
This paper delves deeply into the innovative realm of integrating human emotions with wearable technology. The primary focus is on the conceptualization and development of a kiss transfer device that harnesses the power of wearable technology to bridge the physical gap in human-human interactions. By investigating the intricate nuances of the human-human kissing process, the research seeks to replicate this intimate gesture through a technological medium. The paper not only elaborates on the anatomy, evolution, and hormonal dynamics of kissing but also underscores the transformative potential of wearable technology in capturing and transmitting these intimate moments. This exploration opens up new horizons for long-distance relationships, offering a tangible touchpoint that goes beyond traditional communication methods. Through this pioneering work, the research positions wearable technology as not just a tool for communication but as an extension of our human emotions and expressions.
Full Issue
| View or download the full issue |
We care much about medical fields which are closely related to every one of us. Wearable technology plays a vital role in modern medicine. The topic of medical wearable technology is impossible to be missed. Hence, we honorably invited three of our editor board members to write articles for this issue.
Prof. Guozhi Huang from Southern Medical University reviewed the background of national policies for the construction of healthy China, summarized the many shortcomings that currently restricted the improvement of rehabilitation service capabilities, and proposed the implementation path of intelligent rehabilitation where wearables were salient in health monitoring. Dr. Julián Patiño-Ortiz proposed a method with a systemic-transdisciplinary approach for the design of eHealth devices, to satisfy the requirements and needs of all those involved in the use of the device and comply with the regulations established in the different countries. Ruben Dario Vasquez Salazar from New Mexico State University reviewed different mobility aids for people with visual disabilities, for the purpose of obtaining a clear vision on the progress of technology and techniques used for assistance in this population. To increase the ability to detect obstacles, the most common devices correspond to the integration of sensors and electronic components in canes. You will get details in these excellent articles.
What’s more, we have articles collected in this issue focusing on medical fields such as dentistry, cardiology, etc. Wishing everyone good health!
Editor-in-chief
Dr. Zhen Cao
eHealth has improved the performance of multiple health systems worldwide by integrating Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) into national (structured and coordinated) strategies in the health sector. However, once the foundation is laid for the development and implementation of eHealth solutions, researchers, engineers, doctors and other stakeholders have no single way to develop eHealth solutions. Therefore, a systematic interdisciplinary method is proposed to design electronic health equipment to meet the requirements and needs of all people involved in the use of the equipment, and comply with the laws and regulations of different countries.
On the basis of systematic and interdisciplinary methods, a method is proposed, that is, the collaborative use of different systematic methods allows stakeholders to continue to cooperate and share the experience. Consequently, the method will allow the design of eHealth devices that, regardless of their use, meet the needs of the user, the requirements of the personnel who will use them, the standards and regulations of the country where they are developed, and provide total satisfaction with the device. Finally, the eHealth solution is designed through systematic thinking, through the analysis of needs and needs, and through exploring different perspectives, observation backgrounds, participant participation, discussion and stakeholder consistency, so as to provide a sustainable product that meets all participants.
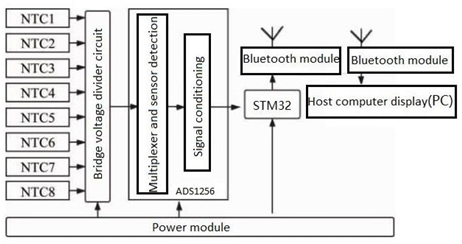
Heart rate, blood oxygen and body temperature are all important physiological information of human body, and designing a small and portable system measurement device will have a large social and clinical economic benefit. An attempt was made to design a portable monitoring device with STM32F103C8T6 as the controller. The heart rate, blood oxygen and body temperature data are collected by MAX30102 and GYMCU90615 modules and the data are sent to an Android smart phone via Bluetooth module for analysis and display, realizing an Android-based heart rate, blood oxygen and body temperature monitoring system. The system has been tested and verified to be stable and reliable.
Reason: Teeth, related to chewing, aesthetics and vocal function, are an essential element. Therefore, the absence of teeth is considered to lead to the deterioration of oral health. Objective: To determine the actual needs of oral restoration in the Northern Health District of camagui city. Methods: A cross-sectional descriptive study was conducted on the population in the Northern Health District of camagui city from October 2013 to April 2015. The study included 574 men and women aged 18 and over.Results: Female patients over 60 years old were dominant. Of the 574 people examined, 401 were determined to need artificial rehabilitation, and tooth loss was the main reason. People over the age of 60 have the greatest actual demand for prosthetics. With regard to gender, it was noted that women needed some prosthetic treatment because it was higher than men. Conclusion: The actual demand for oral restoration in female patients over 60 years old is widespread, and the main reason is the loss of teeth.
To address the problems of complex networking, low transmission rate and poor reliability of current health monitoring systems using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth transmission, an NB-IoT-based health monitoring system for COVID-19 is proposed. The system uses the STM32F103RET6 as the main controller, and the smart wearable device uses the NB-IoT information transmission method to transmit data to the software client platform with the OneNET cloud platform to realize the remote monitoring of key medical parameters of COVID-19. The test results show that the system is stable and reliable in data transmission, reducing the development cost and power consumption of existing health monitoring terminals, and has certain practical value and market prospects.
As every year, the 68th American College of Cardiology (ACC) conference was held in New Orleans, Louisiana, from March 16 to 18. With carnival and jazzas the background, he convened the world cardiology again to promote knowledge by displaying a variety of scientific activities. More than 16000 participants attended and 2300 articles were received, many of which will undoubtedly change current clinical practice. It is also worth noting that the introduction of the guidelines for primary pretreatment of cardiovascular diseases emphasizes that acetylsalicylic acid is almost completely abandoned in primary pretreatment due to the lack of net profit.
We will briefly summarize some of the major scientific papers submitted:
1. Antithrombotic therapy after PCI for acute coronary syndrome or atrial fibrillation—Augustus test
2. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement and balloon dilatation in low-risk patients-partner 3 trial
3. Safety and effectiveness of STEMI femoral artery access: Safari STEMI trial
4. One month after drug-eluting stent implantation, clopidogrel monotherapy was compared with clopidogrel standard 12-month dual antiplatelet therapy. Stop dapt 2 test
5. Results of a large-scale application based study using Smartwatch to identify atrial fibrillation: Apple heart research
The improvement of rehabilitation service capacity is an important part of the construction of a healthy China, and intelligent technology is a powerful means of rehabilitation development. This paper reviews the background of a series of national policies for the construction of a healthy China, analyzes and summarizes the many shortcomings that currently restrict the improvement of rehabilitation service capabilities, and proposes the implementation path of intelligent rehabilitation. By expounding the service process of intelligent rehabilitation, and analyzing in detail the intelligent technical means suitable for integration from the four key links of real-time health monitoring, remote home intelligent rehabilitation intervention, health classification evaluation standard system and health intervention standard system, the general framework of implementation path of intelligent rehabilitation is built. Taking hypertension rehabilitation as an example, the article introduces the intelligent rehabilitation practice exploration and reference model in three aspects: The research and development of hypertension intelligent equipment, the clinical research of hypertension rehabilitation and the construction of hypertension rehabilitation database. Finally, combined with the concept of intelligent interconnection of all things, the definition of “rehabilitation Internet of things” is proposed, and the time is right for intelligent rehabilitation in the context of building a healthy China.
The purpose of this paper is to explore the application of intelligent technology in the industry of the disabled. Through the systematic review of databases (redib, doaj, redalyc, bmj, bvs, dialnet and pubmed), 11 articles were obtained, describing the intelligent technology in ves-tiles devices, which are designed to help patients recover. In an interdisciplinary field, especially in the field of social sciences, there is a new and underutilized phenomenon. This review shows that further research is needed to expand this topic.
Smart wearable devices, as one of the directions of smart terminal development, show great potential for application and penetrate into all aspects of social life. In the application of smart wearable devices, the features of body discipline such as obtaining body data precisely to complete quantified self, human–computer interaction from explicit interaction to implicit interaction, and monitoring of the body from expert dependence to technological dependence and the new human–computer relationship hidden behind them are increasingly highlighted, and the social risk concerns of smart wearable device application will also come into play, which will lead to personal privacy leakage and technological risks. The social risks arising from the disclosure of personal privacy and technological risks, the loss of human subjectivity and the degradation of working capacity, the distortion of social life and the difficulties of social interaction, the deepening of the digital divide and the widening gap between the rich and the poor, the formation of a “digital leviathan” and the potential for public safety, etc., should be of sufficient concern to society.
This paper reviews the literature on mobile assistive devices for visual impaired people, in order to have a clear understanding of the technology and technological progress of helping visual impaired people. In this way, it aims to obtain basic guidelines for analyzing the most relevant equipment to help people with impaired vision and highlight the improvements that can be achieved. The most common device is to integrate different sensors and electronic components into the walking stick to improve their obstacle detection ability. In addition, equipment with cameras, including computer vision algorithms and artificial intelligence technology, has been developed to improve the performance and efficiency of the equipment. Finally, the basic characteristics of the auxiliary system are introduced, and it is found that there is no equipment to meet the needs of users.
As the public’s demand for portable access to personal health information continues to expand, wearable devices are not only widely used in clinical practice, but also gradually applied to the daily health management of ordinary families due to their intelligence, miniaturization, and portability. This paper searches the literature of wearable devices through PubMed and CNKI databases, classifies them according to the different functions realized by wearable devices, and briefly describes the algorithms and specific analysis methods of their applications and made a prospect of its development trend in the field of human health.
Heart failure (HF) continues to be a highly prevalent disease, affecting 1–2% of the population in developed countries, therefore constitutes a health problem due to its high cost. Despite the progress made in drug treatment and implantation devices, the prognosis is poor. About 5% of patients diagnosed with heart failure are in advanced stage or stage D. Heart transplantation (HT) has become the preferred treatment for this high-risk group in the past 30 years. Unfortunately, in addition to the limitation of the current shortage of donors, there is only a limited number of patients meet the appropriate age and with the absence of comorbidities necessary to access this treatment. Due to this and the long waiting lists worldwide, the development and use of ventricular assist devices (VAD) are increasing. In view of the quality of life of patients with this serious disease, these devices improve the short-term and long-term survival rate and gradually reduce the complication rate. These benefits not only provide a choice for patients waiting for HT, but also give those with reversible contraindications the time and opportunity to become suitable candidates or, if impossible, eventually use it as a target treatment. However, these devices have many limitations: their cost, durability, incidence of complications and their limited application. Technological advances in mitigating complications, increased experience in management centers and their promotion to reduce costs are strategies that will continue to strengthen the use of VAD in patients with advanced heart failure.

Prof. Zhen Cao
College of Information Science & Electronic Engineering, Zhejiang University
China, China
Processing Speed
-
-
-
- <5 days from submission to initial review decision;
- 62% acceptance rate
-
-
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.


 Open Access
Open Access



