
Methodology for the management technological innovation in tourist destinations
Vol 3, Issue 1, 2022
Download PDF
Abstract
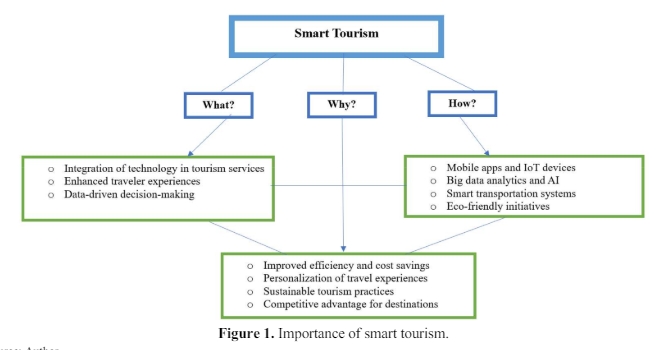
Technological innovation has changed tourism management and practice, and tourism has become one of the largest industries in the world. As a result, tourism authorities must increasingly bet on the development of technology to accommodate tourists’ new image and make them feel included in their destination. In this respect, there is an important effective management of technological innovation in tourist destinations. Therefore, through theoretical methods and statistical committee previously conducted research on this issue, in these research methods are lacking, so this work aims to propose a technological innovation management method for tourist resorts. Thus, we have an approach to managing technological innovation in tourism destinations, expanding and integrating the indicators to be considered, and proposing the scale to measure the indicators. All of these provide the right tools for this purpose and facilitate the development of smart travel destinations.
Keywords
References
- Valderrama JÁ. ¿Cómo ser un destino turístico inteligente? (Spanish) [How to be a smart tourist destination?]. Revista AENOR 2018; (339): 20–23.
- Castro U, González JÁ, Maldonado L. Destinos turísticos inteligentes: ¿Estrategia para el desarrollo local en países pobres? (Spanish) [Smart tourist destinations: Strategy for local development in poor countries?]. Revista Turydes: Turismo y Desarrollo 2017; 22.
- Labrada JRM, Ricardo EdCP, Cueria NF. Influencia de las tendencias del comportamiento del consumidor turístico en el desarrollo responsable del destino Holguín (Spanish) [Influence of tourism consumer behavior trends in the responsible development of the Holguín destination]. Explorador Digital 2021; 5(1).
- Hernández DS, Baute SS. La Laguna, smart tourist destination [Master’s thesis]. San Cristóbal de La Laguna: University of La Laguna; 2016.
- Raffino ME. Innovation [Internet]. Buenos Aires: Editorial Etecé; 2020. Available from: https://concepto.de/innovacion/.
- Muñoz ALdÁ, Sánchez SG. Destinos turísticos inteligentes (Spanish) [Smart tourist destinations]. Revista Economía Industrial 2013; (395): 61–69.
- Júnior AdS, Filho LM, García FA, et al. Smart tourism destinations: Un estudio basado en la visión de los stakeholders (Spanish) [Smart tourism destinations: A study based on the vision of stakeholders]. Revista Turismo em Análise 2017; 28(3): 358–379.
- Espinosa L. Diagnóstico de Quito como destino turístico inteligente (Spanish) [Diagnosis of Quito as a smart tourist destination] [Master’s thesis]. Ecuador: Universidad Católica del Ecuador; 2019.
- García CAG. Smart cities and smart tourist destinations: a comparative analysis [Master’s thesis]. Málaga: Universidad de Málaga; 2015.
- Baidal JI, Monzonís JS, Sánchez DG. Gestión turística y tecnologías de la información y la comunicación (TIC): El nuevo enfoque de los destinos inteligentes (Spanish) [Tourism management and information and communication technologies (ICT): The new approach of smart destinations]. Documents d’Anàlisi Geogràfica 2016; 62(2): 327–346.
- Baidal JI, Bernabeu MC, Serra FF. Guide for the implementation of smart tourist destinations in the Valencian Community [Internet]. Spain: Agència Valenciana del Turisme; 2017. Available from: http://rua.ua.es/dspace/handle/10045/74386.
- Invat.tur, A.V.d.T. Manual Operativo para la configuración de Destinos Turíticos Inteligentes. Alicante, Spain: Invat.tur; 2015. Available from: https://www.thinktur.org/media/Manual-de-destinos-tur%C3%ADsticos-inteligentes.pdf.
- González MAP, López BC. Huatulco desde la perspectiva de los destinos inteligentes (Spanish) [Huatulco from the perspective of smart destinations]. Turismo y Sociedad 2019; XXV: 73–92.
- Ruíz DF, Burgos JP, González MdlOB. La inteligencia en al ámbito turístico. Una nueva formulación en la gestión de los destinos turísticos y su posible adaptación a los destinos culturales (Spanish) [Intelligence in the tourism field. A new formulation in the management of tourist destinations and its possible adaptation to cultural destinations]. Journal of Tourism and Heritage Research 2019; 2(4): 353–381.
- Gascó, M. Ciudades y gobiernos inteligentes: Un fenómeno en auge (Spanish) [Smart cities and governments: A phenomenon on the rise]. In: Tecnologías de Información y Comunicación en la Administración Pública: Conceptos, Enfoques, Aplicaciones y Resultados. UK: INFOTEC; 2017. p. 261–292.
- Gil AML, Fernández BZ, Herrero JLC. Los destinos turísticos inteligentes en el marco de la inteligencia territorial: Conflictos y oportunidades (Spanish) [Smart tourist destinations within the framework of territorial intelligence: Conflicts and opportunities]. Investigaciones Turísticas 2015; (10): 1–25.
- Gidumal JB. Definition of a smart tourist destination [Internet]. Emprendimiento y turismo digital. Available from: http://jbulchand.com/2015/01/definicion-de-destino-turistico-inteligente-smart-destination/.
- Galende HV. Smart cities: Una apuesta de la unión europea para mejorar los servicios públicos urbanos (Spanish) [Smart cities: A commitment of the European Union to improve urban public services]. Revista de Estudios Europeos 2015; (66): 25–51.
- Ruiz DF, Burgos JP, Ugarte BM. ¿Destinos turísticos inteligentes o territorios inteligentes? Estudios de casos en España (Spanish) [Smart tourist destinations or smart territories? Case studies in Spain]. Revista de Estudios Regionales 2018; (113): 193–219.
- Medina MJP, Jurado EN, Plaza AG, et al. Evaluación de los destinos turisticos inteligentes: El caso de Málaga (Spanish) [Evaluation of Smart Tourist Destinations: The case of Malaga]. Congresos-Seminario Destinos Turisticos Inteligentes. Spain: University of Alicante; 2017.
- Bueti C. Indicadores clave de desempeño para ciudades inteligentes y sostenibles (Spanish) [Key performance indicators for smart and sustainable cities] [Internet]. Geneva: ITC; 2015. Available from: http://www.montevideo.gub.uy/sites/default/files/biblioteca/gestioninteligentedeltransporteenbarcelona-antoniocampanozzi-swarco-csi-ciemsa.pdf.
- SEGITTUR. Smart tourist destinations. Spain: SEGITTUR; 2020. Available from: https://www.navarra.es/NR/rdonlyres/33E6A6A5-4F6B-4F77-AD86-5C3839C065AA/459097/TudelaDestinosTuristicosInteligentesdef.pdf.
- Cruz MM, Gândara JMG, Paixão DLD, et al. Curitiba (Brasil) ¿Un destino turístico inteligente? Análisis de la percepción de los miembros del Consejo Municipal de Turismo (COMTUR) (Spanish) [Curitiba (Brazil) A smart tourist destination? Analysis of the perception of the members of the Municipal Tourism Council (COMTUR)]. Estudios y Perspectivas en Turismo 2020; 29(2).
- Cebrián I, Ingelmo R, Martínez FJ, et al. Annex White Paper Smart Cities. Survey of academic experts and tourism professionals. In: Smart Cities White Paper [Internet]. Madrid: Enerlis, Ernst and Young, Ferrovial and Madrid; 2012. p. 131–141. Available from: http://rabida.uhu.es/dspace/bitstream/handle/10272/11270/Anexolibro_blanco.pdf?sequence=2.
- Burgos JP. Territorial intelligence and tourism: The public management of Smart Tourist Destinations [PhD thesis]. Huelva: Universidad de Huelva; 2017.
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2022 Aylen de la Caridad Sánchez Calero, Melisa Segura Alvarez, Justa Ramona Medina Labrada, Leudis Orlando Vega de la Cruz
License URL: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).

Prof. Hung-Che Wu
Nanfang College, Guangzhou
China
Indexing & Archiving
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.



.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)

