
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
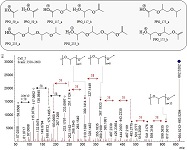
The (partial) replacement of synthetic polymers with bioplastics is due to increased production of conventional packaging plastics causing for severe environmental pollution with plastics waste. The bioplastics, however, represent complex mixtures of known and unknown (bio)polymers, fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardant, pigments, antioxidants, hydrophobic polymers such as poly(lactic acid), polyethylene, polyesters, glycol, or poly(butylene succinate), and little is known of their chemical safety for both the environment and the human health. Polymerization reactions of bioplastics can produce no intentionally added chemicals to the bulk material, which could be toxic, as well. When polymers are used to food packing, then the latter chemicals could also migrate from the polymer to food. This fact compromises the safety for consumers, as well. The scarce data on chemical safety of bioplastics makes a gap in knowledge of their toxicity to humans and environment. Thus, development of exact analytical protocols for determining chemicals of bioplastics in environmental and food samples as well as packing polymers can only provide warrant for reliable conclusive evidence of their safety for both the human health and the environment. The task is compulsory according to legislation Directives valid to environmental protection, food control, and assessment of the risk to human health. The quantitative and structural determination of analytes is primary research task of analysis of polymers. The methods of mass spectrometry are fruitfully used for these purposes. Methodological development of exact analytical mass spectrometric tools for reliable structural analysis of bioplastics only guarantees their safety, efficacy, and quality to both humans and environment. This study, first, highlights innovative stochastic dynamics equations processing exactly mass spectrometric measurands and, thus, producing exact analyte quantification and 3D molecular and electronic structural analyses. There are determined synthetic polymers such as poly(ethylenglycol), poly(propylene glycol), and polyisoprene as well as biopolymers in bags for foodstuffs made from renewable cellulose and starch, and containing, in total within the 20,416–17,495 chemicals per sample of the composite biopolymers. Advantages of complementary employment in mass spectrometric methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is highlighted. The study utilizes ultra-high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic data on biodegradable plastics bags for foodstuffs; high accuracy quantum chemical static methods, molecular dynamics; and chemometrics. There is achieved method performance |r| = 0.99981 determining poly(propylene glycol) in bag for foodstuff containing 20,416 species and using stochastic dynamics mass spectrometric formulas. The results highlight their great capability and applicability to the analytical science as well as relevance to both the fundamental research and to the industry.
The application of microbial immobilization technology in the cleanup of soil contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons
Vol 3, Issue 1, 2022
Download PDF
Abstract
Petroleum hydrocarbons represent a challenging global pollution issue, with their degradation presenting a significant for environmental scientists. Microbial immobilization technology (MIT) offers a promising solution due to its efficiency, stability, cost-effectiveness, and environmental benefits, making it a highly promising approach for soil cleanup. Over recent years, the research on using MIT to remediate petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil has surged in popularity. This technology has emerged as a potent means to enhance the microbial breakdown of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil. The paper reviews the advancements in microbial immobilization technology, outlines the distinct attributes of carrier materials, microorganisms, immobilization techniques, and factors affecting the process, along with their influence on the immobilization outcome. It also discusses the current state and future directions of this technology in the remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil.
Keywords
References
- Hoang SA, Sarkar B, Seshadri B, et al. Mitigation of petroleum-hydrocarbon-contaminated hazardous soils using organic amendments: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2021; 416: 125702. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125702
- Fu B, Liu S, Yan Y, et al. Research Progress on microbial remediation of oil contaminated soil. Environmental protection and circular economy. 2021; 41(3): 54-60.
- Wei X. Hazard and current situation analysis of soil oil pollution. Comprehensive utilization of resources in China. 2020; 38(4): 120-122.
- Kong L, Wang X, Gu M, et al. Analysis on Influencing Factors of biochar enhanced biodegradation of PHS. Environmental Science and technology. 2021; 44(3): 8-15.
- Liu D. Current situation and trend of soil PHS environmental quality standard system in polluted sites in China. China environmental monitoring. 2020; 36(1): 138-146.
- Partovinia A, Rasekh B. Review of the immobilized microbial cell systems for bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons polluted environments. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology. 2018; 48(1): 1-38. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2018.1439652
- Haider FU, Ejaz M, Cheema SA, et al. Phytotoxicity of petroleum hydrocarbons: Sources, impacts and remediation strategies. Environmental Research. 2021; 197: 111031. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111031
- Egret, Wu C, Gu F. Study on Optimization of remediation conditions for oil contaminated soil by immobilized microorganisms. Nonferrous Metals (smelting). 2021; (3): 51-56.
- Ossai IC, Ahmed A, Hassan A, et al. Remediation of soil and water contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbon: A review. Environmental Technology & Innovation. 2020; 17: 100526. doi: 10.1016/j.eti.2019.100526
- Zhang Z, Chen Y, Chen D, et al. Research status of bioremediation of oil contaminated soil. Soil bulletin. 2019; 50(1): 246-252.
- Pan Y, Tang Z, Peng X, et al. Research status and progress of microbial remediation technology for PHS contaminated soil. Progress in chemical industry. 2021; 40(8): 4562-4572.
- Lu F, Li R, Zhang L, et al. Study on immobilization and degradation characteristics of a PHS degrading bacterium. Chemical and biological engineering. 2015; 32(11): 44-47.
- Zhang W, Dong C, Ji Y. Research progress of immobilized materials for petroleum degrading bacteria. Material guide. 2017; 31(S2): 214-218.
- Si Y, Peng J. Immobilized microorganism technology and its application in remediation of contaminated soil. Soil. 2007; 39(5): 673-676.
- Zhang X, Bai X, Xu N, et al. Study on Influencing Factors of oil contaminated soil remediation by immobilized microorganisms. Journal of environmental engineering. 2013; 7(3): 1156-1162.
- Cubitto MA, Gentili AR. Bioremediation of Crude Oil–Contaminated Soil By Immobilized Bacteria on an Agroindustrial Waste—Sunflower Seed Husks. Bioremediation Journal. 2015; 19(4): 277-286. doi: 10.1080/10889868.2014.995376
- Lin M, Liu Y, Chen W, et al. Use of bacteria-immobilized cotton fibers to absorb and degrade crude oil. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation. 2014; 88: 8-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.11.015
- Shen T, Pi Y, Bao M, et al. Biodegradation of different petroleum hydrocarbons by free and immobilized microbial consortia. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts. 2015; 17(12): 2022-2033. doi: 10.1039/c5em00318k
- Nhi-Cong LT, Lien DT, Mai CTN, et al. Advanced materials for immobilization of purple phototrophic bacteria in bioremediation of oil-polluted wastewater. Chemosphere. 2021; 278: 130464. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130464
- Chibata I, Tosa T. Immobilized microbial cells and their applications. Trends in 1980. 5(4): 88-90.
- Hu J, Su X, Han H, Et al. Application prospect of immobilized microorganism technology in remediation of PCB contaminated soil. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014; 25(6): 1806-1814.
- Yang Z, Xu W, Wu Z, et al. Research progress of microbial immobilization and its application in environmental pollution control. Microbiology bulletin. 2020; 47(12): 4278-4292.
- Daronch NA, Kelbert M, Pereira CS, et al. Elucidating the choice for a precise matrix for laccase immobilization: A review. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2020; 397: 125506. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125506
- Zhang X, Wu H, Han Y, et al. Remediation of oil contaminated soil by immobilized microorganisms on modified straw carriers. Journal of Petroleum (petroleum processing). 2014; 30(5): 915-920.
- Wang ZY, Xu Y, Wang HY, et al. Biodegradation of crude oil in contaminated soils by free and immobilized microorganisms. Pedosphere. 2012; 22(5): 717-725.
- Song L, Niu X, Zhang N, et al. Effect of biochar-immobilized Sphingomonas sp. PJ2 on bioremediation of PAHs and bacterial community composition in saline soil. Chemosphere. 2021; 279: 130427. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130427
- Li H, Chen L, Xiao C, et al. Research progress of microbial immobilized carrier materials. Modern chemical industry. 2020; 40(8): 58-61.
- Dike CC, Shahsavari E, Surapaneni A, et al. Can biochar be an effective and reliable biostimulating agent for the remediation of hydrocarbon-contaminated soils? Environment International. 2021; 154: 106553. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.106553
- Galitskaya P, Akhmetzyanova L, Selivanovskaya S. Biochar-carrying hydrocarbon decomposers promote degradation during the early stage of bioremediation. Biogeosciences. 2016; 13(20): 5739-5752. doi: 10.5194/bg-13-5739-2016
- Qian L, Yuan M, Chen B. Research Progress on remediation of pahs contaminated soil by immobilized microorganism technology. Environmental Science. 2012; 33(5): 1767-1776.
- Dzionek A, Wojcieszyńska D, Guzik U. Natural carriers in bioremediation: A review. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology. 2016; 23: 28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ejbt.2016.07.003
- Peng C, Liu T, Gao Y, et al. The latest research progress of microbial immobilized carrier materials. Modern chemical industry. 2021; 41(6): 55-59+64.
- Valdivia-Rivera S, Ayora-Talavera T, Lizardi-Jiménez MA, et al. Encapsulation of microorganisms for bioremediation: Techniques and carriers. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology. 2021; 20(3): 815-838. doi: 10.1007/s11157-021-09577-x
- Yang Y, Li Y, Bai Y, et al. Research progress of carrier materials for enzyme immobilization technology. Chemical bulletin. 2007; (4): 257-263.
- Zdarta J, Meyer AS, Jesionowski T, et al. Multi-faceted strategy based on enzyme immobilization with reactant adsorption and membrane technology for biocatalytic removal of pollutants: A critical review. Biotechnology Advances. 2019; 37(7): 107401. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.05.007
- Li L, Wang Y, Luo, et al. Bioremediation of PHS cadmium contaminated soil by biochar loaded microorganisms. Journal of environmental engineering. 2021; 15(2): 677-687.
- Ren J, Shen J, Zhang L, et al. Preparation and stability of biochar immobilized polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons degrading bacteria. Journal of environmental science. 2020; 40(12): 4517-4523.
- Ren H, Ma L, Wang B, et al. Efficient degradation of petroleum pollutants by biochar based immobilized bacteria. Journal of environmental engineering. 2017; 11(11): 397-403.
- Lu J, Liu L, Wang X, et al. Research Progress on degradation of pesticides in soil by immobilized microorganism technology. Anhui Agricultural Science. 2013; 41(20): 8540-8542.
- Wang X. Research progress of immobilized technology in improving the degradation of PHS in soil by microorganisms. Anhui Agricultural Science. 2018; (30): 13-17.
- Mehrotra T, Dev S, Banerjee A, et al. Use of immobilized bacteria for environmental bioremediation: A review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. 2021; 9(5): 105920. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105920
- Bayat Z, Hassanshahian M, Cappello S. Immobilization of microbes for bioremediation of crude oil polluted environments: A mini review. Open Microbiol J. 2015; 9: 48-54.
- Liu Zhi, Zhao Q, Wang A, et al. Immobilization of marine PHS degrading bacteria and its petroleum degradation performance. Environmental pollution and prevention. 2021; 43(6): 691-696.
- Li Y, Li C, Zhang X, et al. Effect of immobilized Bacillus M1 from tomato straw on remediation of aged soil contaminated by three ring pahs. Agricultural environment and development. 2019; 36(6): 806-813.
- Alvarado-Ramírez L, Rostro-Alanis M, Rodríguez-Rodríguez J, et al. Exploring current tendencies in techniques and materials for immobilization of laccases – A review. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2021; 181: 683-696. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.175
- Bouabidi ZB, El-Naas MH, Zhang Z. Immobilization of microbial cells for the biotreatment of wastewater: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters. 2018; 17(1): 241-257. doi: 10.1007/s10311-018-0795-7
- Huang W, Zhang W, Gan Y, et al. Laccase immobilization with metal-organic frameworks: Current status, remaining challenges and future perspectives. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology. 2020; 52(8): 1282-1324. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2020.1854565
- Wang X, Chen H, Zheng J, et al. Research progress of immobilized technology in improving the degradation of PHS in soil by microorganisms. Anhui Agricultural Science. 2018; 46(30): 13-17.
- Zhang X, Geng C, Fang M, et al. Application of immobilized microorganisms in bioremediation of oil contaminated soil. Journal of petroleum: petroleum processing. 2008; (4): 48-53.
- Wang X, Zheng J, Han Z, et al. Bioremediation of crude oil‐contaminated soil by hydrocarbon‐degrading microorganisms immobilized on humic acid‐modified biofuel ash. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology. 2019; 94(6): 1904-1912. doi: 10.1002/jctb.5969
- ZHENG J, Wang X, Li J, et al. Remediation of PHS contaminated soil by immobilized microorganisms from biomass power plant ash modified with humic acid. Environmental engineering. 2020; 38(8): 34-40.
- Tian X, Wang X, Peng S, et al. Study on remediation of oil pollution by immobilized microorganisms on acetic acid modified ramie fiber. Applied chemical industry. 2019; 48(9): 2045-2049.
- Hasanzadeh R, Abbasi Souraki B, Pendashteh A, et al. Application of isolated halophilic microorganisms suspended and immobilized on walnut shell as biocarrier for treatment of oilfield produced water. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2020; 400: 123197. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123197
- Wang X, Li P, Song S, et al. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil by immobilized microorganisms. Journal of Northeastern University. 2006; (10): 1154-1156.
- Wang X, Gong Z, Li P, et al. Degradation of Pyrene and Benzo(a)pyrene in Contaminated Soil by Immobilized Fungi. Environmental Engineering Science. 2008; 25(5): 677-684. doi: 10.1089/ees.2007.0075
- Guo S, Liu X, Tang J. Enhanced degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons by immobilizing multiple bacteria on wheat bran biochar and its effect on greenhouse gas emission in saline-alkali soil. Chemosphere. 2022; 286: 131663. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131663
- Hu G, Liang C, Li P, et al. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminated soil by immobilized microorganisms. Journal of ecology. 2008; 5: 745-750.
- Li Y, li F. Microbial remediation of oil contaminated soil. Chemical environmental protection. 2017; 37(6): 605-610.
- Ge X, Yang L, Xu J. Cell Immobilization: Fundamentals, Technologies, and Applications. Industrial Biotechnology. Published online November 25, 2016: 205-235. doi: 10.1002/9783527807833.ch7
- Jin J, Sun Y. Research progress of immobilized microorganism technology in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. Hunan Journal of Ecological Sciences. 2021; 8(2): 90-96.
- Varjani SJ, Upasani VN. A new look on factors affecting microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon pollutants. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation. 2017; 120: 71-83.
- Zeng Y, Gao D. Research Progress on immobilization technology of white rot fungi and its influencing factors. Journal of Harbin Institute of technology. 2008; 40(1): 141-146.
- Zhang W, Zhao Y, Wang J, et al. Preparation of biochar immobilized fossil oil degrading bacteria. Jiangsu agricultural science. 2015; 43(6): 341-345.
- Zhang X, Qin L, Huang C, Et al. Selection of microbial immobilization carriers and their properties. Progress in chemical industry. 2011; 30(12): 2781-2786.
- Wang S, Wang D, Yu Z, et al. Advances in research on petroleum biodegradability in soil. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts. 2021; 23(1): 9-27.
- Zhang B, Zhang L, Zhang X. Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil by petroleumdegrading bacteria immobilized on biochar. RSC Advances. 2019; 9(60): 35304-35311.
- LI X, Wang Y, Luo T, et al. Remediation potential of immobilized bacterial strain with biochar as carrier in petroleum hydrocarbon and Ni co-contaminated soil. Environmental Technology. 2018; 40(18): 2345-2353.
- Tao K, Zhang X, Chen X, et al. Response of soil bacterial community to bioaugmentation with a plant residue-immobilized bacterial consortium for crude oil removal. Chemosphere. 2019; 222: 831-838. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.133
- Shao J, Yin H, Peng H, et al. Preliminary study on degradation of crude oil by straw immobilized fossil oil degrading bacteria. Environmental pollution and prevention. 2006; 28(8): 565-568.
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2022 Weitao Liu, Jiantao Li, Zeqi Zheng, Fayun Li

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
.jpg)
Beijing University of Technology, China



