

Volume 2, Issue 1 focuses on research into the evaluation of urban ecological civilization construction and introduces the development and implementation of an evaluation index system for ecological civilization cities. The application of the ecological civilization city evaluation index system allows for a comprehensive understanding of the level of urban ecological civilization construction, fostering its development. In addition, this issue provides an assessment of urban sustainability and an investigation of urban biodiversity indexes. This issue thoroughly analyzes and evaluates the development state of cities, offering valuable information for the development of ecological civilization cities.
Issue release: 30 June 2021
Cities develop in an excessive and disorderly way, losing their original characteristic identity and function. As a response to the deconstruction of the city, sustainable urban design came into being. This study evaluated the performance and sustainability level of Temuco community. The study was conducted in four sectors of the city, which are symbols and representatives of different stages of urban expansion. Through a set of urban design index standards including economic, social and environmental variables, the development of the community and the quality of life of its residents are evaluated. The results show that the Abraham Lincoln community has a better sustainability index, gathering a group that encourages sustenance and the availability of necessities nearby. The study found that new and old neighborhoods have deficiencies in neighborhood sustainability.
Issue release: 30 June 2021
Background: The resulting large amount of construction and demolition waste (CDW) has become a global problem. To this end, Colombia’s legislation seeks to guide its proper management and promote its transformation and reuse. Methodology: Based on the analysis of the national and local legislation of CDW management frontier cities in Colombia, this study puts forward an alternative to the formulation of a comprehensive management plan. Based on this analysis, the conditions and characteristics of medium-sized cities such as Barranquilla are studied and analyzed in order to provide a comprehensive alternative for the management and treatment of this kind of waste. Result: The prevention, storage, collection, transportation, use, and final disposal aspects that should be considered in the CDW integrated management plan most suitable for Barranquilla City are determined. According to these special characteristics and conditions, a scheme of treatment plants is proposed. Conclusion: In view of the rapid development of Barranquilla in recent years, Barranquilla needs to quickly adjust its CDW management mode. The city recognizes that the separation of source and use is at the core of the model needed to achieve sustainable management processes. In addition, the shortcomings of the current management system are found, and combined with the application of the linear economic model, a management model based on the principle of circular economy is proposed.
Issue release: 30 June 2021
Urban research related to sustainability is going through a rich experimental stage to explore different methods to deal with the current and future impacts of climate change on cities. This poses new challenges to the redevelopment of urban areas. These challenges are particularly relevant at a time of major urban transformation in the global south. This paper aims to develop a method to explore and evaluate the sustainable potential of urban morphology in the surrounding areas of medium-sized cities. The method involves six criteria related to the sustainability of built environment: scale, accessibility, diversity, connectivity, density and node. This approach applies to a community in Temuco, southern Chile. The results show the importance of building adaptive capacity to generate use diversity, which in turn promotes greater sustainability of urban morphology. On the other hand, the high population and housing density in residential areas reduce the pedestrian capacity of indoor streets, while the vertical mixed use and the change of urban block density are still the best response to promote social interaction and high collective activities in urban space. This paper summarizes the operational value of this method and reflects on the progress made in promoting the more sustainable urban form development of medium-sized cities in southern Chile in the future.
Issue release: 30 June 2021
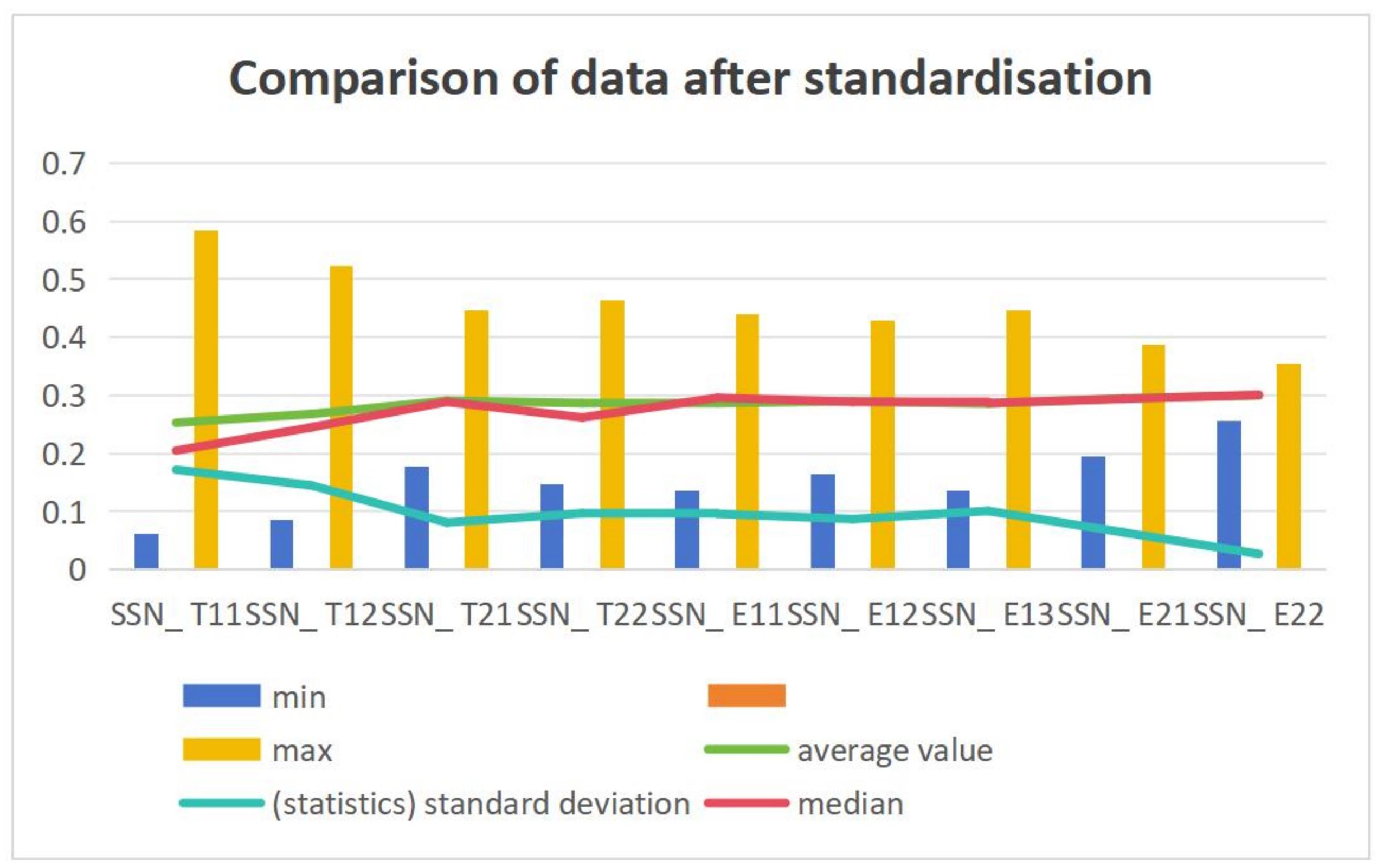
This paper selects 13 evaluation indexes of ecological civilization city construction level in 9 counties of Longnan City, processes the index data by using entropy weight TOPSIS method, calculates the closeness of ecological civilization city construction level in each county, makes an overall ranking of ecological civilization city construction level in each county, and then analyzes the ranking results, in order to provide theoretical guidance for ecological civilization construction in Longnan City.
Issue release: 30 June 2021
Ecological civilization city evaluation is the driving force and main means to promote the construction of urban ecological civilization. The establishment of evaluation index system is the key to the scientific and accuracy of ecological civilization city evaluation. The element structure method is adopted to build the evaluation index model according to the functions of urban government in economy, culture, society and environment. Build an evaluation index system for urban ecological economy, ecological culture, ecological society and ecological environment.

Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Indexing & Archiving
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.


 Open Access
Open Access

.jpg)

.jpg)



