
This paper delves deeply into the innovative realm of integrating human emotions with wearable technology. The primary focus is on the conceptualization and development of a kiss transfer device that harnesses the power of wearable technology to bridge the physical gap in human-human interactions. By investigating the intricate nuances of the human-human kissing process, the research seeks to replicate this intimate gesture through a technological medium. The paper not only elaborates on the anatomy, evolution, and hormonal dynamics of kissing but also underscores the transformative potential of wearable technology in capturing and transmitting these intimate moments. This exploration opens up new horizons for long-distance relationships, offering a tangible touchpoint that goes beyond traditional communication methods. Through this pioneering work, the research positions wearable technology as not just a tool for communication but as an extension of our human emotions and expressions.
Objective: To observe the clinical effect of wearable low back trainer combined with massage in the treatment of chronic non-specific low back pain. Methods: A total of 56 chronic nonspecific low back pain patients were randomly assigned to three groups. The ob group (n=19) was treated with wearable device treatments based on massage for two weeks, once a day, eight minutes each time, five times a week, while the control group (n=19) received massage only for two weeks, once a day, 20 minutes each time, and the blank group (n=18) rest only with closely observation. The therapeutic effect of three groups were evaluated by VAS and ODI scores before the treatment, one week after treatment and two weeks after treatment respectively. Results: There was no significant difference in the VAS score between the observation group and the control group before treatment (P>0.05) while the VAS score difference between the three groups after one week and two weeks of treatment were statistically significant (P<0.05). The VAS scores of the observation group and the control group showed a downward trend with time. After 2 weeks of treatment, the VAS value of the observation group decreased significantly more than the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The decrease of VAS value in the group was significantly greater than that in the blank group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in the ODI score between the observation group and the control group before treatment and after 1 week of treatment (P>0.05). However, there was a statistically significant difference in the ODI score between the three groups after 2 weeks of treatment (P<0.05). The changing trends of ODI values in the three groups were different and both the observation group and the control group showed a downward trend. After two weeks of treatment, the ODI values of the observation group decreased significantly more than the control group with statistically significant differences (P<0.05). However, the ODI value of the blank group decreased after 1 week of treatment and increased again after two weeks of treatment. Conclusion: The use of the wearable low back trainer combined with massage therapy has a better therapeutic effect on chronic non-specific low back pain and can relieve pain more effectively than just simple massage therapy alone.
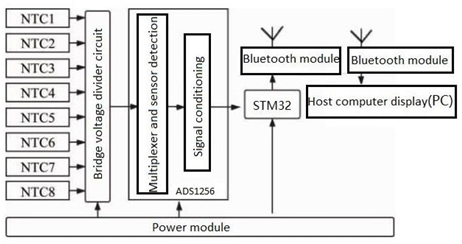
Body temperature is often used to screen infectious diseases and monitor treatment. Through the method of measuring the resistance of constant voltage temperature measuring circuit, a wearable multi-point body temperature monitoring system is researched and designed to determine skin surface temperature. The STM32F103C8T6 chip is used as the core processor, and the negative temperature coefficient thermistor (NTC) as the temperature sensing component. ADS1256 chip is a temperature signal conditioner, Bluetooth module is a wireless transmission unit, and LABVIEW is used to design the host computer interface. The constant voltage bridge circuit composed of thermistor and resistor voltage divider to carry out the acquisition of 8 channels of temperature data, and the 24bits ultra-high-precision analog-to-digital conversion module is configured with differential inputs to amplify, filter and convert analog signals; the converted data is processed and calculated in the single-chip microcomputer; finally, the data is transmitted to the host computer via Bluetooth. The thermistor is linearly compensated using the fourth-order formulation of the Stein-hart formula. Reduce the impact of environmental interference and uneven body temperature distribution from software and hardware. The error during the temperature measurement of temperature sensor is analyzed. The experimental results showed that the resolution of measurement system reached 0. 01 , and the temperature measurement accuracy was up to ± 0. 02 . This design scheme has high stability and accuracy; and the circuit is simple in structure, small in size, and low power consumption which can be used in occasions requiring precise body temperature measurement.
11111
Wearable devices based on Augmented Reality (AR) technology can overlay computer-generated images into the real world, whereas simulation is applied to enable users to view the real world with an overlay of digital data. In the past 10 years, AR technology has moved from research laboratories to gradually a wide range of commercially available technologies for its use in the medical, manufacturing, industrial design, entertainment, marketing and military applications. This review includes an overview of AR wearables in the last 5 years including its development milestone and application cases, where specifically, some successful application cases and implications of AR technology in the oil and gas industry in the past five years are reviewed, with the aim of discussing the aspects of AR technology applications in the design of oil and gas field surface engineering, from station and line designs to its use in supporting construction. Since AR technology can provide real-time information, it will have a non-negligible application prospect in the whole lifecycle of oil and gas field surface engineering from design to operation and maintenance and will occupy a place in the digital transformation of the oil and gas industry.
111

Prof. Zhen Cao
College of Information Science & Electronic Engineering, Zhejiang University
China, China
Processing Speed
-
-
-
- <5 days from submission to initial review decision;
- 62% acceptance rate
-
-
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.


 Open Access
Open Access



