
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
As the globe faces severe challenges such as climate change and environmental pollution, it is critical to investigate the way to achieve sustainable development. Recent research findings provide insights into renewable energy, local leadership, education, and technical cooperation and show diversified strategies for achieving sustainable development. These research findings highlight a crucial concept: achieving sustainable development necessitates multilateral collaboration and innovative thinking. We can create a greener, cleaner, and more sustainable future by investing in education, technical cooperation, and local governance.
Full Issue
| View or download the full issue |
Issue release: 31 December 2024
Agricultural extension and communication is a system that has been subject to very different management by many different institutions in Turkey. In this study, the issue was examined as the period when it was evaluated by local governments with village institutes and the years when it was handled by the central authority. Afterwards, the organizations responsible for agricultural extension today were specified, and their effectiveness was investigated with other studies conducted for the producer. It has been found that the period before 1960, when the desire for enlightenment of the rural area, the belief that one could make a living from agriculture and animal husbandry, and the government policies were based on agriculture, was the brightest period of agricultural extension. It has been determined through secondary data that the effectiveness of the central government’s ministries, cooperatives, producer organizations, and private sector extension system is limited, insufficient to solve problems onsite and on time, or cannot be spread throughout Turkey. The aim of the study is to examine agricultural extension within the framework of rural area policies of governments in Turkey.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
This research explores the link between renewable energy consumption, economic growth, electricity accessibility, greenhouse gas emissions, and environmental degradation in Ghana from 1993 to 2020. Utilizing the autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) model and quantile regression, it analyzes the validity of the Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) hypothesis. ARDL findings imply that renewable energy consumption (REC), greenhouse gas emissions (GHG), and power accessibility (ATE) have positive but statistically negligible long-term associations with CO2 emissions. In contrast, economic growth (ECG) shows a slight negative link. This suggests that current attempts to promote renewable energy and minimize emissions may only partially lower CO2 levels. Quantile regression demonstrates a positive correlation between REC and CO2 emissions, counter to the idea that more renewable energy consumption decreases emissions. GHG strongly affects environmental pollution (EVP) at all levels, whereas power accessibility (ATE) has a favorable effect at lower levels but becomes negative at higher ones. Economic growth’s impact on pollution is detrimental at lower and median values but needs more relevance at more significant levels. These results imply the need for stricter laws, technical breakthroughs, emission limitations, and carbon pricing to mitigate pollution coming from economic expansion.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
This study focuses on a training experience that took place in the academic year 2021–2022 at Gadjah Mada University in Indonesia. A hands-on workshop on ICTeEfS focusing on Participatory Video (PV) and Digital Storytelling (DST) involved 210 teachers in the creation of videos with a two-fold objective: 1) embedding SDGs in school curricula enabled by PV/DST methodologies and 2) innovating teaching methodologies by merging digital and green skills. The process of creating PV/DST videos included a 15-step methodology integrated into four interacting phases starting from planning, moving to production, and then utilization/dissemination. The PV/DST applications produced could be used as learning resources to enrich the school curricula. Uploading PV/DST to school or social media accounts was a good method to get the message out to a wider audience while empowering teachers to address SDGs. The results can be used as guiding principles for teacher educators and teachers as well as for policymakers to integrate PV/DST in teaching, learning, and curricula addressing SDGs.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
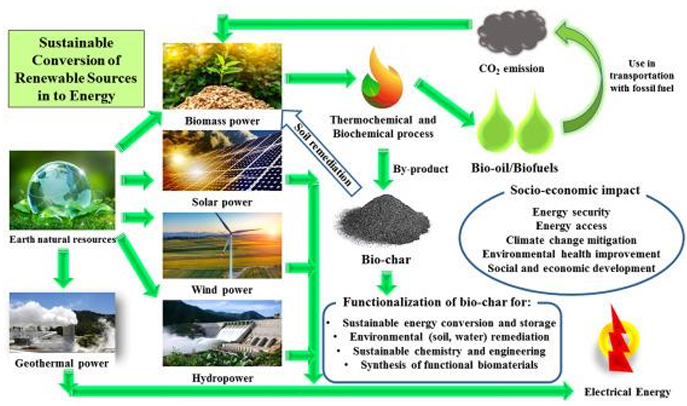
The 21st century poses unprecedented challenges in addressing climate change and environmental degradation, largely driven by the reliance on fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas. These energy sources contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, resulting in detrimental effects on human health and ecosystems. This paper explores the urgent need to transition to renewable energy technologies—including solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biomass—as a sustainable alternative. It highlights the economic viability of renewable energy, emphasizing job creation, reduced energy costs, and enhanced energy security. Effective policy frameworks are crucial for fostering the adoption of renewables and phasing out fossil fuel subsidies, thereby mitigating the adverse impacts of climate change and promoting public health. Ultimately, the integration of renewable energy into global energy portfolios is essential for achieving sustainable development and a cleaner future.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
Governance plays a critical role in advancing Industry 4.0 technologies by enhancing collaboration between industry and academia. This joint relationship significantly accelerates the development of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, improves research quality, and strengthens scientific and technical capabilities. The primary objective of this research is to investigate the impact of advancements in AI technologies on strengthening the relationships between industry and universities. By conducting a qualitative analysis of governance practices in technology development across various countries, this study delves deeply into the dynamics of this relationship. The findings indicate that AI serves a pivotal role in enhancing research capabilities, introducing innovative technologies, promoting collaboration, facilitating technology transfer, and driving innovation, competitive advantage, and sustainable progress in industries. Furthermore, the study focuses on governance strategies related to AI within the context of industry-academia collaboration, including the formation of joint committees, initiation of collaborative research projects, facilitation of technology transfer, and establishment of shared platforms for education and research in AI and related fields. These aspects are meticulously examined within the framework of human capital development and knowledge-based economic growth, underscoring the importance of effective governance structures in leveraging AI advancements to strengthen industry-academia partnerships and stimulate technological innovation.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
This study investigates the critical role of local leadership in sustainable development, focusing on leaders’ behavioral traits and their dynamic interactions with systemic factors. A mixed-methods approach was employed, combining System Dynamics Modeling with qualitative and quantitative data collection. Data were gathered through the stratified sampling of residents., focus groups with 35 participants across domains such as agriculture, education, and health, and public consultations in the Vytina Municipality Unit in Greece. Questionnaires addressed topics including sustainability principles, behaviors, cultural norms, and community goals, while focus group discussions explored sector-specific challenges and strategies. The analysis utilized thematic coding for qualitative data and sensitivity analysis for simulation outputs to evaluate leadership effectiveness. Findings highlight the significance of adaptability in dynamic environments, cultural sensitivity in overcoming resistance to change, and community engagement in fostering trust and participation. Simulation results revealed critical feedback loops, such as the reinforcement of trust through transparency and collaboration, which amplified sustainable development outcomes. This research underscores the potential of System Dynamics Modeling to integrate empirical insights and predict the long-term impacts of leadership behaviors. Key challenges include the model’s reliance on simplified assumptions and its context-specific applicability. Future research should further refine the model and expand its validation in diverse communities to enhance its robustness and utility.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development establishes education as a fundamental tool to raise awareness about the importance of sustainable development, highlighting the importance of aligning educational policies in Argentina with international standards. There is growing interest and some promising initiatives in sustainable education in Argentina, but significant barriers still must be overcome. Teacher training and the integration of sustainability into curricula are key aspects that need attention to move towards an educational system that fosters an active commitment to sustainable development.
Issue release: 31 December 2024
This article explores the innovative sustainable development plan designed for the Municipality Unit (MU) of Vytina, a rural community in Greece. The study focuses on the experience and lessons learned over four years through educational and planning activities led by the Sustainable Development Association. The article highlights challenges, particularly the lack of direct municipal and government support, and emphasizes the necessity of financial, educational, and regulatory mechanisms to improve the effectiveness of bottom-up planning. The methodology combined qualitative and quantitative approaches, including surveys, focus groups, and participatory planning sessions. Findings reveal the importance of empowering residents to shape their sustainability goals while addressing barriers such as limited resources, resistance to change, and institutional gaps. The study proposes measures to streamline planning and align local efforts with broader frameworks like the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. This research contributes to sustainable development discourse by providing a replicable model for rural communities, balancing local realities with global objectives. It highlights the pivotal role of municipalities and governments in fostering effective and inclusive sustainability initiatives.

Prof. Kittisak Jermsittiparsert
University of City Island, Cyprus






It is with deep regret that we announce the cancellation of the Forum on Sustainable Social Development & Computing and Artificial Intelligence, originally scheduled for June 15, 2025.


 Open Access
Open Access