
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
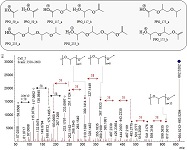
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
Investigation into the correlation between agricultural non-point source pollution and economic expansion in Xinjiang: A Kuznets Curve analysis
Vol 3, Issue 1, 2022
Download PDF
Abstract
Keywords
References
- Sun D, Yang Q, Zhang J, et al. Relationship between agricultural non-point source pollution and agricultural economic development in Guangdong Province. China population, resources and environment. 2016; 26(S1).
- Zhou X, Yang L, Yang L. Estimation and analysis of agricultural non-point source pollutant emissions in Xinjiang. Journal of Agricultural Environmental Sciences. 2017; (7).
- Shahzadi A, Yaseen MR, Anwar S. Relationship between Globalization and Environmental Degradation in Low Income Countries: An Application of Kuznet Curve. Indian Journal of Science and Technology. 2019; 12(19): 1-13. doi: 10.17485/ijst/2019/v12i19/143994
- Bekhet HA, Othman NS, Yasmin T. Interaction Between Environmental Kuznet Curve and Urban Environment Transition Hypotheses in Malaysia. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. 2020; (1).
- Shang J, Shi R, Zhang B. Evolutionary characteristics and dynamic analysis of the relationship between agricultural non-point source pollution and agricultural economic growth. Rural economy. 2019; (9).
- Yan M, Ma Y, Qiao J. Discussion on the relationship between agricultural economic growth and agricultural non-point source pollution in Henan Province—Empirical Analysis Based on EKC theory. Journal of Henan University: Natural Science Edition. 2021; (1).
- Hao S, Zong Y, Dong F. Distribution characteristics of agricultural non-point source pollution load in Niyang River Basin Based on GIS. Journal of irrigation and drainage. 2018; (7).
- Xie J, Zhao X, He B, et al. Analysis on nitrogen and phosphorus emission characteristics of agricultural non-point source pollution in Hanfeng Lake Basin. Environmental Science. 2019; (4).
- Lu S, Zhang P, Pan C, et al. Study on emission characteristics and Control Countermeasures of agricultural non-point source pollution in Dongting Lake. China Environmental Science. 2017; (6).
- Lin J, Wang Y, Fan X. Study on economic driving characteristics of agricultural non-point source pollution in Ningxia. Resources and environment in arid areas. 2021; (3).
- Shang J, Li X, Deng Y. Analysis on the relationship between agricultural economic growth and agricultural non-point source pollution based on EKC—Taking Heilongjiang Province as an example. Ecological economy. 2017; (6).
- Huang J, Liu S. Empirical Study on the impact of agricultural economic growth on agricultural non-point source pollution. Anhui Agricultural Science. 2017; (14).
- Maying, wang Baoli, zhang Fang, et al. Study on cotton farmers’ attitude and willingness to pay for agricultural non-point source pollution control in Xinjiang. Agricultural resources and Regionalization in China, 2016, (7).
- Xie W, Chen T, Liu G. The relationship between agricultural non-point source pollution and agricultural economic growth in Xinjiang—An Empirical Analysis Based on decoupling model and LMDI model. Resources and industry. 2018; (1).
- Ma G, Yu F, Cao D, et al. Calculation and medium and long term prediction of agricultural non-point source pollutant emissions in China. Journal of environmental science. 2012; (2).
- Yang Z, Han H. Technical efficiency of chemical fertilizer application and its influencing factors—Empirical Analysis Based on wheat and maize. Journal of China Agricultural University. 2011; (1).
- Ma Q, Wang Y. External environmental cost assessment of cotton production in Xinjiang. Resources and environment in arid areas. 2015; (6).
- Wang B, Ma Y, He W. Theoretical model analysis on prevention and control of non-point source pollution in cotton production in Xinjiang. Chinese agronomy bulletin. 2018; (23).
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2022 Xiao-li Zhang, Xiaokaiti Xiayire
License URL: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China



