
Image destination engagement from a cultural perspective—A neuromarketing approach for a Spanish-German study
Vol 4, Issue 2, 2023
Download PDF
Abstract
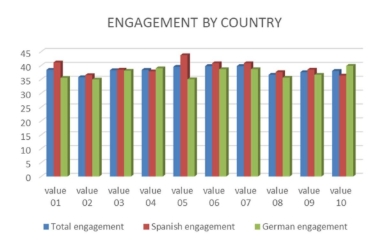
The importance of the image of the tourist destination in the communication and marketing of a tourist destination is beyond doubt. For this reason, numerous studies address these issues. However, not so many do so from the perspective of the emotion the receiver feels, which is why this study deals with analyzing the emotion generated in the receiver through neuromarketing techniques and measuring the level of engagement felt. As a fundamental part of this study, we added the variable of cultural differences, both generically and specifically for gender and age. We are mainly guided by the theories of Life Cycle Theory and Generational Theory to analyze age differences. At the same time, gender differences are approached from the Gender Role Theory. The sample comprises hundred individuals with apparent cultural differences, one sample of German origin and residence and the other of Spanish origin and residence, 50/50. We approached the study from the point of view of the emotion felt by the receiver of the message based on ten neuromarketing techniques (EGG) and ten images used by a famous tourist destination known in both countries. The results suggest that not only are there differences in the emotion felt after viewing images of a tourist destination, but that these differences are also explained by cultural background, gender, and age.
Keywords
References
- Josiassen A, Assaf AG, Woo L, et al. The imagery–image duality model. Journal of Travel Research 2015; 55(6): 789–803. doi: 10.1177/0047287515583358
- Crompton JL. An assessment of the image of mexico as a vacation destination and the influence of geographical location upon that image. Journal of Travel Research 1979; 17(4): 18–23. doi: 10.1177/004728757901700404
- Beerli A, Martín JD. Factors influencing destination image. Annals of Tourism Research 2004; 31(3): 657–681. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2004.01.010
- Bastiaansen M, Straatman S, Mitas O, et al. Emotion measurement in tourism destination marketing: A comparative electroencephalographic and behavioral study. Journal of Travel Research 2020; 61(2): 252–264. doi: 10.1177/0047287520981149
- Hosany S, Martin D, Woodside AG. Emotions in Tourism: Theoretical designs, measurements, analytics, and interpretations. Journal of Travel Research 2020; 60(7): 1391–1407. doi: 10.1177/0047287520937079
- Volo S. Emotions in tourism: From exploration to design. In: Fesenmaier, DR, Xiang Z (editors). Design Science in Tourism: Foundations of Destination Management. Springer; 2017. pp. 31–40. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-42773-7_3
- Bastiaansen M, Straatman S, Driessen E, et al. My destination in your brain: A novel neuromarketing approach for evaluating the effectiveness of destination marketing. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management 2018, 7: 76–88. doi: 10.1016/j.jdmm.2016.09.003
- Michael I, Ramsoy T, Stephens M, et al. A study of unconscious emotional and cognitive responses to tourism images using a neuroscience method. Journal of Islamic Marketing 2019; 10(2): 543–564. doi: 10.1108/jima-09-2017-0098
- Costa PT, Terracciano A, McCrae RR. Gender differences in personality traits across cultures: Robust and surprising findings. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 2001; 81(2): 322–331. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.81.2.322
- Hill, PhD, MPH CV, et al. The national intitute on aging health disparities research framework. Ethnicity & Disease 2015; 25(3): 245. doi: 10.18865/ed.25.3.245
- Brumfiel EM, Robin C. 1 gender, households, and society: An introduction. Archaeological Papers of the American Anthropological Association 2008; 18(1): 1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-8248.2008.00001.x
- Malakhova N. Gender as a subject of interdisciplinary research. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Contemporary Education, Social Sciences and Humanities (ICCESSH 2018); 25–27 April 2018; Moscow, Russia. doi: 10.2991/iccessh-18.2018.332
- Zehetner A, Zehetner D, Lepeyko T, et al. Generation Z’s expectations of their leaders: A cross-cultural, multi-dimensional investigation of leadership styles. European Conference on Management Leadership and Governance 2022; 18(1): 447–455. doi: 10.34190/ecmlg.18.1.891
- Chiappori PA, Molina JA. The intra-spousal balance of power within the family: Cross-cultural evidence. In: Halford WK, van de Vijver F (editors). Cross-Cultural Family Research and Practice. Academic Press; 2020. pp. 185–209. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-815493-9.00006-5
- Cole ER. Intersectionality and research in psychology. American Psychologist 2009; 64(3): 170–180. doi: 10.1037/a0014564
- Rice C, Harrison E, Friedman M. Doing justice to intersectionality in research. Cultural Studies ↔ Critical Methodologies 2019; 19(6): 409–420. doi: 10.1177/1532708619829779
- Goold A, Craig A, Coldwell J. Accommodating culture and cultural diversity in online teaching. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology 2007; 23(4). doi: 10.14742/ajet.1248
- Roos P, Gelfand M, Nau D, et al. Societal threat and cultural variation in the strength of social norms: An evolutionary basis. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 2015; 129: 14–23. doi: 10.1016/j.obhdp.2015.01.003
- Scholtens B, Dam L. Cultural values and international differences in business ethics. Journal of Business Ethics 2007; 75(3): 273–284. doi: 10.1007/s10551-006-9252-9
- Manuti A, Scardigno R, Mininni G. Me, myself, and God: Religion as a psychocultural resource of meaning in later life. Culture & Psychology 2016; 22(1): 3–34. doi: 10.1177/1354067x14551294
- Hanel PHP, Maio GR, Soares AKS, et al. Cross-cultural differences and similarities in human value instantiation. Frontiers in Psychology 2018; 9. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00849
- Welz G. The cultural swirl: Anthropological perspectives on innovation. Global Networks 2003; 3(3): 255–270. doi: 10.1111/1471-0374.00061
- Shaw LA, Wainryb C. The outsider’s perspective: Young adults’ judgments of social practices of other cultures. British Journal of Developmental Psychology 1999; 17(3): 451–471. doi: 10.1348/026151099165393
- Tomasello M, Carpenter M, Call J, et al. Understanding and sharing intentions: The origins of cultural cognition. Behavioral and Brain Sciences 2005; 28(5): 675–691. doi: 10.1017/s0140525x05000129
- Lehman DR, Chiu C-Y, Schaller M. Psychology and culture. Annual Review of Psychology 2004; 55(1): 689–714. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.55.090902.141927
- Park SO, Choi SU, Kim ST, et al. The relationship between corporate culture and value at different life cycle stages. Sustainability 2021; 13(4): 2334. doi: 10.3390/su13042334
- Yang Y, Heijungs R. On the use of different models for consequential life cycle assessment. The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment 2017; 23(4): 751–758. doi: 10.1007/s11367-017-1337-4
- Taji W, Scrivner C, Maestripieri D. Toward a general theory of human individual differences: Can evolutionary psychology meet the challenge? Evolutionary Behavioral Sciences 2020; 14(4): 384–389. doi: 10.1037/ebs0000216
- Woodruff DS, Birren JE. Age changes and cohort difference in personality. Developmental Psychology 1972; 6(2): 252–259. doi: 10.1037/h0032086
- Ledimo O. Generational Differences In Organizational Justice Perceptions: An exploratory investigation across three generational cohorts. Foundations of Management 2015; 7(1): 129–142. doi: 10.1515/fman-2015-0031
- Bisin A, Verdier T. The Economics of Cultural Transmission and Socialization. Available online: https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w16512/w16512.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Jacobs RC, Campbell DT. The perpetuation of an arbitrary tradition through several generations of a laboratory microculture. The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology 1961; 62(3): 649–658. doi: 10.1037/h0044182
- Endendijk JJ, Groeneveld MG, van der Pol LD, et al. Gender differences in child aggression: Relations with gender‐differentiated parenting and parents’ gender‐role stereotypes. Child Development 2016; 88(1): 299–316. doi: 10.1111/cdev.12589
- Fallon MA, Jome LM. An exploration of gender-role expectations and conflict among women rugby players. Psychology of Women Quarterly 2007; 31(3): 311–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-6402.2007.00374.x
- Cobb RA, Walsh CE, Priest JB. The cognitive-active gender role identification continuum. Journal of Feminist Family Therapy 2009; 21(2): 77–97. doi: 10.1080/08952830902911339
- Bowleg L. The problem with the phrase women and minorities: Intersectionality—An important theoretical framework for public health. American Journal of Public Health 2012; 102(7): 1267–1273. doi: 10.2105/ajph.2012.300750
- Aspinall C, Jacobs S, Frey R. Intersectionality and nursing leadership: An integrative review. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2022; 32(11-12): 2466–2480. doi: 10.1111/jocn.16347
- Ray R. An Intersectional analysis to explaining a lack of physical activity among middle class black women. Sociology Compass 2014; 8(6): 780–791. doi: 10.1111/soc4.12172
- Hofstede G. Dimensionalizing cultures: The Hofstede model in context. Online Readings in Psychology and Culture 2011; 2(1). doi: 10.9707/2307-0919.1014
- Connell RW, Messerschmidt JW. Hegemonic masculinity. Gender & Society 2005; 19(6): 829–859. doi: 10.1177/0891243205278639
- Reeser TW. Concepts of masculinity and masculinity studies. In: Horlacher S (editor). Configuring Masculinity in Theory and Literary Practice. Brill; 2020.
- Karandashev V. Cultural Models of Emotions. Springer International Publishing; 2021. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58438-2
- Lucassen G, Lubbers M. Who fears what? Explaining far-right-wing preference in Europe by distinguishing perceived cultural and economic ethnic threats. Comparative Political Studies 2011; 45(5): 547–574. doi: 10.1177/0010414011427851
- Brinkmann S. Culture as practices: A pragmatist conception. Journal of Theoretical and Philosophical Psychology 2007; 27-28(2-1): 192–212. doi: 10.1037/h0091293
- Giorgi S, Lockwood C, Glynn MA. The many faces of culture: Making sense of 30 years of research on culture in organization studies. Academy of Management Annals 2015; 9(1): 1–54. doi: 10.5465/19416520.2015.1007645
- Cheung ML, Pires G, Rosenberger PJ. The influence of perceived social media marketing elements on consumer–brand engagement and brand knowledge. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics 2020; 32(3): 695–720. doi: 10.1108/apjml-04-2019-0262
- Ergün N, Özkan Z, Griffiths MD. Social media addiction and poor mental health: Examining the mediating roles of internet addiction and phubbing. Psychological Reports 2023. doi: 10.1177/00332941231166609
- Shi Y, Gao Y, Cao R. Research on the construction of analytic hierarchy process of cultural tourism competitiveness. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Economy, Judicature, Administration and Humanitarian Projects (JAHP 2019); 12–14 September 2019; Kaifeng, China. doi: 10.2991/jahp-19.2019.173
- Li M, Zhang H, Xiao H, et al. A grid-group analysis of tourism motivation. International Journal of Tourism Research 2013; 17(1): 35–44. doi: 10.1002/jtr.1963
- Tiberghien G, Bremner H, Milne S. Performance and visitors’ perception of authenticity in eco-cultural tourism. Tourism Geographies 2017; 19(2): 287–300. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2017.1285958
- Wang C, Liu J, Zhang T. ‘What if my experience was not what I expected?’: Examining expectation-experience (dis)confirmation effects in China’s rural destinations. Journal of Vacation Marketing 2021; 27(4): 365–384. doi: 10.1177/13567667211006763
- Malone T, Wilder H. Chasing ubuntu: Using ICTs to promote reflective practice. Multicultural Education & Technology Journal 2008; 2(2): 118–125. doi: 10.1108/17504970810883388
- Betsy N, Gloria H. An integrated cognitive perspective of travel motivation and repeated travel behaviour. Annals of Cognitive Science 2018; 2(1). doi: 10.36959/447/341
- Gimenez-Nadal JI, Molina JA, Ortega R. Like my parents at home? Gender differences in children’s housework in Germany and Spain. Empirical Economics 2016; 52(4): 1143–1179. doi: 10.1007/s00181-016-1100-x
- Baluku MM, Groh J, Dalbert C, et al. Cultural differences in geographic mobility readiness among business management students in Germany and Spain ahead of graduation. SN Social Sciences 2021; 1(7). doi: 10.1007/s43545-021-00171-0
- Wilde A, Diekman AB. Cross-cultural similarities and differences in dynamic stereotypes: A comparison between Germany and the United States. Psychology of Women Quarterly 2005; 29(2): 188–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-6402.2005.00181.x
- Scollon CN, Diener E, Oishi S, et al. Emotions across cultures and methods. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology 2004; 35(3): 304–326. doi: 10.1177/0022022104264124
- Kumar V, Kaushal V, Kaushik AK. Building relationship orientation among travellers through destination brand authenticity. Journal of Vacation Marketing 2022; 29(3): 331–347. doi: 10.1177/13567667221095589
- Garcia-Retamero R, Galesic M, Gigerenzer G. Enhancing understanding and recall of quantitative information about medical risks: A cross-cultural comparison between Germany and Spain. The Spanish Journal of Psychology 2011; 14(1): 218–226. doi: 10.5209/rev_SJOP.2011.v14.n1.19
- FUR—Forschungsgemeinschaft Urlaub und Reisen. First selected results:53. Travel analysis (German). Available online: https://tano.travel/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/RA2023_Erste_Ergebnisse_Broschuere_DE.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- Mas JM, Gómez A, Carrero O. Emotions in fear communication: A cross‐cultural neuromarketing approach. Psychology & Marketing 2023. doi: 10.1002/mar.21947
- García-Madariaga J, Blasco López MF, Burgos IM, et al. Do isolated packaging variables influence consumers’ attention and preferences? Physiology & Behavior 2019; 200: 96–103. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2018.04.030
- Biercewicz K, Borawski M, Duda J. Method for selecting an engagement index for a specific type of game using cognitive neuroscience. International Journal of Computer Games Technology 2020; 2020: 1–19. doi: 10.1155/2020/2450651
- Moya I, García-Madariaga J, Blasco MF. What can neuromarketing tell us about food packaging? Foods 2020; 9(12): 1856. doi: 10.3390/foods9121856
- Mora M, Elzo-Aizarna J, Rozas-Fuertes S, et al. Implicit reaction vs explicit emotional response: Protected designation of origin in apple cider. Food Quality and Preference 2020; 79: 103773. doi: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2019.103773
- Çakar T, Gez K. Neuroscience applications on the assessments of TV Ads. In: Santos MAD (editor). Applying Neuroscience to Business Practice. IGI Global; 2017. pp. 231–256. doi: 10.4018/978-1-5225-1028-4.ch010
- Millan YA, Liliana Chaves M, Barrero JC. A review on biometric devices to be applied in ASD interventions. In: Proceedings of the 2020 Congreso Internacional de Innovación y Tendencias en Ingeniería (CONIITI); 30 September 2020–2 October 2020; Bogota, Colombia. doi: 10.1109/coniiti51147.2020.9240291
- Dmochowski JP, Sajda P, Dias J, et al. Correlated components of ongoing eeg point to emotionally laden attention—A possible marker of engagement? Frontiers in Human Neuroscience 2012; 6. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2012.00112
- Fernandez‐Lores S, Crespo‐Tejero N, Fernández‐Hernández R, et al. Framing, risk perception and social health campaigns: A neuroscientific analysis. Journal of Consumer Behaviour 2023; 23(1): 76–89. doi: 10.1002/cb.2151
- Hsu M. Neuromarketing: Inside the mind of the consumer. California Management Review 2017; 59(4): 5–22. doi: 10.1177/0008125617720208
- Steele A, Jacobs D, Siefert C, et al. Leveraging synergy and emotion in a multi-platform world. Journal of Advertising Research 2013; 53(4): 417–430. doi: 10.2501/jar-53-4-417-430
- Casado‐Aranda L, Sánchez‐Fernández J, Bigne E, et al. The application of neuromarketing tools in communication research: A comprehensive review of trends. Psychology & Marketing 2023; 40(9): 1737–1756. doi: 10.1002/mar.21832
- Kågesten A, Gibbs S, Blum RW, et al. Understanding factors that shape gender attitudes in early adolescence globally: A mixed-methods systematic review. PLoS ONE 2016; 11(6): e0157805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157805
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2023 José Manuel Mas, Kathrin Jaszus, Andrés Gómez, Fernando García Monleon
License URL: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).

Prof. Hung-Che Wu
Nanfang College, Guangzhou
China
Indexing & Archiving
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.



.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)

