
Publication Frequency
Semi-annual
Journal Articles
Search
Search scope
Volume Arrangement
Featured Articles
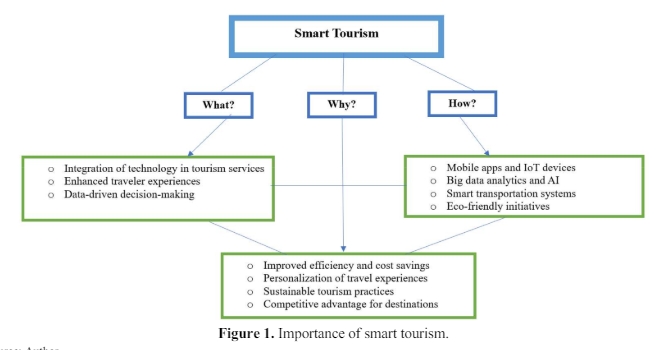
This commentary critically examines the integration of smart tourism technologies within the tourism and hospitality sectors, focusing on their role in enhancing tourist experiences and operational efficiencies. Through a multidisciplinary approach encompassing a literature review, case studies, and empirical data analysis, the analysis adopts a constructivist perspective to explore tourists’ subjective experiences with technology. It highlights significant personalization, efficiency, and sustainability advancements while acknowledging challenges related to digital infrastructure and privacy concerns. Advocating for a balanced and sustainable approach that respects environmental integrity and cultural heritage, the commentary concludes with recommendations for future research on the socio-economic impacts of smart tourism, ethical data usage, and the adaptation of technologies to diverse contexts. It calls for increased investment in digital infrastructure and stakeholder collaborative efforts to promote sustainable and inclusive tourism development.
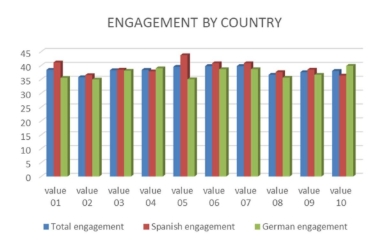
The importance of the image of the tourist destination in the communication and marketing of a tourist destination is beyond doubt. For this reason, numerous studies address these issues. However, not so many do so from the perspective of the emotion the receiver feels, which is why this study deals with analyzing the emotion generated in the receiver through neuromarketing techniques and measuring the level of engagement felt. As a fundamental part of this study, we added the variable of cultural differences, both generically and specifically for gender and age. We are mainly guided by the theories of Life Cycle Theory and Generational Theory to analyze age differences. At the same time, gender differences are approached from the Gender Role Theory. The sample comprises one hundred individuals with apparent cultural differences, one sample of German origin and residence and the other of Spanish origin and residence, 50/50. We approached the study from the point of view of the emotion felt by the receiver of the message based on ten neuromarketing techniques (EGG) and ten images used by a famous tourist destination known in both countries. The results suggest that not only are there differences in the emotion felt after viewing images of a tourist destination, but that these differences are also explained by cultural background, gender, and age.
Disruptive tourism: Smart tourism routes
Article ID: 1704
Vol 2, Issue 2, 2021
DOI: https://doi.org/10.54517/st.v2i2.1704
Vol 2, Issue 2, 2021
Received: 2 September 2021; Accepted: 5 October 2021; Available online: 21 October 2021; Issue release: 30 October 2021
Download PDF
Abstract
The present research aims to support the possible utilization of tourist routes and circuits in a smart way, for this purpose it is proposed to consolidate the usefulness of smart tourism territory, data visualization, data access in connectivity and sensorization infrastructures within a Smart Tourism Destination model. The objective is to understand the evolution of Information and Communication Technologies within a given space that generates information in real time of the natural and cultural tourist attractions, the accesses to them and the facilities at the time of leisure and recreation activities. The proposed route model considers transcending in the current reality of the tourism sector, which is open to work in a multidisciplinary way with other sectors that propitiate the sustainable use of cultural and natural resources through the Internet of Things.
Keywords
smart territory; routes; circuits; data visualization; Smart Tourism Destinations
References
- Blanco LV. El camino de Santiago (Spanish) [The road to Santiago]. Madrid: Editorial Complutense; 1995.
- Boullon R. Intelligent tourism development exploration. Mexico: Spatial planning Editorial Trillas; 1995.
- Cabezuelo-Lorenzo F, Bonete-Vizcaíno F, Sánchez- Martínez M. Analysis of Spanish scientific information and documentation on the phenomenon of smart cities, the habitat of digital natives. Cuadernos de documentación multimedia 2016; 27(1): 102–124.
- Valles DM. Las tecnologias de la información y el turismo (Spanish) [Information technologies and tourism]. Estudios turísticos 1999; (142): 3–24.
- Lansdale D, Castro P, Guerrero C. Smart destinations: Harnessing technology to promote transformation and sustainability through ecotourism in emerging market communities. Springer Nature Switzerland AG; 2020; Zero Hunger and Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals; 2020.
- Castro M. Data visualization of the inventory of tourist attractions of the city of Cuenca and the Santa Barbara Valley [Master’s thesis]. Ecuador: University of Azuay; 2010.
- Castro P, Vasques Y, Salgado E. Proposal of a management model for the Intelligent Tourist Destination (ITD). Tech Converge, Scientific Journal 2020; (02): 2661–2858.
- Fernández M, Cuadrado R. The impact of new technologies in the tourism sector: Application of augmented reality to cultural tourism. Culture, Development and New Technologies: VII Conference on Tourism Research 2014; (1): 317–333.
- Aguayo A, Guevara A, Rossi C, et al. α integrated destination management system. Malaga: Turitec Congress; 2010.
- Valencian Community. Manual of intelligent tourist destinations. Spain: Valencia; 2014; p. 36.
- Consejo de Ministros de Espane. Plan Nacional Integral de Turismo 2012-2015 (Spanish) [Integral National Tourism Plan 2012-2015]. Madrid: Ministro de Industria, Energía y Turismo; 2012.
- Segittur. Destinos turísticos inteligentes (Spanish) [Smart tourist destinations] [Internet]. Madrid: Segittur; 2015. Available from: https://www.segittur.es/destinos-turisticos-inteligentes/
- Guzmán TJL, Canizares SMS. Turismo comunitário y generación de riqueza en países en vias de desarrollo: Un estudio de caso en El Salvador. REVESCO (Spanish) [Community-based tourism and wealth generation in developing countries: A case study in El Salvador REVESCO]. Revista de Estudios Cooperativos 2009; (99): 85–103.
- Buhalis D, Amaranggana A. Smart tourism destinations enhancing tourism experience through personalization of services. Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2015; 377–389. Available from: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-14343-9_28
- Castro P. Propuesta metodológica para el inventario de atractivos turísticos (Spanish) [Methodological proposal for the inventory of tourist attractions]. Habana: Universidad de La Habana; 2016.
- Vila LB. El camino de Santiago (Spanish) [The road to Santiago]. Madrid: Editorial Complutense; 1995.
- Cuenca Destino Turístico Inteligente [Internet]. 2020. Available from: http://www.smarturcuenca.com
- Blanco J. Libro bianco de los destinos turísticos inteligentes: Estratégias y soluciones para fomentar la innovación en el turismo digital (Spanish) [Libro bianco de los destinos turísticos inteligentes: Strategies and solutions to foster innovation in digital tourism]. Espanha: LID Editorial Empresarial; 2015.
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2021 Santiago Patricio Pulla Pesantez, Adriana Lucila Ortega Echeverria, Kleber Patricio Castro Pacheco
License URL: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
Editor-in-Chief

Prof. Hung-Che Wu
Nanfang College, Guangzhou
China
Indexing & Archiving
News & Announcements
2025-01-09
A Thank You Letter from Smart Tourism!
As we bid farewell to 2024, we take immense pride in reflecting on the 28 distinguished works that have been meticulously published online following a rigorous peer-review process. We extend our heartfelt gratitude for authors' invaluable contributions, reviewers' steadfast support, and EBM's insightful guidance throughout the year. Your dedication and expertise have been instrumental in propelling Smart Tourism towards its current success.
2024-07-05
Call for Reading: Volume 5 Issue 1 Available
We are pleased to announce the release of Volume 5 Issue 1 of Smart Tourism. We sincerely invite researchers to download and read articles in this issue. It is hopeful that the content will bring readers new perspectives and inspire the research in related field.
2024-01-15
New layout style in 2024
In 2024, Smart Tourism will adopt a new layout style. Please turn to the "Author Guidelines" for preparing your manuscripts.
Journal Center
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.



.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)

