
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
Development of novel nanostructured biosensors for rapid detection of pathogens in clinical diagnostics
Vol 5, Issue 2, 2024
Download PDF
Abstract
The prompt and precise identification of microorganisms is crucial for successful clinical diagnostics and the prevention of infectious disease outbreaks. Traditional diagnostic methods often suffer from limitations such as extended processing durations, elevated expenses, and the necessity for specialized laboratory equipment. In this research, we propose the development of novel nanostructured biosensors that utilize the distinct characteristics of nanomaterials to improve the accuracy, specificity, and efficiency of identifying pathogens. These biosensors are created with the intention of offering point-of-care testing functionality, thus rendering them appropriate for utilization in a range of clinical settings. The integration of advanced nanotechnology with bioanalytical methods aims to create a reliable system for the real-time identification of bacterial, viral, and fungal pathogens. This review encompasses the design, fabrication, and testing of the biosensors, along with a comprehensive analysis of their performance in comparison to conventional diagnostic techniques. The results demonstrate the potential of nanostructured biosensors to revolutionize pathogen detection, offering significant improvements in efficiency and accuracy, which are essential for timely medical intervention and public health management.
Keywords
References
- Dye C. After 2015: infectious diseases in a new era of health and development. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2014; 369(1645): 20130426. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0426
- Cesewski E, Johnson BN. Electrochemical biosensors for pathogen detection. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2020; 159: 112214. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112214
- Mokhtarzadeh A, Eivazzadeh-Keihan R, Pashazadeh P, et al. Nanomaterial-based biosensors for detection of pathogenic virus. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry. 2017; 97: 445-457. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2017.10.005
- Ahmed A, Rushworth JV, Hirst NA, et al. Biosensors for Whole-Cell Bacterial Detection. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 2014; 27(3): 631-646. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00120-13
- Dutta S, Ray U. Paratracheal abscess by plant fungus Chondrostereum purpureum- first case report of human infection. Medical Mycology Case Reports. 2023; 40: 30-32. doi: 10.1016/j.mmcr.2023.03.001
- Stoia D, De Sio L, Petronella F, et al. Recent advances towards point-of-care devices for fungal detection: Emphasizing the role of plasmonic nanomaterials in current and future technologies. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2024; 255: 116243. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2024.116243
- Vidyadharani G, Vijaya Bhavadharani HK, Sathishnath P, et al. Present and pioneer methods of early detection of food borne pathogens. Journal of Food Science and Technology. 2021; 59(6): 2087-2107. doi: 10.1007/s13197-021-05130-4
- Castillo-Henríquez L, Brenes-Acuña M, Castro-Rojas A, et al. Biosensors for the Detection of Bacterial and Viral Clinical Pathogens. Sensors. 2020; 20(23): 6926. doi: 10.3390/s20236926
- Chao J, Zhu D, Zhang Y, et al. DNA nanotechnology-enabled biosensors. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2016; 76: 68-79. DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.07.00
- Clark LC, Lyons C. Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1962; 102(1): 29-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb13623.x
- Awang MS, Bustami Y, Hamzah HH, et al. Advancement in Salmonella Detection Methods: From Conventional to Electrochemical-Based Sensing Detection. Biosensors. 2021; 11(9): 346. doi: 10.3390/bios11090346
- Yunus G, Singh R, Raveendran S, et al. Electrochemical biosensors in healthcare services: bibliometric analysis and recent developments. PeerJ. 2023; 11: e15566. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15566
- Choi C. Integrated nanobiosensor technology for biomedical application. Nanobiosensors in Disease Diagnosis. 2012: 1. doi: 10.2147/ndd.s26422
- Bellan LM, Wu D, Langer RS. Current trends in nanobiosensor technology. WIREs Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology. 2011; 3(3): 229-246. doi: 10.1002/wnan.136
- Kulkarni MB, Ayachit NH, Aminabhavi TM. Recent Advancements in Nanobiosensors: Current Trends, Challenges, Applications, and Future Scope. Biosensors. 2022; 12(10): 892. doi: 10.3390/bios12100892
- Malik S, Singh J, Goyat R, et al. Nanomaterials-based biosensor and their applications: A review. Heliyon. 2023; 9(9): e19929. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19929
- Choi HK, Yoon J. Nanotechnology-Assisted Biosensors for the Detection of Viral Nucleic Acids: An Overview. Biosensors. 2023; 13(2): 208. doi: 10.3390/bios13020208
- Naresh V, Lee N. A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors. 2021; 21(4): 1109. doi: 10.3390/s21041109
- Ding R, Chen Y, Wang Q, et al. Recent advances in quantum dots-based biosensors for antibiotics detection. J Pharm Anal 2022; 12: 355–364. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2021.08.002.
- Norouzi M, Ghobadi MZ, Golmimi M, et al. Quantum Dot-Based Biosensor for the Detection of Human T-Lymphotropic Virus-1. Analytical Letters. 2017; 50(15): 2402-2411. doi: 10.1080/00032719.2017.1287714
- Karim SSA, Dee CF, Majlis BY, et al. Recent Progress on Fabrication of Zinc Oxide Nanorod-based Field Effect Transistor Biosensors. Sains Malaysiana. 2019; 48(6): 1301-1310. doi: 10.17576/jsm-2019-4806-19
- Singh R, Mukherjee MD, Sumana G, et al. Biosensors for pathogen detection: A smart approach towards clinical diagnosis. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical. 2014; 197: 385-404. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2014.03.005
- Thakare S, Shaikh A, Bodas D, et al. Application of dendrimer-based nanosensors in immunodiagnosis. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. 2022; 209: 112174. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.112174
- Achi F, Attar AM, Ait Lahcen A. Electrochemical nanobiosensors for the detection of cancer biomarkers in real samples: Trends and challenges. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry. 2024; 170: 117423. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2023.117423
- Zhu C, Yang G, Li H, et al. Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors Based on Nanomaterials and Nanostructures. Analytical Chemistry. 2014; 87(1): 230-249. doi: 10.1021/ac5039863
- Janik-Karpinska E, Ceremuga M, Niemcewicz M, et al. Immunosensors—The Future of Pathogen Real-Time Detection. Sensors. 2022; 22(24): 9757. doi: 10.3390/s22249757
- Ahangari A, Mahmoodi P, Mohammadzadeh A. Advanced nano biosensors for rapid detection of zoonotic bacteria. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 2022; 120(1): 41-56. doi: 10.1002/bit.28266
- Ahovan ZA, Hashemi A, De Plano LM, et al. Bacteriophage Based Biosensors: Trends, Outcomes and Challenges. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(3): 501. doi: 10.3390/nano10030501
- Wang X, Zhou J, Wang H. Bioreceptors as the key components for electrochemical biosensing in medicine. Cell Reports Physical Science. 2024; 5(2): 101801. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrp.2024.101801
- Ngashangva L, Hemdan B, El-Liethy M, et al. Emerging Bioanalytical Devices and Platforms for Rapid Detection of Pathogens in Environmental Samples. Micromachines. 2022; 13(7): 1083. doi: 10.3390/mi13071083
- Sun F, Zhang J, Yang Q, et al. Quantum dot biosensor combined with antibody and aptamer for tracing food-borne pathogens. Food Quality and Safety. 2021; 5. doi: 10.1093/fqsafe/fyab019
- Gao J, Chakraborthy A, He S, et al. Graphene-Based Sensors for the Detection of Microorganisms in Food: A Review. Biosensors. 2023; 13(6): 579. doi: 10.3390/bios13060579
- Jiang Z, Feng B, Xu J, et al. Graphene biosensors for bacterial and viral pathogens. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2020; 166: 112471. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112471
- Mustafa F, Hassan R, Andreescu S. Multifunctional Nanotechnology-Enabled Sensors for Rapid Capture and Detection of Pathogens. Sensors. 2017; 17(9): 2121. doi: 10.3390/s17092121
- Zheng X, Gao S, Wu J, et al. Recent Advances in Aptamer-Based Biosensors for Detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2020; 11. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.605229
- Léguillier V, Heddi B, Vidic J. Recent Advances in Aptamer-Based Biosensors for Bacterial Detection. Biosensors. 2024; 14(5): 210. doi: 10.3390/bios14050210
- Park SH, You Y. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Colorimetric Biosensing for Foodborne Pathogen Detection. Foods. 2023; 13(1): 95. doi: 10.3390/foods13010095
- Wang P, Yu G, Wei J, et al. A single thiolated-phage displayed nanobody-based biosensor for label-free detection of foodborne pathogen. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2023; 443: 130157. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130157
- Jiang T, Liu R, Huang X, et al. Colorimetric screening of bacterial enzyme activity and inhibition based on the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Chemical Communications. 2009; (15): 1972. doi: 10.1039/b818853j
- Mollarasouli F, Kurbanoglu S, Ozkan SA. The Role of Electrochemical Immunosensors in Clinical Analysis. Biosensors. 2019; 9(3): 86. doi: 10.3390/bios9030086
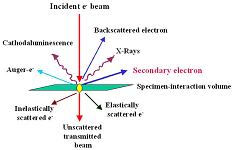
- Goldstein JI, Newbury DE, Echlin P, et al. Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Microanalysis. Springer US; 2003. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0215-9
- Zhou W, Wang ZL. Scanning Microscopy for Nanotechnology. Springer New York; 2007. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-39620-0
- Pennycook SJ. Transmission Electron Microscopy: A Textbook for Materials Science, Second Edition by David B. Williams and C. Barry Carter. Microscopy and Microanalysis. 2010; 16: 111.
- Egerton RF. Physical principles of electron microscopy: An introduction to TEM, SEM, and AEM. Springer; 2005.
- Cullity BD. Elements of X-ray Diffraction - Bernard Dennis Cullity. Google Books. 1956.
- Jenkins R, Snyder RL. Introduction to X‐ray Powder Diffractometry. Wiley-Interscience; 1996. doi: 10.1002/9781118520994
- Griffiths PR. The Early Days of Commercial FT-IR Spectrometry: A Personal Perspective. Applied Spectroscopy. 2017; 71(3): 329-340. doi: 10.1177/0003702816683529
- Stuart B. Infrared Spectroscopy. Analytical Techniques in Forensic Science. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2020: 145-160. doi: 10.1002/9781119373421.ch7
- Bubert H, Rivière JC, Werner WSM. X‐Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS). In: Surface and Thin Film Analysis. Wiley; 2011. pp. 7-41. doi: 10.1002/9783527636921.ch2
- Skoog DA, Holler FJ, Crouch SR, et al. Principal of Instrumental Analysis, 7th ed. Sunder College Publisher, New York; 2017.
- Watts JF, Wolstenholme J. An Introduction to Surface Analysis by XPS and AES. Wiley; 2003. doi: 10.1002/0470867930
- Karakaş İ, Sağır L. B, Hacıoğlu Doğru N. Biological activities of green synthesis silver nanoparticles by Plantago lanceolata L. leaves. GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2023; 22(2): 290-296. doi: 10.30574/gscbps.2023.22.2.0079
- Yadav S, Parihar A, Sadique MA, et al. Emerging Point-of-Care Optical Biosensing Technologies for Diagnostics of Microbial Infections. ACS Applied Optical Materials. 2023; 1(7): 1245-1262. doi: 10.1021/acsaom.3c00129
- Deng J, Zhao S, Liu Y, et al. Nanosensors for Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases. ACS Applied Bio Materials. 2020; 4(5): 3863-3879. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.0c01247
- Noah NM, Ndangili PM. Current Trends of Nanobiosensors for Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Journal of Analytical Methods in Chemistry. 2019; 2019: 1-16. doi: 10.1155/2019/2179718
- Ya N, Zhang D, Wang Y, et al. Recent advances of biocompatible optical nanobiosensors in liquid biopsy: towards early non-invasive diagnosis. Nanoscale. 2024; 16(29): 13784-13801. doi: 10.1039/d4nr01719f
- Fu Y, Liu T, Wang H, et al. Applications of nanomaterial technology in biosensing. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices. 2024; 9(2): 100694. doi: 10.1016/j.jsamd.2024.100694
- Welch EC, Powell JM, Clevinger TB, et al. Advances in Biosensors and Diagnostic Technologies Using Nanostructures and Nanomaterials. Advanced Functional Materials. 2021; 31(44). doi: 10.1002/adfm.202104126
- Antiochia R. Nanobiosensors as new diagnostic tools for SARS, MERS and COVID-19: from past to perspectives. Microchimica Acta. 2020; 187(12). doi: 10.1007/s00604-020-04615-x
- Khan A, Rao TS. Nanobiosensors for virus detection in the environment. In: Nanomaterials for Air Remediation. ResearchGate; 2020. pp. 61-87. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-818821-7.00004-x
- Islam MA, Karim A, Ethiraj B, et al. Antimicrobial peptides: Promising alternatives over conventional capture ligands for biosensor-based detection of pathogenic bacteria. Biotechnology Advances. 2022; 55: 107901. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2021.107901
- Kumari M, Gupta V, Kumar N, et al. Microfluidics-Based Nanobiosensors for Healthcare Monitoring. Molecular Biotechnology. 2023; 66(3): 378-401. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00760-9
- Vakili S, Samare-Najaf M, Dehghanian A, et al. Gold Nanobiosensor Based on the Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance is Able to Diagnose Human Brucellosis, Introducing a Rapid and Affordable Method. Nanoscale Research Letters. 2021; 16(1). doi: 10.1186/s11671-021-03600-4
- Lifson MA, Ozen MO, Inci F, et al. Advances in biosensing strategies for HIV-1 detection, diagnosis, and therapeutic monitoring. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2016; 103: 90-104. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.05.018
- Valenzuela-Amaro HM, Aguayo-Acosta A, Meléndez-Sánchez ER, et al. Emerging applications of nanobiosensors in pathogen detection in water and food. Biosensors 2023;13:922. doi: 10.3390/bios13100922.
- Pang B, Zhao C, Li L, et al. Development of a low-cost paper-based ELISA method for rapid Escherichia coli O157: H7 detection. Analytical Biochemistry. 2018; 542: 58-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2017.11.010
- Hyeon JY, Deng X. Rapid detection of Salmonella in raw chicken breast using real-time PCR combined with immunomagnetic separation and whole genome amplification. Food Microbiology. 2017; 63: 111-116. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2016.11.007
- Herrada CA, Kabir MdA, Altamirano R, et al. Advances in Diagnostic Methods for Zika Virus Infection. Journal of Medical Devices. 2018; 12(4). doi: 10.1115/1.4041086
- Alhadrami HA, Al-Amer S, Aloraij Y, et al. Development of a Simple, Fast, and Cost-Effective Nanobased Immunoassay Method for Detecting Norovirus in Food Samples. ACS Omega. 2020; 5(21): 12162-12165. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00502
- Carter LJ, Garner LV, Smoot JW, et al. Assay Techniques and Test Development for COVID-19 Diagnosis. ACS Central Science. 2020; 6(5): 591-605. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.0c00501
- Wang Y, Alocilja EC. Gold nanoparticle-labeled biosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of bacterial pathogens. Journal of Biological Engineering. 2015; 9(1). doi: 10.1186/s13036-015-0014-z
- Duan N, Wu S, Dai S, et al. Simultaneous detection of pathogenic bacteria using an Aptamer based biosensor and dual fluorescence resonance energy transfer from quantum dots to carbon nanoparticles. Microchimica Acta. 2014; 182(5-6): 917-923. doi: 10.1007/s00604-014-1406-3
- Afsahi S, Lerner MB, Goldstein JM, et al. Novel graphene-based biosensor for early detection of Zika virus infection. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2018; 100: 85-88. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.08.051
- Guo J, Liu D, Yang Z, et al. A photoelectrochemical biosensor for rapid and ultrasensitive norovirus detection. Bioelectrochemistry. 2020; 136: 107591. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2020.107591
- Behrouzi K, Lin L. Gold nanoparticle based plasmonic sensing for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid proteins. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2022; 195: 113669. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113669
- Mazzu-Nascimento T, Morbioli GG, Milan LA, et al. Improved assessment of accuracy and performance indicators in paper-based ELISA. Analytical Methods. 2017; 9(18): 2644-2653. doi: 10.1039/c7ay00505a
- Fruncillo S, Su X, Liu H, et al. Lithographic Processes for the Scalable Fabrication of Micro- and Nanostructures for Biochips and Biosensors. ACS Sensors. 2021; 6(6): 2002-2024. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.0c02704
- Ferreira D, Seca AML, Silva AMS. Targeting human pathogenic bacteria by siderophores: A proteomics review. Journal of Proteomics. 2016; 145: 153-166. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.04.006
- Zhao VXT, Wong TI, Zheng XT, et al. Colorimetric biosensors for point-of-care virus detections. Materials Science for Energy Technologies. 2020; 3: 237-249. doi: 10.1016/j.mset.2019.10.002
- Chan WS, Tang BSF, Boost MV, et al. Detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using a gold nanoparticle-based colourimetric polymerase chain reaction assay. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2014; 53: 105-111. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2013.09.027
- Andrade S, Ramalho MJ, Santos SB, et al. Fighting Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus with Targeted Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(10): 9030. doi: 10.3390/ijms24109030
- Fong WK, Modrusan Z, Mcnevin JP, et al. Rapid Solid-Phase Immunoassay for Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Using Cycling Probe Technology. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 2000; 38(7): 2525-2529. doi: 10.1128/jcm.38.7.2525-2529.2000
- Fernandes AR, Baptista PV. Gold Nanoparticles for Diagnostics. Material MattersTM Publications. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/BD/en/technical-documents/technical-article/materials-science-and-engineering/biosensors-and-imaging/gold-nanoparticles-for-biomolecular-diagnostics (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- Hernández R, Vallés C, Benito AM, et al. Graphene-based potentiometric biosensor for the immediate detection of living bacteria. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2014; 54: 553-557. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2013.11.053
- Ahari H, Hedayati M, Akbari-adergani B, et al. Staphylococcus aureus exotoxin detection using potentiometric nanobiosensor for microbial electrode approach with the effects of pH and temperature. International Journal of Food Properties. 2017: 1-10. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2017.1347944
- Suaifan GARY, Alhogail S, Zourob M. Rapid and low-cost biosensor for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2017; 90: 230-237. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.11.047
- Allafchian A, Hosseini SS. Antibacterial magnetic nanoparticles for therapeutics: a review. IET Nanobiotechnology. 2019; 13(8): 786-799. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2019.0146
- Vasconcelos I, Santos T. Nanotechnology Applications in Sepsis: Essential Knowledge for Clinicians. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(6): 1682. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061682
- Lee MS, Hyun H, Park I, et al. Quantitative Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (FISH) of Magnetically Confined Bacteria Enables Early Detection of Human Bacteremia. Small Methods. 2022; 6(3). doi: 10.1002/smtd.202101239
- Zhang C, Wu L, de Perrot M, et al. Carbon Nanotubes: A Summary of Beneficial and Dangerous Aspects of an Increasingly Popular Group of Nanomaterials. Frontiers in Oncology. 2021; 11. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.693814
- Walling BE, Kuang Z, Hao Y, et al. Helical Carbon Nanotubes Enhance the Early Immune Response and Inhibit Macrophage-Mediated Phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE. 2013; 8(11): e80283. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080283
- Ambhorkar P, Wang Z, Ko H, Lee S, Koo K-I, Kim K, et al. Nanowire-Based biosensors: From growth to applications. Micromachines 2018;9:679. doi: 10.3390/mi9120679.
- Bhattacharyya D, Sarswat PK, Free ML. Quantum dots and carbon dots based fluorescent sensors for TB biomarkers detection. Vacuum. 2017; 146: 606-613. doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2017.02.003
- Abdel-Salam M, Omran B, Whitehead K, et al. Superior Properties and Biomedical Applications of Microorganism-Derived Fluorescent Quantum Dots. Molecules. 2020; 25(19): 4486. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194486
- Napi MLM, Sultan SM, Ismail R, et al. Electrochemical-Based Biosensors on Different Zinc Oxide Nanostructures: A Review. Materials. 2019; 12(18): 2985. doi: 10.3390/ma12182985
- Wang F, Wang Y, Liu X, et al. Rapid, Simple, and Highly Specific Detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae With Visualized Recombinase Polymerase Amplification. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 2022; 12. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.878881
- Nidzworski D, Pranszke P, Grudniewska M, et al. Universal biosensor for detection of influenza virus. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2014; 59: 239-242. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.03.050
- Chaudhari A, Dandekar P. Graphene-based biosensors for the detection of Zika virus. In: Zika Virus Impact, Diagnosis, Control, and Models. Academic Press. 2021; pp. 263–272. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-820267-8.00025-x
- Thongkum W, Hadpech S, Tawon Y, et al. Semi-quantification of HIV-1 protease inhibitor concentrations in clinical samples of HIV-infected patients using a gold nanoparticle-based immunochromatographic assay. Analytica Chimica Acta. 2019; 1071: 86-97. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2019.04.060
- Kumar A, Mazinder Boruah B, Liang XJ. Gold Nanoparticles: Promising Nanomaterials for the Diagnosis of Cancer and HIV/AIDS. Journal of Nanomaterials. 2011; 2011: 1-17. doi: 10.1155/2011/202187
- Gulati S, Singh P, Diwan A, et al. Functionalized gold nanoparticles: promising and efficient diagnostic and therapeutic tools for HIV/AIDS. RSC Medicinal Chemistry. 2020; 11(11): 1252-1266. doi: 10.1039/d0md00298d
- Shi W, Li K, Zhang Y. The Advancement of Nanomaterials for the Detection of Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus. Molecules. 2023; 28(20): 7201. doi: 10.3390/molecules28207201
- Mousavi SM, Hashemi SA, Yari Kalashgrani M, et al. The Pivotal Role of Quantum Dots-Based Biomarkers Integrated with Ultra-Sensitive Probes for Multiplex Detection of Human Viral Infections. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(7): 880. doi: 10.3390/ph15070880
- Hussain KK, Malavia D, Johnson E M, et al. Biosensors and Diagnostics for Fungal Detection. Journal of Fungi. 2020; 6(4): 349. doi: 10.3390/jof6040349
- Seong M, Lee DG. Reactive oxygen species-independent apoptotic pathway by gold nanoparticles in Candida albicans. Microbiological Research. 2018; 207: 33-40. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2017.11.003
- Clack K, Sallam M, Matheson C, et al. Towards a Wearable Feminine Hygiene Platform for Detection of Invasive Fungal Pathogens via Gold Nanoparticle Aggregation. Micromachines. 2024; 15(7): 899. doi: 10.3390/mi15070899
- Kattke MD, Gao EJ, Sapsford KE, et al. FRET-Based Quantum Dot Immunoassay for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Aspergillus amstelodami. Sensors. 2011; 11(6): 6396-6410. doi: 10.3390/s110606396
- Niemirowicz K, Durnaś B, Tokajuk G, et al. Formulation and candidacidal activity of magnetic nanoparticles coated with cathelicidin LL-37 and ceragenin CSA-13. Scientific Reports. 2017; 7(1). doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04653-1
- Prabowo BA, Cabral PD, Freitas P, et al. The Challenges of Developing Biosensors for Clinical Assessment: A Review. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(11): 299. doi: 10.3390/chemosensors9110299
- Haleem A, Javaid M, Singh RP, et al. Biosensors applications in medical field: A brief review. Sensors International. 2021; 2: 100100. doi: 10.1016/j.sintl.2021.100100
- Kang H, Lee D, Yang Y, et al. Emerging low-cost, large-scale photonic platforms with soft lithography and self-assembly. Photonics Insights. 2023; 2(2): R04. doi: 10.3788/pi.2023.r04
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2024 Md Jasim Uddin, Shahrin Risa Sejuti, Sharmin Lucky, Mili Akter, Sumaya Binty Hussain
License URL: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
1.jpg)
Prof. Sivanesan Subramanian
Anna University, India





.jpg)
