
Asia Pacific Academy of Science Pte. Ltd. (APACSCI) specializes in international journal publishing. APACSCI adopts the open access publishing model and provides an important communication bridge for academic groups whose interest fields include engineering, technology, medicine, computer, mathematics, agriculture and forestry, and environment.
Synergizing climate action: Integrating renewable energy, and biodiversity conservation for sustainable development
Vol 3, Issue 2, 2025
Download PDF
Abstract
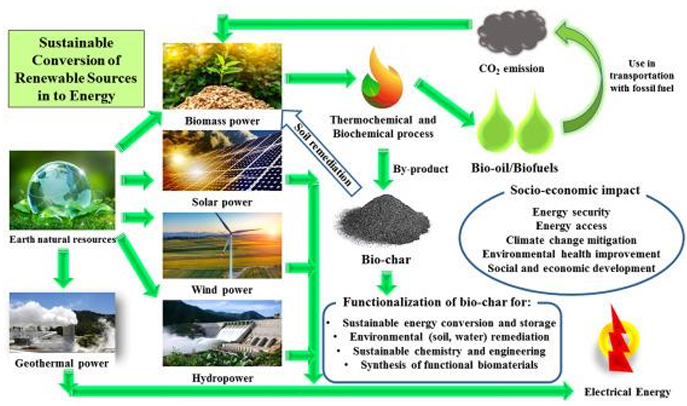
Coordinated actions to protect biodiversity, incorporate renewable energy, and implement climate action are needed for sustainable development to be achieved in the context of global challenges like climate change, ecosystem destruction, and resource depletion. Climate action seeks to reduce the negative impact and strengthen the adaptive capacity of natural and human society. Climate action includes both adaptation and mitigation strategies. The transition to renewable power sources is of utmost importance to climate action because it helps to slow environmental degradation, curtail fossil fuel dependence, and significantly diminish greenhouse gas emissions. The adoption of renewable energy, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, is more environmentally friendly than conventional energy sources, but it may also pose potential risks towards biodiversity, so measures should be taken in planning to avoid negative environmental impacts. It is crucial to protect biodiversity around the world because it plays an important role in the delivery of ecosystem services such as soil fertility, pollination, water purification, and the sequestration of carbon that are vital to people’s existence. In addition, strong ecosystems reduce the severity of climate change impacts, such as storms, droughts, and flooding. However, there may be trade-offs when striving for the increase of renewable energy and biodiversity conservation. Renewable energy development should always be complemented with biodiversity protection. This approach preserves the environmentally delicate ecosystems that are crucial to achieving climate action targets. The combination of climate action, renewable energy, and the need for biodiversity makes it possible to reap many benefits. These include stronger ecosystems and better human health, as well as economic growth and job creation. One example of such a nature-based solution is agrovoltaics, which combines solar energy production and farming. Restoring ecosystems, like forests or wetlands, can also greatly enhance carbon sequestration, reduce global warming, and protect endangered wildlife. This strategy aligns with international initiatives such as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs), specifically SDGs 7, 13, and 15. It serves as a building block towards a more sustainable future. Despite the clear possibilities of synergy, there are still barriers that must be tackled. Policy fragmentation, resource competition, and lack of inter-sector cooperation are some of the challenges that inhibit effective integration. Therefore, equitable governance and the adoption of nature-based techniques are essential.
Keywords
References
- Cardinale BJ, Duffy JE, Gonzalez A, et al. Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature. 2012; 486(7401): 59-67. doi: 10.1038/nature11148
- Gasparatos A, Doll CNH, Esteban M, et al. Renewable energy and biodiversity: Implications for transitioning to a Green Economy. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2017; 70: 161-184. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.08.030
- McManamay RA, Vernon CR, Jager HI. Global Biodiversity Implications of Alternative Electrification Strategies Under the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Biological Conservation. 2021; 260: 109234. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2021.109234
- Hamed TA, Alshare A. Environmental Impact of Solar and Wind energy- A Review. Journal of Sustainable Development of Energy, Water and Environment Systems. 2022; 10(2): 1-23. doi: 10.13044/j.sdewes.d9.0387
- Baranovskaya T, Fursov V. Impact of renewable energy transition on aquatic ecosystems. Zhihao W, Hui G, Papadakis S, Martinez F, Mendez C, eds. E3S Web of Conferences. 2025; 614: 04020. doi: 10.1051/e3sconf/202561404020
- Liu G, Chen T, Sui X, Solangi YS, Examining and prioritizing the effect of sustainable energy on the job market to advance China’s green workforce, Heliyon. 2023; 9: e22710. doi: 10.1016/J.HELIYON.2023.E22710
- Matwani J, Ojija F. Exploring the link between energy resources and global biodiversity. Sustainable Social Development. 2025; 3(2): 3245. doi: 10.54517/ssd3245
- John Raphael L, Mromba C. Reforestation for Mitigation and Adaptation to Climate Change in North-Eastern Highlands of Tanzania: Beyond Carbon Sequestration. Tanzania Journal for Population studies and Development. 2024; 31(2): 1-15. doi: 10.56279/tjpsd.v31i2.271
- Filho WL, Wall T, Salvia AL, et al. The central role of climate action in achieving the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals. Scientific Reports. 2023; 13(1). doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47746-w
- Bhatt RP. Achievement of SDGS globally in biodiversity conservation and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by using green energy and maintaining forest cover. GSC Advanced Research and Reviews. 2023; 17: 001–021. doi: 10.30574/gscarr.2023.17.3.0421
- Country Environmental Analysis Environmental Trends and Threats, and Pathways to Improved Sustainability, 2019. Available online: www.worldbank.org (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Nature-Positive Insurance: Evolving Thinking and Practices. UNEP FI’s Principles for Sustainable Insurance Initiative and Nature Team; 2023.
- Jessel S, Sawyer S, Hernández D. Energy, Poverty, and Health in Climate Change: A Comprehensive Review of an Emerging Literature. Front Public Health. 2019; 7: 470168.
- Gan KE, Taikan O, Gan TY, et al. Enhancing Renewable Energy Systems, Contributing to Sustainable Development Goals of United Nation and Building Resilience Against Climate Change Impacts. Energy Technology. 2023; 11(11). doi: 10.1002/ente.202300275
- Dagnachew A, Hof A, Van Soest H, Van Vuuren D. Climate change measures and sustainable development goals Mapping synergies and trade-offs to guide multi-level decision-making note, 2021. Available online: www.pbl.nl/en (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Wang Z, Wang T, Zhang X, et al. Biodiversity conservation in the context of climate change: Facing challenges and management strategies. Science of The Total Environment. 2024; 937: 173377. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173377
- Lyanda RP, Ojija F. Energy resources: Their causal relationship with ecology and environments. Sustainable Social Development. 2025; 3(2): 3223. doi: 10.54517/ssd3223
- Shivanna KR. Climate change and its impact on biodiversity and human welfare. Proceedings of the Indian National Science Academy. 2022; 88(2): 160-171. doi: 10.1007/s43538-022-00073-6
- Jayachandran M, Gatla RK, Rao KP, et al. Challenges in achieving sustainable development goal 7: Affordable and clean energy in light of nascent technologies. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments. 2022; 53: 102692. doi: 10.1016/j.seta.2022.102692
- Kafumu DW, Ojija F. Biodiversity and renewable energy in a warming world: Pathway to mitigate climate change while preserving ecosystem. Sustainable Social Development. 2025; 3(1): 3228. doi: 10.54517/ssd3228
- de Jong L, De Bruin S, Knoop J, et al. Understanding land-use change conflict: a systematic review of case studies. Journal of Land Use Science. 2021; 16(3): 223-239. doi: 10.1080/1747423x.2021.1933226
- Rehbein JA, Watson JEM, Lane JL, et al. Renewable energy development threatens many globally important biodiversity areas. Global Change Biology. 2020; 26(5): 3040-3051. doi: 10.1111/gcb.15067
- Santangeli A, Di Minin E, Toivonen T, et al. Synergies and trade‐offs between renewable energy expansion and biodiversity conservation – a cross‐national multifactor analysis. GCB Bioenergy. 2016; 8(6): 1191-1200. doi: 10.1111/gcbb.12337
- Hildingsson R, Johansson B. Governing low-carbon energy transitions in sustainable ways: Potential synergies and conflicts between climate and environmental policy objectives. Energy Policy. 2016; 88: 245-252. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2015.10.029
- Bertoldi P, Kona A, Rivas S, et al. Towards a global comprehensive and transparent framework for cities and local governments enabling an effective contribution to the Paris climate agreement. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability. 2018; 30: 67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2018.03.009
- Kabir Z, Khan I. Environmental impact assessment of waste to energy projects in developing countries: General guidelines in the context of Bangladesh. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments. 2020; 37: 100619. doi: 10.1016/j.seta.2019.100619
- Jackson ALR. Renewable energy vs. biodiversity: Policy conflicts and the future of nature conservation. Global Environmental Change. 2011; 21(4): 1195-1208. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2011.07.001
- Nasir N, Ahmed W. Green Finance Initiatives and Their Potential to Drive Sustainable Development. In: Climate Change and Finance. Sustainable Finance. Springer, Cham; 2024. pp. 3–29. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-56419-2_1
- EU renewable energy policies, global biodiversity, and the UN SDGs A report of the EKLIPSE project. European Commission.
- Santangeli A, Toivonen T, Pouzols FM, et al. Global change synergies and trade‐offs between renewable energy and biodiversity. GCB Bioenergy. 2015; 8(5): 941-951. doi: 10.1111/gcbb.12299
- Gasparatos A, Doll CNH, Esteban M, et al. Renewable energy and biodiversity: Implications for transitioning to a Green Economy. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2017; 70: 61–184. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.08.030
- Sternberg R, Hydropower’s future, the environment, and global electricity systems. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2010; 14: 713–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2009.08.016.
- Nazir MS, Bilal M, Sohail HM, et al. Impacts of renewable energy atlas: Reaping the benefits of renewables and biodiversity threats. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 2020; 45(41): 22113-22124. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.05.195
- Olowookere G. A systematic review of the impacts of operational wind turbines on small birds and effectiveness of mitigation strategies. Available online: https://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:hh:diva-54535 (accessed 28 December 2024).
- Sternberg R. Hydropower’s future, the environment, and global electricity systems. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2010; 14(2): 713-723. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2009.08.016
- May R, Reitan O, Bevanger K, et al. Mitigating wind-turbine induced avian mortality: Sensory, aerodynamic and cognitive constraints and options. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2015; 42: 170-181. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.10.002
- Hernandez RR, Hoffacker MK, Murphy-Mariscal ML, et al. Solar energy development impacts on land cover change and protected areas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U. S. A. 2015; 112: 13579–13584.
- Bai R, Liu X, Liu X, et al. The development of biodiversity conservation measures in China’s hydro projects: A review. Environment International. 2017; 108: 285-298. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.09.007
- Kaliyannan GV, Gunasekaran R, Rathanasamy R, et al. Challenges and Prospects in Photovoltaic Waste Management: Towards Sustainable Recycling and Disposal of End-of-Life Solar Panels. World Sustainability Series Part F. 2025; 3811: 61–82. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-77327-3_4
- White TB, Viana LR, Campbell G, et al. Using technology to improve the management of development impacts on biodiversity. Business Strategy and the Environment. 2021; 30(8): 3502-3516. doi: 10.1002/bse.2816
- Jager HI, Efroymson RA, McManamay RA. Renewable energy and biological conservation in a changing world. Biological Conservation. 2021; 263: 109354. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2021.109354
- Cohen B, Cowie A, Babiker M, et al. Co-benefits and trade-offs of climate change mitigation actions and the Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainable Production and Consumption. 2021; 26: 805-813. doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2020.12.034
- Algarni S, Tirth V, Alqahtani T, et al. Contribution of renewable energy sources to the environmental impacts and economic benefits for sustainable development. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments. 2023; 56: 103098. doi: 10.1016/j.seta.2023.103098
- Batra G. Renewable Energy Economics: Achieving Harmony between Environmental Protection and Economic Goals. Social Science Chronicle. 2023; 3(1). doi: 10.56106/ssc.2023.009
- Liu G, Chen T, Sui X, et al. Examining and prioritizing the effect of sustainable energy on the job market to advance China’s green workforce. Heliyon. 2023; 9(12): e22710. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22710
- Thomas V. Climate Change and Natural Disasters. Routledge Taylor & Francis Group; 2017. p. 158.
- Parkhill KA, Shirani F, Butler C, Henwood KL, Groves C, Pidgeon NF. We are a community [but] that takes a certain amount of energy: Exploring shared visions, social action, and resilience in place-based community-led energy initiatives, Environ Sci Policy. 2015; 53: 60–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVSCI.2015.05.014.
- Sovacool BK, Drupady IM. Energy Access, Poverty, and Development: The Governance of Small-Scale Renewable Energy in Developing Asia. Routledge Taylor & Francis Group; 2016; pp. 1–306.
- Parkhill KA, Shirani F, Butler C, et al. ‘We are a community [but] that takes a certain amount of energy’: Exploring shared visions, social action, and resilience in place-based community-led energy initiatives. Environmental Science & Policy. 2015; 53: 60-69. doi: 10.1016/j.envsci.2015.05.014
- Raihan A. A review of the global climate change impacts, adaptation strategies, and mitigation options in the socio-economic and environmental sectors. Journal of Environmental Science and Economics. 2023; 2(3): 36-58. doi: 10.56556/jescae.v2i3.587
- Daba MH, Dejene SW. The Role of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services in Carbon Sequestration and its Implication for Climate Change Mitigation. Int J Environ Sci Nat Res. 2018; 11(2): 555810.
- Ingle KN, Polikovsky M, Fenta MC, et al. Integration of multitrophic aquaculture approach with marine energy projects for management and restoration of coastal ecosystems of India. Ecological Engineering. 2022; 176: 106525. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2021.106525
- Akter M. Global Environmental Agreements. Intersecting Environmental Governance with Technological Advancements. IGI Global; 2024. pp. 31-62. doi: 10.4018/979-8-3693-7001-8.ch002
- Pratiwi S, Juerges N. Review of the impact of renewable energy development on the environment and nature conservation in Southeast Asia. Energy, Ecology and Environment. 2020; 5(4): 221-239. doi: 10.1007/s40974-020-00166-2
- Anjanappa J, Samant S, Thakur B. Mainstreaming Biodiversity into Power Sector Planning and Policy to Deliver Better Outcomes for Nature and the Climate. SSRN. 2024. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.4965343
- Wiseman HJ, Wiseman SR, Wright C. Farming Solar on the Margins. Boston University Law Review. 2023; 103(2).
- Docrat N. The negative impact of wind turbines on wildlife in South Africa. University of the Witwatersrand; 2023.
- Rathoure AK. Impact of societal development and infrastructure on biodiversity decline, Impact of Societal Development and Infrastructure on Biodiversity Decline. IGI Globla; 2024. pp. 1–374.
- Hoffmann S. Challenges and opportunities of area-based conservation in reaching biodiversity and sustainability goals. Biodiversity and Conservation. 2021; 31(2): 325-352. doi: 10.1007/s10531-021-02340-2
- Olajide HE. Community Engagement and Social Acceptance of Renewable Energy Projects in Agricultural Regions. Published online 2024. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.4969730
- Jobson B, Cook A, Fletcher C, et al. Opportunities for enhancing biodiversity at wind and solar energy developments. IUCN.
- Priyadarshini MC, Iyyanar S, Kanagaraj K, et al. The Nano Frontier: Emerging Technologies for Environmental Remediation and Sustainable Energy. E3S Web of Conferences. 2024; 588: 01016. doi: 10.1051/E3SCONF/202458801016
- Anjanappa J. Unveiling the Green Paradox - Biodiversity Risk in Renewable Energy Investments in India. SSRN Electronic Journal. Published online 2024. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.4722554
- Srivastav DrAK, Das DrP, Srivastava AK. Future Trends, Innovations, and Global Collaboration. In: Biotech and IoT. Apress, Berkeley, CA; 2024. pp. 309–398. doi: 10.1007/979-8-8688-0527-1_10
Supporting Agencies
Copyright (c) 2025 Author(s)
License URL: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).

Prof. Kittisak Jermsittiparsert
University of City Island, Cyprus






It is with deep regret that we announce the cancellation of the Forum on Sustainable Social Development & Computing and Artificial Intelligence, originally scheduled for June 15, 2025.

