 May 2020).
- Ortega M, Cardona JM. Methodology for the evaluation of urban environmental noise in the city of Medellín. Revista facultad nacional de salud pública. 2005; 23(2): 70-77.
- Medrano H, Antezana J. Noise map of districts 10, 11 and 12 of the city of Cochabamba. Acta Nova. 2006; 3(3): 458-474.
- Guzmán R, Barceló, C. Estimation of traffic noise pollution in Havana City, 2006. Cuban Journal of Hygiene and Epidemiology. 2008; 46(2).
- Pacheco J, Franco JF, Behrentz E. Characterization of noise pollution levels in Bogotá: Pilot study. Revista de ingeniería. 2009; 30: 72-80. doi: 10.16924%2Friua.v0i30.230
- Olague-Caballero CO, Wenglas-Lara G, Duarte-Rodríguez JG. Noise pollution on access roads to the city of Chihuahua. Ciencia UAT. 2016; 11(1): 101-115. doi: 10.29059/cienciauat.v11i1.551
- Morelli X, Foraster M, Aguilera I, et al. Short-term associations between traffic-related noise, particle number and traffic flow in three European cities. Atmospheric Environment. 2015; 103: 25-33. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.12.012
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2021 Zamorano-González Benito, Peña-Cárdenas Fabiola, Velázquez-Narváez Yolanda, Vargas-Martínez José Ignacio, Parra-Sierra Víctor

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China



